3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has a wide range of materials available for creating objects. The choice of material depends on factors such as the desired properties of the final object, the type of 3D printer being used, and the intended application. Here are some common 3D printing materials:
PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is one of the most popular 3D printing materials. It's biodegradable and derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane. PLA is easy to print with, has a low melting point, and is often used for prototypes, consumer goods, and decorative items.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is known for its strength and durability. It can withstand higher temperatures than PLA, making it suitable for functional parts like automotive components and consumer electronics. ABS can produce strong, impact-resistant objects, but it may require a heated bed and good ventilation due to fumes during printing.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG offers a balance between PLA and ABS. It's durable, impact-resistant, and has good chemical resistance. PETG is commonly used for mechanical parts, food containers, and outdoor applications due to its UV resistance.
Nylon: Nylon is a strong and flexible material with excellent layer adhesion. It's often used for parts that require toughness, such as gears, bearings, and functional prototypes. Nylon is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air, so it needs to be stored properly.
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer): TPEs are flexible, rubber-like materials that can be used for creating soft and elastic objects. They are commonly used for gaskets, phone cases, and toys.
PC (Polycarbonate): PC is a high-temperature material known for its strength and impact resistance. It's used in applications where parts need to withstand high temperatures, like aerospace and automotive components.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is a flexible and elastic material with good chemical resistance. It's commonly used for producing flexible and durable items like phone cases, shoe soles, and wearables.
Metal Filaments: Various metal-filled filaments are available, allowing you to 3D print objects that resemble metal. These materials often contain a mixture of metal powders (e.g., brass, copper, bronze) and a base polymer. They are used for decorative and functional parts where a metallic appearance is desired.
Wood Filaments: Wood-filled filaments combine PLA with wood fibers, producing objects with a wood-like texture and appearance. They are often used for decorative pieces and artistic projects.
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Filaments: These filaments contain carbon fibers, which enhance the strength and stiffness of printed objects. They are used in applications that require lightweight but strong parts, such as drones and racing car components.
Ceramic and Composite Filaments: Some 3D printing materials are designed to produce ceramic or composite objects, suitable for applications like jewelry, art, and specialized components.
Resin: In addition to filament-based 3D printing, there is resin-based stereolithography (SLA) and digital light processing (DLP) printing. Resins come in various types, including standard, flexible, and dental resins, each with specific properties suited for their intended use.
The choice of the best material for 3D printing depends on your specific needs, the intended application, and your preferences. There is no one-size-fits-all answer because different materials offer different properties and advantages.
1. PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is an excellent choice for beginners and general-purpose 3D printing. It's easy to work with, has a low melting point, and produces minimal fumes. PLA is suitable for prototypes, decorative items, and objects that don't require high-temperature resistance.
2. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is known for its durability and strength. It's suitable for functional parts, mechanical components, and items that need to withstand higher temperatures. However, it can be more challenging to print with due to its tendency to warp, and it may require a heated bed and proper ventilation.
3. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG offers a balance between PLA and ABS. It is durable, impact-resistant, and has good chemical resistance. PETG is a versatile choice for a wide range of applications.
4. Nylon: Nylon is a strong and flexible material with excellent layer adhesion. It's ideal for parts that require toughness and can withstand some flexing or bending. Nylon is used for gears, bearings, and functional prototypes.
5. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is the go-to material for flexible and elastic objects. It's used for producing items like phone cases, shoe soles, and wearables.
6. PC (Polycarbonate): PC is known for its high-temperature resistance and strength. It's suitable for applications in aerospace, automotive, and industrial settings where parts need to endure challenging conditions.
7. Specialized Filaments: Depending on your specific needs, you might consider specialized filaments such as carbon fiber reinforced filaments for lightweight strength, metal-filled filaments for a metallic appearance, or wood-filled filaments for a wooden texture.
8. Resin: If you're using resin-based 3D printing (SLA or DLP), the best resin will depend on your project. Standard resins are versatile, while specialty resins like flexible or dental resins are tailored to specific applications.

The cost of 3D printing materials can vary depending on several factors, including the type of material, brand, quality, and where you purchase it. Generally, some materials are more affordable than others. Here are some of the cheaper 3D printing materials:
1. PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is often one of the most cost-effective 3D printing materials. It's widely available and derived from renewable resources, making it an economical choice for many projects. PLA is a popular option for beginners and is suitable for a wide range of applications.
2. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG is also reasonably priced and offers good durability and ease of use. It's an excellent alternative to PLA or ABS for those looking for a balance between cost and performance.
3. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is a flexible filament that is often competitively priced. It's used for producing items like phone cases, shoe soles, and other flexible parts.
4. Wood-Infused Filaments: Wood-filled filaments, which combine PLA with wood fibers, can be an affordable way to add a wood-like texture to your prints. These are commonly used for decorative items and can provide a unique appearance.
5. Basic Resins (for SLA/DLP Printing): When it comes to resin-based 3D printing, there are some cost-effective options for basic resins. These resins are suitable for a variety of applications, including jewelry, figurines, and prototypes.

While 3D printing has made significant advancements in terms of materials, not all materials can be used for 3D printing. The main limitation is that materials for 3D printing must be in a form that can be melted, solidified, or otherwise manipulated by a 3D printer.
1. Non-meltable Materials: 3D printers work by melting or softening a material and then building up layers to create an object. Materials that cannot be melted or softened by heat are not suitable for 3D printing. For example, metals with extremely high melting points like tungsten or ceramics that require sintering at very high temperatures cannot be 3D printed with typical desktop 3D printers.
2. Liquid Materials: While there are resin-based 3D printing technologies like Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) that use liquid resins, these resins are specifically formulated for 3D printing. Regular liquids, like water or oil, cannot be used in standard 3D printers.
3. Gases: Gases, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or helium, cannot be used as 3D printing materials. 3D printing relies on the deposition and solidification of a material layer by layer, which is not possible with gases.
4. Non-Uniform Materials: Materials that are not uniform in composition or consistency, such as mixtures of liquids and solids or materials with varying properties within the same object, are challenging or impossible to 3D print. The 3D printer needs a consistent material to work with.
5. Highly Reactive or Dangerous Materials: Materials that are highly reactive, toxic, or dangerous to handle, such as explosives, radioactive substances, or hazardous chemicals, should not be used for 3D printing due to safety concerns.
6. Extremely Soft or Viscous Materials: While flexible materials like TPU can be used for 3D printing, extremely soft or highly viscous materials may not work well with standard 3D printers. They may not maintain their shape during printing or may cause other issues.
7. Biological Materials: Traditional 3D printers cannot directly print living biological materials like cells or tissues. However, there are specialized bioprinters designed for this purpose, which can deposit biological materials in a controlled manner.
It's important to note that the range of materials available for 3D printing is continuously expanding, and researchers are working on new techniques and materials for various applications. Some of these materials include biocompatible materials for medical applications, conductive materials for electronics, and composite materials for enhanced properties. Always refer to your 3D printer's manufacturer guidelines and consult with experts when working with non-standard materials to ensure safety and compatibility.
When you are looking for a high quality and reliable 3D printing service partner, Richconn is definitely your first choice!
QUALITY GUARANTEED: The Richconn team has advanced 3D printing technology and extensive experience to ensure that your projects are of exceptional quality.
MULTIPLE MATERIALS AVAILABLE: We offer a wide range of material options including PLA, ABS, PETG, metals, ceramics, and more to meet a variety of project needs.
CUSTOMIZED SOLUTIONS: Whether you need rapid prototyping, low-volume production, or specific parts, we have the best solution for you.
FAST DELIVERY: Our efficient production process and prompt delivery time will ensure that your project is completed on time.
COMPETITIVE PRICING: We offer competitive pricing to ensure you get high quality 3D printing services at a reasonable cost.
CUSTOMER FIRST: With customer satisfaction at the core of our business, we are committed to exceeding expectations to ensure you are satisfied with our services.
Whether you are trying 3D printing for the first time or looking for a trusted partner for your 3D printing needs, Richconn will provide you with the best solution. Contact us to realize your ideas and projects together!
 How to Maximize the Effectiveness of CNC Machining Technology?August 14, 2023Positive Innovation of Mechanical CNC Machining EquipmentIn order to maximize the application effect of CNC machining technology, it is necessary to analyze the characteristics of CNC machining ODM te...view
How to Maximize the Effectiveness of CNC Machining Technology?August 14, 2023Positive Innovation of Mechanical CNC Machining EquipmentIn order to maximize the application effect of CNC machining technology, it is necessary to analyze the characteristics of CNC machining ODM te...view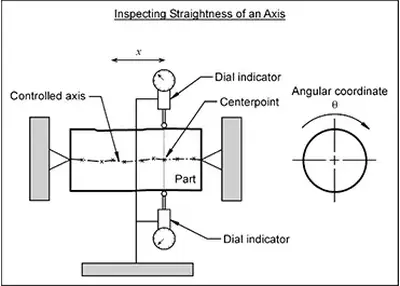 Understanding Straightness: Unveiling Precision in EngineeringNovember 21, 2023Welcome to a journey through the realm of straightness—a fundamental concept in the world of engineering and precision manufacturing. Ever wondered how straightness impacts the quality of products or the efficiency of industrial processes? Join me as we explore the nuances and practical applications of this crucial element.view
Understanding Straightness: Unveiling Precision in EngineeringNovember 21, 2023Welcome to a journey through the realm of straightness—a fundamental concept in the world of engineering and precision manufacturing. Ever wondered how straightness impacts the quality of products or the efficiency of industrial processes? Join me as we explore the nuances and practical applications of this crucial element.view Aluminum Alloy Anodic Oxidation Common ProblemsOctober 23, 2023Anodizing is one of the most common metal surface treatment operations performed on aluminum parts. It is an electrochemical process that involves immersing aluminum parts in a series of tanks to transform the aluminum surface into a durable and corrosion-resistant finish.view
Aluminum Alloy Anodic Oxidation Common ProblemsOctober 23, 2023Anodizing is one of the most common metal surface treatment operations performed on aluminum parts. It is an electrochemical process that involves immersing aluminum parts in a series of tanks to transform the aluminum surface into a durable and corrosion-resistant finish.view Boring Machining Process GuideNovember 22, 2023In CNC machining, boring technology is used as a precision machining process with a spindle mounted sleeve. Boring is a machining process in which the internal surface of a workpiece is cut by a rotating tool on a boring machine to determine the precise hole diameter and surface quality.view
Boring Machining Process GuideNovember 22, 2023In CNC machining, boring technology is used as a precision machining process with a spindle mounted sleeve. Boring is a machining process in which the internal surface of a workpiece is cut by a rotating tool on a boring machine to determine the precise hole diameter and surface quality.view The Basics For the Right ThreadOctober 16, 2023At Richconn, you can easily add threaded holes to your CNC machined parts. Adding by turning gives you many additional threading options. There are two types when it comes to threading: Internal threads and external threads.view
The Basics For the Right ThreadOctober 16, 2023At Richconn, you can easily add threaded holes to your CNC machined parts. Adding by turning gives you many additional threading options. There are two types when it comes to threading: Internal threads and external threads.view How Do I Get the Part to Meet the Machining Conditions?October 30, 2023Featuring intricate geometries, often complex CNC parts may require the machining of a series of contours, holes, and recesses to achieve the desired shape and size. Read on to learn more about the complexity of CNC machined part geometries and some of our best tips for reducing design complexity.view
How Do I Get the Part to Meet the Machining Conditions?October 30, 2023Featuring intricate geometries, often complex CNC parts may require the machining of a series of contours, holes, and recesses to achieve the desired shape and size. Read on to learn more about the complexity of CNC machined part geometries and some of our best tips for reducing design complexity.view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru