Springs play a crucial role in various products, providing motion and shock absorption. They are vital mechanical components used in watches, cell phones, and many other products. Prototyping technologies like 3D printing and CNC machining enable the production of different types of springs to meet specific design requirements.
Springs are extensively utilized in a wide range of popular products, highlighting the importance of understanding their selection and application. This article aims to discuss the benefits and limitations of springs and explore what are springs, the working of springs, and their applications. By gaining insights into these aspects, readers can comprehensively understand how to make springs and how they contribute to product design and functionality.
Spring mechanism works by stretching or compressing when a force is applied and then returning to its original shape when the force is removed. They store energy when they're stretched or compressed and release it when they're allowed to go back to their normal state. This makes them useful for absorbing shocks, providing support, and allowing for controlled motion in various devices and machines.
Spring characteristics refer to the specific properties and attributes that describe the behavior and performance of a spring. These characteristics include:
Spring Rate
The spring rate, also known as the stiffness or spring constant, is a measure of how much force is required to compress or extend a spring by a certain amount. It describes the relationship between the applied force and the resulting displacement. The higher the spring rate, the stiffer the spring.
Load Capacity
The load capacity of a spring refers to the maximum amount of force or load that the spring can handle without permanent deformation or failure. It is an important consideration in selecting the appropriate spring sketch for a specific application.
Deflection
Deflection refers to the amount of displacement or compression that a spring undergoes when a force is applied to it. It is a measure of the spring's flexibility and its ability to absorb shocks or provide cushioning.
Fatigue Life
Fatigue life characterizes a spring's ability to withstand repeated loading and unloading cycles without experiencing a decrease in performance or failure. It is an essential consideration, particularly in applications where the spring undergoes frequent or cyclic loading.
A spring is a lightweight component that generates a force proportional to its displacement when it is stretched or compressed from its natural length. When an object connected to a spring is pulled away from its resting position and then released, the spring's restoring force will bring the object back to its original equilibrium. In a spring-mass system placed on a flat surface, the only force acting on the mass in the direction of displacement is the restoring force produced by the spring.
The Spring force formula is given by, F = k (x – x0)
The force exerted by the spring is denoted as F, while the position at equilibrium is represented as xo. The displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position is indicated by x, and the constant that characterizes the spring's stiffness is known as k. The negative sign indicates that the observed spring force functions as a restoring force, pulling in the opposite direction.
Springs are utilized in a wide range of applications due to their diverse materials, shapes, and functions. As a result, define springs in three main categories, each comprising different subcategories. Some common spring shapes include:
A helical spring is defined as a coil spring and is widely recognized as the predominant type of spring used in the manufacturing of various products. This spring-loaded mechanism is formed by coiling wire into a helix shape, which gives it its name. Helical springs can be created using wire with different cross-sections, allowing for customization based on specific design requirements. Below are the different types of helical springs:
1. Compression Springs

Compression springs are helical springs or other words for springs with an open-coil design, characterized by a constant diameter and a variable shape. These springs are specifically designed to resist axial compression forces.
An easy-to-understand application of compression springs can be found in ballpoint pens, where they play a crucial role in creating the "popping" effect when the pen tip is clicked in and out. Compression springs also find usage in valves and suspension systems, among other applications.
2. Extension Springs
Unlike compression springs, extension springs are helical springs with closed coils. They are designed to create tension, store energy, and utilize that energy to restore the spring to its original shape.
An easy-to-understand application of extension springs can be seen in garage doors, where they provide the necessary tension to counterbalance the weight of the door. Additionally, extension springs are used in pull levers, jaw pliers, and weighing machines, among other devices and mechanisms.

3. Torsion Springs
A torsion spring loading mechanism is connected to two separate components by its two ends, maintaining a specific angle between them. These springs utilize the radial direction when subjected to rotational forces. Furthermore, CNC machining can manufacture custom two-bodied torsion springs in large quantities.
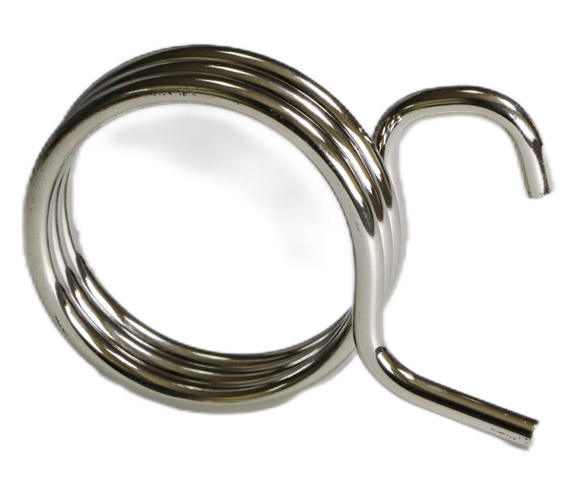

4. Spiral Springs
Spiral springs are produced by coiling flat, rectangular metal strips into a spiral shape. When engaged, these springs can store a considerable amount of energy and release it at a consistent rate. This consistent release of energy makes spiral springs ideal for applications such as mechanical watches, toys, and seat recliners.
Table 1: Comparison of Common Helical Spring Types
Helical Spring Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Common Applications |
Compression Springs | Can handle repeated compression without significant wear. | Limited resistance to pulling or twisting forces. | Ballpoint pens and suspension systems |
Efficient in storing and releasing energy. | Possible issues with buckling or misalignment. | ||
Extension Springs | Provide resistance against stretching or tension forces. | Potential for coil clash or misalignment. | Garage doors, pull levers, jaw pliers, and weighing machines |
Can absorb and store energy when extended. | Solid height limitations. | ||
Torsion Springs | Designed to withstand twisting or torque forces. | Limited functionality in compression or tension applications. | Clothespins, mouse traps, and automotive applications |
Store and release energy in torsional motion. | May experience coil clash or misalignment. | ||
Spiral Springs | Provide continuous force over a longer range of motion. | More challenging to manufacture compared to simple coil springs. | Mechanical watches, toys, and seat recliners |
Offer high energy storage capacity. | May experience wear and fatigue over time. |

Leaf springs, also referred to as leaves, are a category of springs constructed from rectangular metal plates. These metal plates, which are bolted and clamped together, are primarily utilized in heavy-duty vehicles. Types of leaf springs include:
1. Elliptical Leaf Spring
The elliptical leaf spring is created by connecting two semi-elliptical springs in opposite directions, forming the shape of a spring. The axle and frame of a vehicle are attached to these elliptical leaf springs. In this design, spring shackles are not required as the two semi-elliptical springs elongate by the same amount during compression. It is worth noting that while elliptical leaf springs were once commonly used in older cars, their application has become less common in modern vehicles.
2. Quarter Elliptical Leaf Spring
The quarter elliptical leaf spring also referred to as the cantilever-type leaf spring, is another type of leaf spring commonly associated with older designs. It features one end securely fixed to the side member of the frame using a U-Clamp or I-Bolt, while the other end remains free and connected to the front axle. When the front axle beam experiences a shock load, the leaves of the quarter elliptical leaf spring straighten to effectively absorb and mitigate the impact.
3. Three-quarter Elliptical Leaf Spring
An example of the application of the leaf spring is seen in a door hinge mechanism. When the door is opened, the leaf spring stores rotational energy. Upon releasing the door, the stored energy in the spring is utilized to return the door to its original position. The rotational force generated by the spring depends on its rotation.
This type of leaf spring is a combination of the quarter elliptical spring and the semi-elliptical spring. In this configuration, one end of the semi-elliptical part is attached to the vehicle frame, while the other end is connected to the quarter elliptical spring. The opposing end of the quarter elliptical spring is attached to the frame and head through the use of an I-bolt.
4. Transverse Leaf Spring
The transverse leaf spring is created by horizontally mounting a semi-elliptical leaf spring across the width of a vehicle. In this arrangement, the longest leaf of the spring is positioned at the bottom, while the middle portion is secured to the frame using a U-bolt. Transverse leaf springs typically employ two shackles for attachment. However, they can contribute to a rolling motion, making them unsuitable for automotive applications.
Is leaf spring shop near me? Do you have a product, and you worry about making it functional? Why not contact Richconn today? And we will give the suggestions on leaf springs.
Table 2: Leaf Spring Diagram
Leaf Spring Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Common Applications |
Elliptical Leaf Spring | Enhanced load-carrying capacity. | Requires more space for installation. | Heavy-duty vehicles, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery |
Improved ride quality. | Limited flexibility | ||
Quarter Elliptical Leaf Spring | Provides a compact and lightweight design. | Reduced load-carrying capacity compared to other types. | Vintage vehicles and small trailers |
Offers specific load requirements. | Limited flexibility in suspension tuning. | ||
Three-Quarter Elliptical Leaf Spring | Improved load-carrying capability compared to quarter elliptical springs. | Requires sufficient space for installation. | Automotive, recreational, and industrial settings |
Improved load-carrying capability compared to quarter elliptical springs. | |||
Transverse Leaf Spring | Provides weight distribution across the vehicle's width. | Limited to specific vehicle applications. | Sports cars and independent Suspension |
Offers design flexibility. |
Leaf springs and coil springs are two common types of springs used in various applications. Here's a comparison between the two:
Table 3: Diagram of Leaf Spring and Coil Spring
Difference | Leaf Springs | Coil Springs |
Construction | Leaf springs consist of multiple layers of curved metal strips, called leaves, stacked on top of each other and bound together. The leaves are typically tapered and attached to an axle or frame using brackets or shackles. | Coil springs are made from a single or multiple coiled wire, forming a helical shape. They are often installed around shocks or struts or mounted between control arms and the vehicle chassis. |
Load Capacity | Leaf springs are known for their durability and ability to withstand heavy loads, making them suitable for rough terrains and demanding conditions. | Coil springs come in a range of load capacities, from light-duty to heavy-duty, and are used in various applications, including passenger cars, motorcycles, and industrial machinery. |
Durability | Leaf springs have a high load-carrying capacity and are commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as trucks, SUVs, and trailers. | Coil springs offer good durability, although the material and manufacturing quality can affect their longevity. |
Weight | Leaf springs tend to be heavier compared to coil springs, which can affect the overall weight of the vehicle or system. | Coil springs are generally lighter in weight compared to leaf springs, which can contribute to overall weight reduction for improved fuel efficiency. |
Ride Comfort | Leaf springs can provide a stiffer ride compared to coil springs, leading to a less smooth and more rigid suspension feel. | Coil springs provide a smoother and more comfortable ride compared to leaf springs, as they offer better shock absorption and flexibility. |
Cost | Leaf springs are typically more affordable to manufacture and replace compared to coil springs. | Coil springs can be more expensive to manufacture and replace compared to leaf springs, depending on the application. |
Disk springs, also known as Belleville springs, are individual or multiple springs arranged in series or parallel configurations. This setup enables them to efficiently absorb and distribute high loads within limited spaces. Below are the different types of disk spring and their applications.
1. Belleville Disk Spring
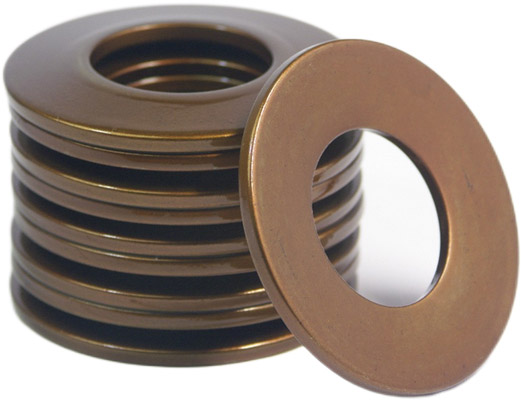

The Belleville disk spring, also referred to as a circular spring, features a unique cupped construction. Unlike flat springs, these mechanical springs take on a conical shape that allows them to effectively handle heavy loads. Their design enables them to compress under pressure, offering increased load-carrying capacity and enhanced performance.
2. Curved Disk Spring
Crescent washers, also known as Belleville washers, are specifically designed to apply a light but consistent pressure to the mating parts, effectively counteracting loosening caused by vibration. These washers play a crucial role in distributing loads evenly across threaded bolts, screws, and nuts in machinery that experiences continuous vibration. Their design ensures that the fasteners remain securely in place, reducing the risk of unintended loosening and maintaining the integrity of the assembly.
3. Slotted Disk Spring
By incorporating slots along the outer and inner diameter, a slotted disk spring can be created. This design modification transforms the disk spring into a lever-like structure, allowing for reduced spring load and increased deflection. Slotted disk springs find extensive application in various mechanisms such as automatic transmissions, clutches, and overload couplings, where their unique characteristics provide advantageous performance and functionality.
4. Wave Disk Spring
Wave disk springs feature multiple waves per turn, offering predictable and precise loading characteristics. They excel in applications where cushioning and stress absorption from axial compression is required. These springs act as a buffer, effectively absorbing and distributing stress and preventing excessive compression. Their unique wave design allows for reliable performance and consistent load application, making them ideal for various applications requiring controlled and predictable spring behavior.
Table 4: Comparison of Common Disk Springs Type
Disk Springs Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Common Applications |
Belleville Disk Spring | High load capacity with small deflection. | Limited range of deflection. | clutches, valves, electrical connections, and other systems that require high load capacity and small deflection |
Can withstand high temperatures. | Sensitive to overloading. | ||
Curved Disk Spring | Provides linear load-deflection characteristics. | More challenging to manufacture than flat disk springs. | switches, connectors, actuators, and systems where linear load-deflection characteristics and significant deflection |
Offers consistent force distribution. | Occupies more space compared to other types. | ||
Slotted Disk Sprin | Allows for reduced spring load and increased deflection. | Reduced load capacity compared to non-slotted disk springs. | automotive suspensions, engine mounts, and industrial machinery |
Minimizes stress concentrations. | Increased complexity due to the presence of slots. | ||
Wave Disk Spring | Can act as a cushion by absorbing axial compression stress. | Increased complexity due to the wave design. | clutch systems, shock absorbers, damping devices, and applications that require precise loading, cushioning, and stress absorption |
Suitable for applications requiring controlled deflection. | May experience stress concentration at wave crests. |
Unlike the conventional assumption that springs come from iron, it is important to know how are springs made. The types of materials, therefore, determine the properties, types of springs, and their applications. Below are the common materials:
Springs made from copper alloys, like beryllium copper, are really strong and don't change shape easily over time. They're also great at conducting electricity. These alloys can be shaped into complex designs, which is good for making springs that need to fit specific needs. Because of these qualities, copper alloy springs are commonly used in musical instruments, measurement devices, and even making bullets. They're valued for their strength, reliability, and ability to do specific jobs.
Ceramic
Ceramic materials are great for making springs that need to work in really hot places. They can resist damage from rubbing and water, so they last a long time in tough conditions. Ceramics are also very hard, so they don't wear down easily when under pressure. They have a low friction, which means they don't create much resistance when they touch other surfaces. Ceramics are also lightweight, which is helpful in applications where weight is important. Because of these special qualities, ceramics are perfect for making springs that can handle high temperatures, resist wear, and last a long time.
Glass Fiber
Glass fiber is a robust and durable material made by reinforcing glass fibers. Due to its superior strength, manufacturers are currently exploring its potential as a material for producing various types of springs. The exceptional strength exhibited by this composite material makes it a promising candidate for spring manufacturing applications.
Rubber
These materials are well-suited for creating springs that have a cylindrical or non-coil design. They are known for being safe and dependable. Additionally, their non-conductive properties make them highly useful in cases where magnetism, corrosion, and vibration can pose challenges. These materials provide effective solutions for applications where electrical conductivity needs to be avoided and where the prevention of magnetism, corrosion, and vibration-related issues is crucial.
Steel Alloys
Steel alloy springs are the most widely used and popular type of spring. They have exceptional strength and durability, and while they can be further enhanced with additional materials, they possess impressive qualities on their own. Their widespread popularity is due to their reliable performance, excellent strength, and long-lasting durability.
If you're in need of on-demand products with springs, Richconn offers a comprehensive one-stop solution. From sourcing and purchasing the specific springs you require to manufacturing the necessary parts and assembling your products, Richconn ensures a streamlined and efficient process. With a quick turnaround time, you can expect your products to be completed and returned to you on time. The convenient and efficient service provided by Richconn allows you to meet your manufacturing needs promptly and effectively.
Springs play a significant role in products that involve movement. They have the ability to store and release energy when compressed or expanded. The selection of an appropriate spring relies on understanding the different types of springs used today. Each type of spring possesses distinct features and characteristics determined by factors such as the materials used, design considerations, and manufacturing methods. Therefore, when deciding to incorporate a spring into your product, it is essential to consider these factors in order to ensure an appropriate and effective choice.
 CNC Machining: Insights into Mass and Small Batch ProductionsJuly 19, 2024Dive into the detailed exploration of CNC machining to empower your business decisions! Let’s discover the pros of mass and small batch production, shifts in the industry, and tips for choosing the best.view
CNC Machining: Insights into Mass and Small Batch ProductionsJuly 19, 2024Dive into the detailed exploration of CNC machining to empower your business decisions! Let’s discover the pros of mass and small batch production, shifts in the industry, and tips for choosing the best.view Understanding Straightness: Unveiling Precision in EngineeringNovember 21, 2023Welcome to a journey through the realm of straightness—a fundamental concept in the world of engineering and precision manufacturing. Ever wondered how straightness impacts the quality of products or the efficiency of industrial processes? Join me as we explore the nuances and practical applications of this crucial element.view
Understanding Straightness: Unveiling Precision in EngineeringNovember 21, 2023Welcome to a journey through the realm of straightness—a fundamental concept in the world of engineering and precision manufacturing. Ever wondered how straightness impacts the quality of products or the efficiency of industrial processes? Join me as we explore the nuances and practical applications of this crucial element.view How to remove chrome plating from sheet metal?November 24, 2023Chrome plating is a common metal finish that improves the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, aesthetics and hardness of the metal.view
How to remove chrome plating from sheet metal?November 24, 2023Chrome plating is a common metal finish that improves the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, aesthetics and hardness of the metal.view Application of 5-Axis Machining Center in High-Speed Blower Impeller ManufacturingMarch 24, 2023With the rapid development of technology, high-speed blowers have been widely used in various fields. In order to improve the performance and efficiency of the blowers, it is necessary to manufacture ...view
Application of 5-Axis Machining Center in High-Speed Blower Impeller ManufacturingMarch 24, 2023With the rapid development of technology, high-speed blowers have been widely used in various fields. In order to improve the performance and efficiency of the blowers, it is necessary to manufacture ...view Ten Questions and Answers About Stainless Steel Valves: Unlocking the Secrets of Check ValvesAugust 11, 2023IntroductionIn this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the mysteries of stainless steel valves, with a particular focus on the working principles and applications of check valves across di...view
Ten Questions and Answers About Stainless Steel Valves: Unlocking the Secrets of Check ValvesAugust 11, 2023IntroductionIn this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the mysteries of stainless steel valves, with a particular focus on the working principles and applications of check valves across di...view What is the Powder Bed Fusion Process?November 28, 2023Powder bed fusion (PBF) is a type of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, that uses a heat source, such as a laser or an electron beam, to melt and fuse material powder together to create solid parts.view
What is the Powder Bed Fusion Process?November 28, 2023Powder bed fusion (PBF) is a type of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, that uses a heat source, such as a laser or an electron beam, to melt and fuse material powder together to create solid parts.view