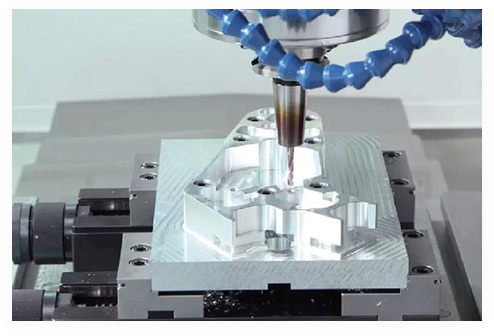
Are you ready to dive into the world of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines? If you're fascinated by precision engineering and the wonders it can achieve, you've come to the right place. If you're fascinated by precision engineering and the wonders it can achieve, you've come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, I will walk you through the intricate web of components that make up a CNC machine. Whether you're an engineer, a manufacturer, or just a curious mind, understanding the inner workings of CNC machines is a powerful tool that can unlock a realm of possibilities.
The basic components of a CNC lathe can be categorized into the machine body, the CNC system, the tooling system, the fixturing system, and the cooling and lubrication system.

Bed: The bed of CNC lathe is the main structure of the entire machine tool, usually made of cast iron or welded structure, with sufficient rigidity and stability to withstand cutting forces and vibration.
Spindle: The spindle is the core component of the CNC lathe, which is responsible for rotating the workpiece and cutting tools. The spindle is usually made of high-strength alloy steel and equipped with bearings and lubrication system to maintain high precision and smooth operation.
Supporting guideway: Supporting guideway is used to support and guide the movement of tool holder or table to ensure accuracy and stability during machining. Common types of guideways include linear guideways and ball screw guideways.
Motion systems: The machine body is equipped with different types of motion systems, including spindle drives, transverse and longitudinal feed systems, for precise motion control of the workpiece and tool in three axes.
Tool holders: Tool holders are support structures for tools and usually have multiple tool positions to accommodate different types and sizes of tools. The tool holder can switch tools manually or automatically.
Tailstock: The tailstock supports the other end of the workpiece and allows the center of rotation of the workpiece to be adjusted to accommodate different lengths of workpieces.
Feed Mechanism: The feed mechanism controls the feed movement of the table or tool holder and usually includes servo motors, ball screws, guide rails, and encoders for high-precision feed control.
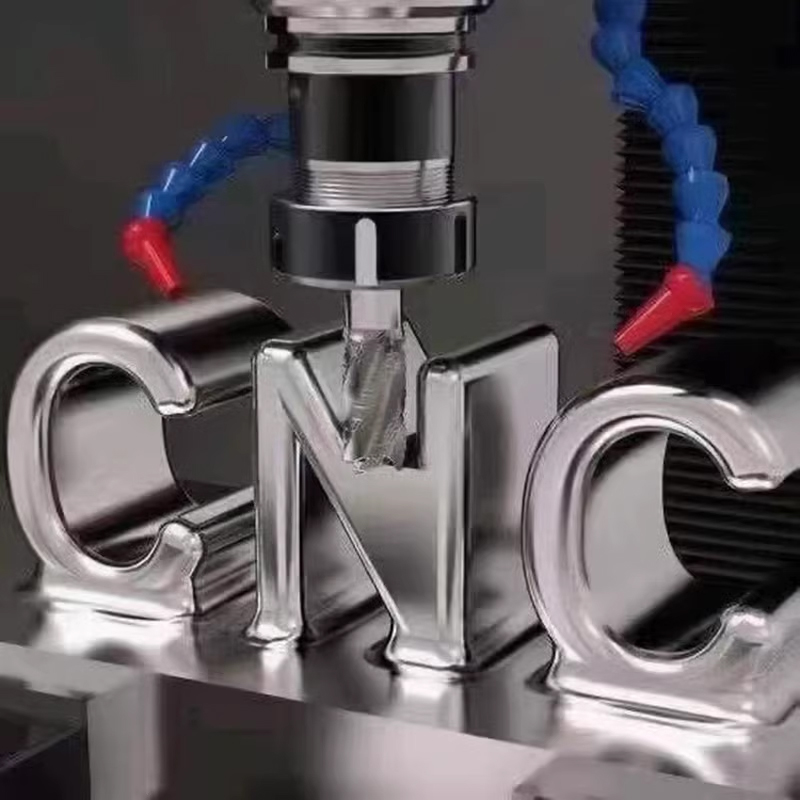

The CNC system is the intelligent core of a CNC machine tool, which is responsible for controlling and managing the entire machining process. The CNC system consists of several key elements that work closely together to ensure that the machine tool operates and the workpiece is machined with high precision and efficiency.
The CPU is the core component of the CNC system, which is similar to the brain of a computer and is responsible for executing the machining program, interpreting the G-code, controlling the movement of the machine tool and monitoring the machining process. Modern CNC machine tools are usually equipped with high-performance multi-core CPUs to cope with complex machining tasks.
Input devices are used to input machining programs and commands into the CNC. The most common input devices are keyboards and mice, but USB drives, LAN connections, or other data transfer methods can also be used to load machining programs. The operator can use the input devices to edit programs, set machining parameters, and perform other operations.
The machine control panel is the physical interface on a CNC machine tool that allows the operator to manually control the machine's motion, select tools, set machining speeds, and perform diagnostics. Control panels typically include buttons, knobs, displays, and indicators that allow the operator to interact directly with the machine tool.
PLC is an important component of a CNC system and is used to perform special control functions such as automated workpiece clamping, cooling and lubrication system control, safety functions, etc. PLCs can be programmed to adapt to different production requirements while maintaining safe and reliable operation of the machine tool.
The servo control unit is responsible for controlling the motion of each axis of motion (usually including X-axis, Y-axis, Z-axis, etc.) to achieve precise positioning and movement of workpieces and tools. The servo control unit consists of servo motors, encoders, and feedback systems, and ensures high-precision motion through closed-loop control.
The display unit is usually an important part of the CNC system, providing a graphical interface for the operator to interact with the machine and monitor the machining process. The display unit shows a graphical preview of the machining program, tool paths, machining status and alarms, allowing the operator to monitor the machine in real time.
Tool shank: The tool shank is the supporting part of the tool, which connects the tool head to the tool holder and transmits the cutting force.
Tool head: The tool head is the part that actually performs the cutting. Different types of tool heads are used for different machining tasks, such as turning tools, drills, milling cutters etc.
Tool magazine: CNC lathes may be equipped with a tool magazine for automatic tool change. These libraries can hold a wide range of tools and automatically select and change tools as required by the machining program.
Fixtures: fixtures are used to hold the workpiece to ensure positional and positioning accuracy of the workpiece during machining. The design and selection of the fixture depends on the shape and size of the workpiece.
Clamping devices: Clamping devices are used to hold the workpiece and usually include chucks, jaws, pneumatic clamps, etc. They can be operated manually or automatically.
COOLING LUBRICANT TANKS: The cooling lubrication system consists of a fluid storage and supply system used to provide a cooling lubricant (usually cutting oil or cutting fluid) to cool the tool and the workpiece, reducing friction and extending tool life.
Cooling Lubrication System Pump: The pump is used to deliver cooling lubricant to the cutting area of the tool and workpiece to ensure consistent cooling and lubrication.
Cooling Lubrication System Nozzles: Nozzles are used to distribute the cooling lubricant evenly to the cutting area to maintain the stability and quality of the machining process.
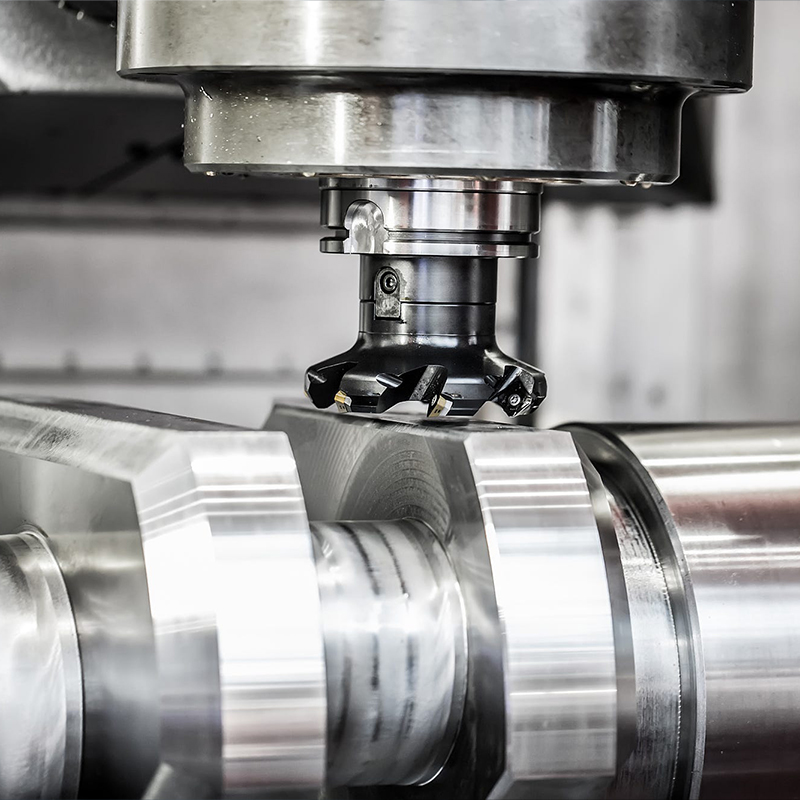

A CNC (numerical control) toolholder is a key component used on CNC machine tools to hold and support the cutting tool, and usually consists of three main parts that play an important role in the installation and use of the cutting tool. These three main parts are:
The main part of the shank (Shank): the main part of the shank is a long rod-like structure, which is usually cylindrical but can be of other geometrical shapes, depending on the type and use of the cutting tool. The body of the shank is usually made of high-strength alloy steel or other materials suitable for cutting applications to ensure stability and rigidity of the tool. The outer surface of the shank body is usually smooth to facilitate clamping and positioning.
Flanges or Flats: One end of the shank usually has a flange for clamping and positioning the cutting tool. Flanges can have different shapes, such as flats, grooves or bumps, to accommodate different types of shank clamping devices. The design and shape of the tool end needs to match the clamping device to ensure that the cutting tool is safely and securely mounted on the toolholder.
Tool Holder: The tool holder is the other end of the shank that holds the cutting tool. Tool holders usually have holes or slots that match the shape and size of the cutting tool to ensure that the cutting tool is properly mounted on the toolholder. The tool holder typically has a clamping device, such as a jaw, screw, or chuck, to ensure that the cutting tool is securely fastened to the toolholder for the cutting operation.
These three main components work together to allow the cutting tool to be attached to the spindle of the CNC machine and remain stable and controllable during the cutting process. The design and selection of a toolholder depends on the type of cutting tool, the requirements of the machining task and the specifications of the CNC machine tool. Proper selection and use of toolholders is important to ensure high accuracy and stability of the machining process.
Understanding the components of a CNC machine is the key to unlocking its full potential. From the structure of the machine to the controls, power, table, tooling, cooling and safety systems, each component plays a vital role in achieving accuracy and efficiency. By making smart choices and staying up-to-date on the latest advances, you can harness the power of CNC technology to bring your ideas to life with unparalleled precision. So start your precision machining journey today and make CNC machines your tool of choice for superior craftsmanship!
A1: A CNC lathe consists of several key components, including the spindle, tool turret, chuck, tailstock, and control unit.
A2: The spindle is responsible for rotating the workpiece or the tool. It can be adjusted for speed and direction to perform various cutting operations.
A3: The tool turret holds multiple cutting tools and can quickly rotate to select the appropriate tool for a specific operation, reducing downtime.
A4: The chuck is used to securely hold the workpiece in place during machining. It provides stability and ensures precise machining of the material.
A5: The control unit interprets the programmed instructions (G-code) and sends signals to the motors and actuators to control the movement and machining operations of the lathe.
 Electroforming vs Electroplating: How They Work and What They DoDecember 6, 2023Electroforming and electroplating are two common metal forming processes that use electricity to deposit metal onto a surface. Both processes involve passing an electric current through a solution called an electrolyte, which contains metal ions.view
Electroforming vs Electroplating: How They Work and What They DoDecember 6, 2023Electroforming and electroplating are two common metal forming processes that use electricity to deposit metal onto a surface. Both processes involve passing an electric current through a solution called an electrolyte, which contains metal ions.view Machining Tungsten Guide: Can Tungsten be Machined?November 13, 2023Welcome to the cutting-edge world of machining tungsten, where precision meets excellence. As the forefront player in CNC machining, Richconn is here to unravel the intricacies of working with tungsten, answering the pivotal question: Can tungsten be machined?view
Machining Tungsten Guide: Can Tungsten be Machined?November 13, 2023Welcome to the cutting-edge world of machining tungsten, where precision meets excellence. As the forefront player in CNC machining, Richconn is here to unravel the intricacies of working with tungsten, answering the pivotal question: Can tungsten be machined?view Unveiling Precision: Mastering Surface Profile for Engineering ExcellenceNovember 21, 2023Engineering precision is more than a requirement; it's a commitment to excellence. Amidst the intricate world of engineering, understanding the nuances of surface profile becomes paramount.view
Unveiling Precision: Mastering Surface Profile for Engineering ExcellenceNovember 21, 2023Engineering precision is more than a requirement; it's a commitment to excellence. Amidst the intricate world of engineering, understanding the nuances of surface profile becomes paramount.view Application of 5-Axis Machining Center in High-Speed Blower Impeller ManufacturingMarch 24, 2023With the rapid development of technology, high-speed blowers have been widely used in various fields. In order to improve the performance and efficiency of the blowers, it is necessary to manufacture ...view
Application of 5-Axis Machining Center in High-Speed Blower Impeller ManufacturingMarch 24, 2023With the rapid development of technology, high-speed blowers have been widely used in various fields. In order to improve the performance and efficiency of the blowers, it is necessary to manufacture ...view Boring Machining Process GuideNovember 22, 2023In CNC machining, boring technology is used as a precision machining process with a spindle mounted sleeve. Boring is a machining process in which the internal surface of a workpiece is cut by a rotating tool on a boring machine to determine the precise hole diameter and surface quality.view
Boring Machining Process GuideNovember 22, 2023In CNC machining, boring technology is used as a precision machining process with a spindle mounted sleeve. Boring is a machining process in which the internal surface of a workpiece is cut by a rotating tool on a boring machine to determine the precise hole diameter and surface quality.view What Is the Threading Method for CNC Machining Centers?April 4, 2023Tapping is a common method in CNC machining technologyIt is generally used in the machining of small-diameter threads, but its precision is relatively poor. Therefore, if high precision is required, t...view
What Is the Threading Method for CNC Machining Centers?April 4, 2023Tapping is a common method in CNC machining technologyIt is generally used in the machining of small-diameter threads, but its precision is relatively poor. Therefore, if high precision is required, t...view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru