There is no single process for manufacturing gear because several processes are required based on the type and application. The gears need to be in absolutely perfect condition to adapt to strenuous conditions. That is why gear manufacturing is highly specialized with tight tolerances and little room for error. This article will take you back to gear manufacturing, covering their common types and application, the processes that manufacture gear, and post-processing for gear manufacturing.
There are various types of gears, as well as their applications and advantages. Your application, performance parameters, and a variety of other considerations all influence the type of gear you use. Here are the five types of mechanical gear you'll encounter.

Spur gears are the most basic type of mechanical gear and have straight teeth parallel to the gear axis. They are widely used in applications that require speed reduction or torque multiplication, such as powerplants, aerospace components, and industrial machines. Straight teeth are the simplest to produce and are capable of high weights and speeds. They are unsuitable for applications where you also need smooth operations, and they make a lot of noise.
Helical gears have teeth that are inclined at an angle to the gear axis, forming a helix shape. These gears provide smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears because the angled teeth play a huge role in reducing the impact load and making the operations smoother. Compared to spur gears, a helical gear train will have more losses and, due to its design, will require thrust bearings. They are commonly used in heavy machinery, automotive transmissions, and industrial equipment.
Bevel gears are used to transmit power between intersecting shafts, with the gear mechanical teeth cut on a cone-shaped surface. They are often used in applications where the direction of the rotational axis needs to be changed, such as in differentials, hand drills, and miter saws
Worm gears consist of a worm (a screw-like gear) and a worm wheel (a gear with spiral teeth). Common applications include conveyor systems, winches, and elevators. The worm wheel configuration is neither fast nor efficient. However, it has a distinctive feature that is essential for self-locking mechanisms. Because of the gear angles, the worm can often turn the wheel but vice versa can’t happen. Another thing to keep in mind is that worm-wheel gears contain a lot of friction and may require continuous friction to function effectively.
Rack and pinion
Rack and pinion gears convert rotary motion into linear motion. A rack is a straight-toothed bar, while the pinion is a small gear meshing with the rack. As a result, you can work on both parallel and angled axes. They are widely used in steering systems, lifting equipment, and linear actuators.
The common gear manufacturing processes are as follows:
Casting is a simpler procedure that is mostly used to manufacture blanks or cylinders for mechanical gears, while machining is utilized to prepare the teeth. For gear production, the most popular casting methods are shell casting, die casting, sand casting, and permanent mold casting. However, there is one sector where casting is the industry's preferred manufacturing method. That is the manufacture of extraordinarily massive gears.
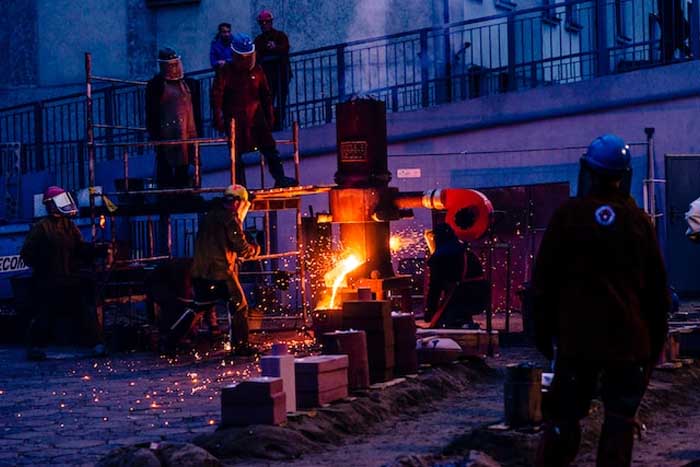

In this process, metal is heated and shaped using compressive forces to obtain the desired gear shape. The forged gear is then machined to achieve the final specifications. Manufacturing gears with forging has been done for a very long time. This is particularly true when producing gear blanks that will later be cut or machined into the proper configuration. Open-die forging, closed-die forging, and hot upset forging have all been used for producing gear blanks. Precision-forged gears with little or no finish machining are now commonly used in the automobile, truck, off-highway, aerospace, railroad, agriculture, and material handling industries, as well as energy and mining.
Extrusion involves forcing a metal billet through a die to create a gear shape of consistent cross-section. While cold drawing is a widely used gear-forming process with advantages like closer dimensional tolerances, higher quality finish, and excellent mechanical qualities as compared to hot-forming processes. The gear-forming process is more versatile and simpler. Extrusion does have a lower tool consumption; however, it is not the most cost-effective procedure. Today, it’s used for multiple manufacturing processes for gear manufacturers.
Powder metallurgy gears are a cost-effective alternative to machine-finished steel or cast iron gears. In many cases, the powder metallurgy (P/M) method produces net-shape or near-net-shape parts, requiring little or no machining to create a final part. As a result, the technique provides dimensional tolerances and mechanical qualities that are compatible with a wide range of applications.
Gear manufacturing post-processing refers to the additional steps taken after the initial gear manufacturing process to improve the quality and performance of gears. The post-processing techniques are commonly used in gear mechanics:
1. Grinding
Grinding is the process of removing material from the gear's surface using an abrasive wheel. It helps to improve the gear's dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and tooth profile.
2. Lapping
Lapping involves rubbing two gear surfaces together with an abrasive paste between them. This process is used to achieve a high level of surface finish, flatness, and tight tolerances.
3. Honing
Honing is a finishing process that uses a rotating abrasive tool to improve the surface texture and roundness of the gear teeth.
4. Shaving
The gear-shaving process involves removing a small amount of material from the gear's tooth surface. It helps to improve gear accuracy, reduce noise, and increase surface finish.
5. Burnishing
Burnishing is a process that involves applying pressure to the gear's surface using a rotating tool with a smooth, hard surface.
Gear manufacturing is a highly skilled industry that requires excellent precision and accuracy. Gears are an essential part of any mechanical system, and even minor manufacturing flaws can have serious effects. As a result, you must exercise caution while selecting a gear manufacturer.
Richconn is experienced in OEM CNC machining for gear parts and has the most professional team that delivers the best performance at the most competitive price. Fill out our contact form or request a quote immediately for additional information.
Contact us and get an instant quote today!
Click it ⬇⬇⬇
 Navigating the World of Horizontal Boring TechnologyNovember 23, 2023Horizontal boring technology encompasses a realm of precision and innovation within precision CNC machining. At its core, it involves the utilization of specialized machinery, notably horizontal boring machines and mills, to create intricate cavities, bores, and holes with utmost accuracy.view
Navigating the World of Horizontal Boring TechnologyNovember 23, 2023Horizontal boring technology encompasses a realm of precision and innovation within precision CNC machining. At its core, it involves the utilization of specialized machinery, notably horizontal boring machines and mills, to create intricate cavities, bores, and holes with utmost accuracy.view CNC Machining Titanium: Precision Craftsmanship and ApplicationsNovember 6, 2023Are you ready to dive into the world of CNC machining titanium? If you're an engineer, designer, or manufacturer seeking to master the art of CNC machining this remarkable metal, you've come to the right place. In this article, I will guide you through the intricacies of CNC machining titanium, offering valuable insights, best practices, and real-world applications.view
CNC Machining Titanium: Precision Craftsmanship and ApplicationsNovember 6, 2023Are you ready to dive into the world of CNC machining titanium? If you're an engineer, designer, or manufacturer seeking to master the art of CNC machining this remarkable metal, you've come to the right place. In this article, I will guide you through the intricacies of CNC machining titanium, offering valuable insights, best practices, and real-world applications.view Titanium vs Steel: Is Titanium Stronger Than Steel?August 29, 2023Is titanium stronger than steel? Here's a brief guide that compares steel to titanium from different aspects.view
Titanium vs Steel: Is Titanium Stronger Than Steel?August 29, 2023Is titanium stronger than steel? Here's a brief guide that compares steel to titanium from different aspects.view The Purpose and Importance of Metal Surface FinishApril 4, 2023Nowadays, metal surface finish technology is applied in many fields, which brings about innovation in metal surface finish and oil stain cleaning technology. Metal surface finish pretreatment is an in...view
The Purpose and Importance of Metal Surface FinishApril 4, 2023Nowadays, metal surface finish technology is applied in many fields, which brings about innovation in metal surface finish and oil stain cleaning technology. Metal surface finish pretreatment is an in...view One Article Tells You What CNC Machining isSeptember 27, 2023The term CNC stands for "Computer Numerical Control" and CNC machining is defined as a subtractive manufacturing process that typically employs computer-controlled and machine tools to remove layers of material from a stock part (known as a blank or workpiece) and produce a custom-designed part.view
One Article Tells You What CNC Machining isSeptember 27, 2023The term CNC stands for "Computer Numerical Control" and CNC machining is defined as a subtractive manufacturing process that typically employs computer-controlled and machine tools to remove layers of material from a stock part (known as a blank or workpiece) and produce a custom-designed part.view What Is the Difference Between 304 Stainless Steel and 316 Stainless Steel?October 27, 2023It is alloyed from steel, chromium, nickel and other elements, where steel is the main component of stainless steel, while chromium is the main corrosion prevention element of stainless steel, and nickel helps to improve the corrosion resistance and strength of stainless steel.view
What Is the Difference Between 304 Stainless Steel and 316 Stainless Steel?October 27, 2023It is alloyed from steel, chromium, nickel and other elements, where steel is the main component of stainless steel, while chromium is the main corrosion prevention element of stainless steel, and nickel helps to improve the corrosion resistance and strength of stainless steel.view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru 



