In CNC manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. Whether you're producing complex aerospace components or assembling consumer electronics, the role of jigs and fixtures cannot be overstated. These unassuming tools serve as the backbone of modern production, streamlining processes, enhancing quality, and ultimately contributing to the bottom line.
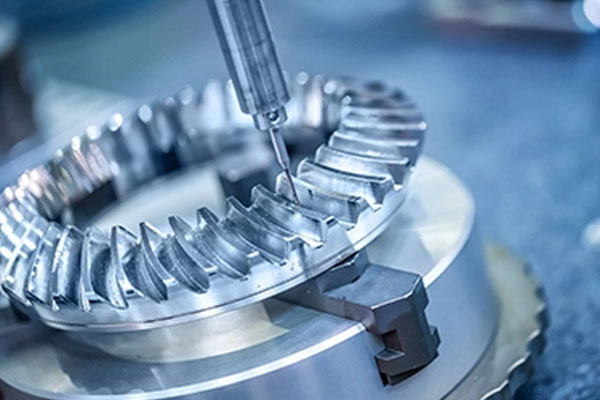

When it comes to the jig meaning. The term "jig" finds its roots in the Old French word "giguer," which translates to "to dance or leap." Over time, this term evolved to denote mechanical devices used to aid in various tasks, particularly those requiring precision and control.
What are jigs? At its core, a jig is a specialized tool designed to guide, control, or hold workpieces and tools during manufacturing operations. These ingenious devices serve as the linchpin of precision, ensuring that each component is crafted with accuracy and consistency.
Their primary function is to guide and support tools, ensuring consistent part geometry. By precisely positioning the workpiece relative to the tool, jigs enable accurate drilling, reaming, tapping, and other repetitive tasks.
1. Template Jig
Among the most common types, template jigs are tailored for repetitive operations where precise duplication of components is paramount. These jigs feature templates or patterns that guide the machining tool along predetermined paths, ensuring uniformity across multiple workpieces.
2. Plate Jig
Suited for flat workpieces, plate jigs provide a stable and secure platform for machining operations. These jigs typically consist of a flat plate with drilled holes or other guiding mechanisms, allowing for precise positioning and alignment of the workpiece.
3. Channel Jig
Channel jigs excel in guiding tools along complex geometries or irregular shapes. By providing a channel or groove for the tool to traverse, these jigs ensure consistent and accurate machining, even in challenging workpiece configurations.
4. Leaf Jig
Engineered for thin workpieces, leaf jigs offer delicate yet robust support during machining operations. These jigs feature thin, flexible elements that conform to the contours of the workpiece, minimizing distortion and ensuring precise machining.
5. Angle Plate Jig
Angular machining poses unique challenges, requiring specialized tools to achieve precise orientation and alignment. Angle plate jigs are specifically designed to address these challenges, providing a stable platform for machining operations at various angles and inclinations.
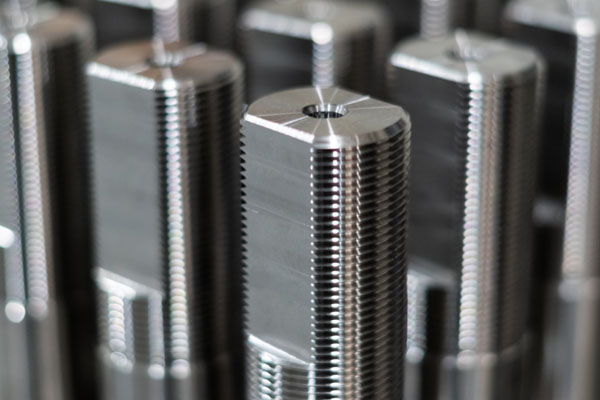

A fixture is one of the fundamental components in manufacturing. By providing stability, fixtures prevent movement, vibration, and distortion, allowing accurate machining.
To answer what is fixturing. Fixturing (fixture manufacturing) is the process of securely holding and supporting workpieces during machining or assembly operations. Therefore, fixtures are specialized tools designed to ensure the precise positioning, stability, and alignment of workpieces, facilitating accurate and efficient manufacturing processes.
1. Vise Fixture
Among the most ubiquitous types, vise fixtures are commonly used in milling operations. These fixtures utilize a vise mechanism to securely clamp and hold workpieces in place, providing stability and rigidity during machining.
2. Plate Fixture
Ideal for flat workpieces, plate fixtures offer a simple yet effective solution for securing components during machining operations. These fixtures typically consist of a flat plate with clamping mechanisms or locating pins to hold the workpiece firmly in position.
3. Angle Plate Fixture
Angular machining presents unique challenges, requiring specialized fixtures to achieve precise orientation and alignment. Angle plate fixtures are specifically designed to address these challenges, providing a stable platform for machining operations at various angles and inclinations.
4. Indexing Fixture
Indexing fixtures enable precise rotation or positioning of workpieces, ensuring accurate machining at predefined intervals or angles. It can be used particularly for those involving complex geometries.
5. Rotary Fixture
Circular workpieces pose unique challenges in manufacturing, requiring specialized fixtures to facilitate multi-sided machining operations. Rotary fixtures are designed to accommodate circular workpieces, allowing for precise rotation and positioning during machining.
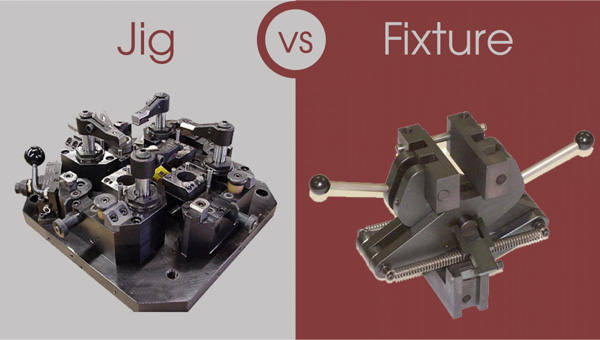
While both jigs and fixtures play crucial roles in manufacturing, they serve distinct purposes: jigs guide and control the cutting tool, whereas fixtures secure and support the workpiece during machining operations. Have a look at their key differences in detail:
Jigs Guide Cutting Tools
A jig's core function is to guide the cutting tool to a predetermined location on the workpiece. They provide support and precise positioning for the part. Jigs ensure uniformity in hole spacing, surface finishes, and critical dimensions by controlling tool movement.
Fixtures Support and Locate Workpieces
Fixtures are primarily responsible for securely holding, supporting, and locating workpieces during machining or assembly operations. They offer a stable platform for workpieces, minimizing movement, vibration, and distortion.
Complexity
Jigs are generally simpler to use compared to fixtures.
Fixtures may require a certain level of skill from machinists before operation.
Weight
Jigs are typically lighter than fixtures due to their design.
Fixtures are heavier to withstand cutting forces and vibrations during machining.
Attachment to the Machine
Jigs can be held or fixed on the table depending on the specific requirements of the work.
Fixtures typically require clamping and may benefit from additional accessories for optimal performance.
Design Complexity
Jigs tend to be more intricate than fixtures due to their multifaceted requirements in guiding cutting tools and supporting workpieces accurately.
Jigs and fixtures are encompassing a myriad of tangible benefits that are instrumental in driving operational excellence and fostering innovation.
Increased Productivity
By providing a standardized framework for machining operations, these tools enable machinists to optimize workflow, reduce setup times, and maximize throughput, ultimately leading to heightened productivity levels.
Enhanced Part Accuracy
By guiding cutting tools and securing workpieces with stability, these tools mitigate the risk of errors and deviations, resulting in parts that meet exact specifications with accuracy.
Cost Savings
Jigs and fixtures offer a pathway to savings through various avenues. By minimizing scrap rates and rework, these tools optimize material utilization, reducing waste and enhancing resource efficiency. Additionally, the increased productivity and enhanced part accuracy afforded by jigs and fixtures translates directly into cost savings, as manufacturers can achieve higher output with fewer resources.
Consistent Quality
Quality lies at the heart of customer satisfaction and brand reputation. By providing a stable and controlled environment for machining operations, these tools eliminate variability and deviations, resulting in parts that exhibit consistent quality and performance characteristics.
Safety Improvements
By securely holding workpieces and guiding cutting tools with precision, these tools mitigate the potential for mishaps, creating a conducive environment for operators to work with confidence and peace of mind.

Jigs and fixtures are versatile tools that find extensive application across various manufacturing processes, serving as indispensable aids in achieving precision, efficiency, and consistency.
1. Drilling
In drilling operations, jigs and fixtures can guide drills to precise locations on workpieces. By providing accurate positioning and alignment, jigs ensure uniform hole spacing and depth. They can be used in applications ranging from metal fabrication to woodworking.
2. Milling
Milling operations often involve intricate machining tasks that demand precise control and stability. Jigs and fixtures excel in this domain by securely holding workpieces in place while guiding milling cutters along predefined paths. This ensures the precise shaping and machining of components with complex geometries and tight tolerances.
3. Grinding
Precision grinding requires meticulous attention to detail to achieve smooth surfaces and accurate dimensions. Jigs and fixtures aid in this process by providing stable support for workpieces and guiding grinding tools with precision. Whether it's surface grinding, cylindrical grinding, or internal grinding, these tools ensure consistent results and superior surface finishes.
4. Welding
Welding operations benefit greatly from the use of jigs and fixtures to hold workpieces in the correct orientation and alignment. By providing a stable platform for welding, fixtures ensure that joints are welded accurately and securely, minimizing distortion and ensuring structural integrity. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
5. Assembly
Assembly processes rely on jigs and fixtures to streamline operations and ensure the accurate alignment and positioning of components. Whether it's assembling intricate electronic devices or constructing large-scale machinery, jig machines, and fixtures facilitate the assembly process by providing guidance and support at each stage. This results in faster assembly times, reduced errors, and improved product quality.
Jigs and fixtures offer a multitude of advantages that translate into tangible benefits for businesses.
1. Faster Setup Times
One of the foremost benefits of utilizing jigs and fixtures is the significant reduction in setup times. These specialized tools streamline the preparation process by providing standardized setups for machining operations. As a result, machinists can quickly position and secure workpieces, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
2. Reduced Scrap
Scrap material can be a significant source of waste and expense in manufacturing operations. Jigs and fixtures mitigate this risk by ensuring precise alignment and accurate machining of workpieces. By minimizing errors and deviations, these tools help prevent costly mistakes that result in scrapped parts. This reduction in scrap not only translates into cost savings but also contributes to environmental sustainability by minimizing waste generation.
3. Improved Repeatability
Jigs and fixtures excel in providing consistent results by ensuring repeatability in machining operations. Once a setup is established, these tools enable machinists to replicate the same process with utmost precision, resulting in uniformity across multiple workpieces.
4. Efficient Use of Resources
Jigs and fixtures optimize resource utilization by maximizing machine efficiency and minimizing material wastage. By facilitating accurate positioning and alignment of workpieces, these tools enable machinists to optimize cutting parameters and minimize excess material removal.

The creation of jigs and fixtures is a meticulous process that requires careful consideration of design, choice of materials, and manufacturing techniques.
Designing jigs and fixtures involves considering several critical factors to ensure optimal performance and functionality. Some key considerations include:
Workpiece geometry and dimensions
Machining operation requirements
Accessibility for tooling and operators
Tolerance and accuracy specifications
Ergonomics and ease of use
Integration with existing machinery and workflows
The choice of materials for jigs and fixtures depends on factors such as application requirements, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Common materials used for constructing jigs and fixtures include:
Steel
Known for its strength and durability, steel is often used for heavy-duty applications where rigidity and stability are paramount.
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum is favored for applications requiring easy handling and versatility.
Plastic
Certain plastic materials, such as nylon or high-density polyethylene, offer advantages such as chemical resistance, low friction, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for specific applications.
Traditional Methods
Machining: Traditional machining processes, such as milling, turning, and grinding, are commonly used to fabricate jigs and fixtures from solid metal or plastic stock.
Welding: Welding is often employed to join metal components or attach clamping mechanisms to jigs and fixtures. Various welding techniques, including arc welding, TIG welding, and MIG welding, may be utilized based on the materials and design requirements.
Modern Approaches
3D Printing: 3D printing offer flexibility and design freedom for creating complex jigs and fixtures. Additive manufacturing allows for rapid prototyping and customization, enabling designers to iterate quickly and cost-effectively.
CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has revolutionized the production of jigs and fixtures, offering high precision, repeatability, and efficiency. CNC machines can accurately mill, turn, or drill intricate features and geometries from various materials, resulting in high-quality jigs and fixtures with tight tolerances.
Jigs and fixtures have evolved from ancient origins to meet modern needs in CNC machining and additive manufacturing. Their benefits include increased productivity, cost savings, and improved quality. Choosing a reliable CNC service provider to produce jig and fixture is essential for achieving the best success.
Richconn is known for its strengths in producing high-quality jigs and fixtures for various industrial applications. Richconn excels in precision engineering with a strong track record of customizing jigs and fixtures. Moreover, its expertise in working with a wide range of materials allows them to create jigs and fixtures that are durable, reliable, and suitable for the intended applications, contributing to long-term operational stability. These strengths position Richconn as a reliable and capable partner for businesses seeking high-quality jigs and fixtures to support their manufacturing operations. Try contacting Richconn for your projects now!
 Aluminium Extrusion: A Versatile and Innovative Manufacturing ProcessNovember 30, 2023Aluminium extrusion is a process of forcing aluminium alloy material through a die to create a continuous shape or product. The material can be solid, liquid, or semi-solid, and it can be metal, plastic, ceramic, or food.view
Aluminium Extrusion: A Versatile and Innovative Manufacturing ProcessNovember 30, 2023Aluminium extrusion is a process of forcing aluminium alloy material through a die to create a continuous shape or product. The material can be solid, liquid, or semi-solid, and it can be metal, plastic, ceramic, or food.view Plastics For Medical Devices and ApplicationsOctober 17, 2023Are you designing medical parts? Just as there are countless medical procedures, there is now a seemingly endless abundance of polymer types. Which ones are best suited for medical applications? Good question.view
Plastics For Medical Devices and ApplicationsOctober 17, 2023Are you designing medical parts? Just as there are countless medical procedures, there is now a seemingly endless abundance of polymer types. Which ones are best suited for medical applications? Good question.view Top 10+ Must-have Machinist ToolsFebruary 26, 2024Understanding the right machinist tools can boost productivity. This article highlights three essential tool categories.view
Top 10+ Must-have Machinist ToolsFebruary 26, 2024Understanding the right machinist tools can boost productivity. This article highlights three essential tool categories.view Unlocking Precision: Exploring the Parts of a CNC MachineSeptember 22, 2023Are you ready to dive into the world of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines? If you're fascinated by precision engineering and the wonders it can achieve, you've come to the right place.view
Unlocking Precision: Exploring the Parts of a CNC MachineSeptember 22, 2023Are you ready to dive into the world of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines? If you're fascinated by precision engineering and the wonders it can achieve, you've come to the right place.view Learn More About Manufacturing Options For Elastomeric ComponentsOctober 18, 2023Materials scientists like to give their creations complicated names. Polyethylene terephthalate (a form of polyester). Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (this opaque thermoplastic is better known as ABS). These are just two examples of the thousands of polymers in use today. Many of them have fundamentally changed our lives.view
Learn More About Manufacturing Options For Elastomeric ComponentsOctober 18, 2023Materials scientists like to give their creations complicated names. Polyethylene terephthalate (a form of polyester). Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (this opaque thermoplastic is better known as ABS). These are just two examples of the thousands of polymers in use today. Many of them have fundamentally changed our lives.view 5 Important Facts About 5 Axis Machining | Basics Information, Benefits, Limitations, Applications & TipsFebruary 20, 20245 axis CNC machining technology is important in manufacturing. Learn more about its basics, pros &cons, applications, and tips to enhance your project performance.view
5 Important Facts About 5 Axis Machining | Basics Information, Benefits, Limitations, Applications & TipsFebruary 20, 20245 axis CNC machining technology is important in manufacturing. Learn more about its basics, pros &cons, applications, and tips to enhance your project performance.view