Resin materials are synthetic or natural substances that can be molded or shaped into various forms. They are widely used in many industries and applications, such as art, crafts, jewelry, furniture, electronics, medical, aerospace, etc. Resin materials have many advantages over other materials, such as high strength, durability, flexibility, resistance to corrosion, heat, and chemicals, etc. However, resin materials also have some disadvantages, such as high cost, toxicity, environmental impact, etc.
There are many types of resin materials, but they can be broadly classified into three main categories: thermoset and thermoplastic and elastomer. Each category has its own properties and characteristics that make it suitable for different purposes.

Thermoset resins are resins that undergo a chemical reaction when heated or cured, which makes them hard and irreversible. They cannot be melted or reshaped once they are set. Thermoset resins have high strength, stability, and resistance to heat and chemicals, but they are also brittle, difficult to process, and prone to cracking. Some examples of thermoset resins are epoxy, polyester, phenolic, etc.

Thermoplastic resins are resins that can be melted and reshaped repeatedly when heated and cooled. They are soft and flexible when heated and hard and rigid when cooled. Thermoplastic resins have high ductility, elasticity, and recyclability, but they are also susceptible to deformation, creep, and degradation. Some examples of thermoplastic resins are polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, etc.

Elastomer resins are resins that have rubber-like properties, such as high elasticity, flexibility, and resilience. They can stretch and recover their original shape when subjected to stress or strain. Elastomer resins have high impact resistance, vibration damping, and noise reduction, but they are also vulnerable to abrasion, tearing, and aging. Some examples of elastomer resins are silicone, rubber, polyurethane, etc.
Resin printing and PLA printing are two common methods of 3D printing, which is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by depositing layers of material. Resin printing uses liquid resin that is cured by light, while PLA printing uses solid plastic filament that is melted by heat. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of strength and durability.
Resin prints are generally stronger and more detailed than PLA prints, as they have higher resolution, accuracy, and smoothness. Resin prints can also create complex shapes and structures that PLA prints cannot. However, resin prints are also more brittle and sensitive to UV light, which can cause them to degrade over time. Resin prints are also more expensive, toxic, and difficult to clean than PLA prints.
PLA prints are generally weaker and less detailed than resin prints, as they have lower resolution, accuracy, and smoothness. PLA prints can also suffer from warping, cracking, and shrinking due to temperature changes. However, PLA prints are also more flexible and resistant to UV light, which can make them last longer. PLA prints are also cheaper, safer, and easier to handle than resin prints.
The best printing method and material for a given project depends on the purpose, budget, and preference of the user. Some tips and recommendations for choosing the best printing method and material are:
If the project requires high strength, durability, and detail, resin printing is a better option than PLA printing.
If the project requires low cost, safety, and ease of use, PLA printing is a better option than resin printing.
If the project requires both strength and flexibility, a hybrid printing method that combines resin and PLA can be used, such as using resin for the core and PLA for the shell of the object.
If the project requires different colors, textures, or effects, different types of resin or PLA can be used, such as transparent, glow-in-the-dark, metallic, etc.
Molds are hollow containers that are used to shape or form objects by pouring or injecting a liquid or a soft material into them. Molds can be used for various purposes, such as art, crafts, jewelry, food, etc. Molds can be made of different materials, such as metal, wood, clay, plaster, etc. However, resin materials are often preferred for molds because they have many advantages, such as:
• Resin materials can create smooth, detailed, and durable molds that can capture the fine features and textures of the original object.
• Resin materials can resist high temperatures, pressures, and chemicals, which can prevent the molds from cracking, warping, or deforming.
• Resin materials can be easily colored, painted, or decorated, which can enhance the appearance and quality of the molds and the final products.
However, not all resin materials are suitable for molds. Different types of resin materials have different properties and characteristics that affect their performance and compatibility with the molding process and the material to be molded. Therefore, it is important to select the best resin material for molds based on the following criteria:
The resin material should be able to reproduce the size, shape, and details of the object without distortion or loss of quality. The resin material should also be able to release the object from the mold without sticking or breaking.
The resin material should be compatible with the material to be molded, such as plastic, metal, clay, wax, etc. The resin material should also be able to withstand the temperature, pressure, and chemical reactions of the material to be molded. The resin material should also be economical and efficient for the amount of material to be molded.
The resin material should be easy to use and handle for the molding process, such as pouring, injecting, casting, etc. The resin material should also be able to cure or harden quickly and evenly for the molding process. The resin material should also be durable and reusable for multiple molding cycles.

Epoxy resin is a thermoset resin that is composed of two parts: a resin and a hardener. Epoxy resin is one of the most popular and versatile resin materials for molds, as it has high strength, hardness, and resistance to heat and chemicals. Epoxy resin can create smooth, clear, and glossy molds that can capture the finest details and textures of the object. Epoxy resin can also be easily colored, painted, or decorated. Epoxy resin is suitable for molding various materials, such as plastic, metal, clay, wax, etc. Epoxy resin is also easy to use and handle, as it can be mixed and poured into the mold. Epoxy resin can cure or harden in a few hours or days, depending on the type and amount of the hardener. Epoxy resin can also be durable and reusable for many molding cycles. However, epoxy resin can also have some disadvantages, such as high cost, toxicity, shrinkage, and sensitivity to moisture and UV light.

Polyester resin is another thermoset resin that is composed of two parts: a resin and a catalyst. Polyester resin is similar to epoxy resin in terms of strength, hardness, and resistance to heat and chemicals. Polyester resin can also create smooth, clear, and glossy molds that can capture the details and textures of the object. Polyester resin can also be easily colored, painted, or decorated. Polyester resin is suitable for molding various materials, such as plastic, metal, clay, wax, etc. Polyester resin is also easy to use and handle, as it can be mixed and poured into the mold. Polyester resin can cure or harden in a few minutes or hours, depending on the type and amount of the catalyst. Polyester resin can also be durable and reusable for many molding cycles. However, polyester resin can also have some disadvantages, such as high cost, toxicity, odor, shrinkage, and sensitivity to moisture and UV light.

Polyurethane resin is another thermoset resin that is composed of two parts: a resin and a hardener. Polyurethane resin is different from epoxy and polyester resins in terms of flexibility, elasticity, and resilience. Polyurethane resin can create soft, flexible, and rubbery molds that can adapt to the shape and movement of the object. Polyurethane resin can also create hard, rigid, and tough molds that can resist impact and abrasion. Polyurethane resin can also be easily colored, painted, or decorated. Polyurethane resin is suitable for molding various materials, such as plastic, metal, clay, wax, etc. Polyurethane resin is also easy to use and handle, as it can be mixed and poured or injected into the mold. Polyurethane resin can cure or harden in a few minutes or hours, depending on the type and amount of the hardener. Polyurethane resin can also be durable and reusable for many molding cycles. However, polyurethane resin can also have some disadvantages, such as high cost, toxicity, odor, shrinkage, and sensitivity to moisture and temperature.
![]()
Silicone resin is a type of elastomer resin that is composed of one or two parts: a resin and a catalyst or a hardener. Silicone resin is the most flexible, elastic, and resilient resin material for molds, as it can stretch and recover its original shape without deformation or damage. Silicone resin can create smooth, soft, and rubbery molds that can release the object from the mold without sticking or breaking. Silicone resin can also create clear, translucent, or opaque molds that can capture the details and textures of the object. Silicone resin can also be easily colored, painted, or decorated. Silicone resin is suitable for molding various materials, such as plastic, metal, clay, wax, etc. Silicone resin is also easy to use and handle, as it can be mixed and poured or injected into the mold. Silicone resin can cure or harden in a few minutes or hours, depending on the type and amount of the catalyst or the hardener. Silicone resin can also be durable and reusable for many molding cycles. However, silicone resin can also have some disadvantages, such as high cost, toxicity, shrinkage, and sensitivity to temperature and UV light.
Medical grade resin is a type of resin material that is specially designed and certified for medical applications, such as implants, devices, instruments, etc. Medical grade resin has to meet strict requirements and standards for safety, biocompatibility, sterility, performance, etc. Medical grade resin has to undergo rigorous testing and validation before it can be used for medical purposes.
Medical grade resin is used for various medical products and applications, such as:
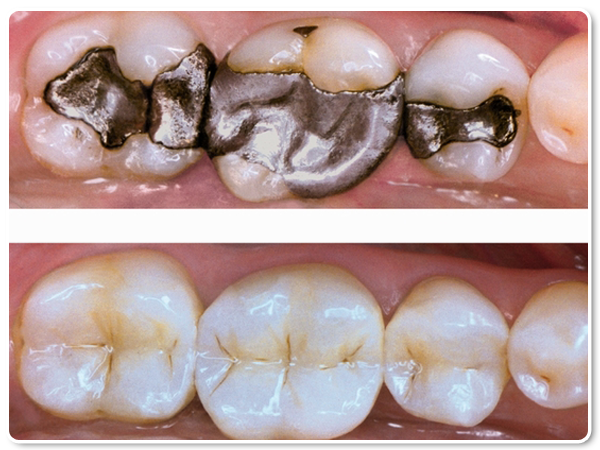
Dental resin is a type of resin material that is used for dental restorations, such as fillings, crowns, bridges, dentures, etc. Dental resin has to be strong, durable, and resistant to wear and tear. Dental resin also has to match the color, shape, and texture of the natural teeth. Dental resin can be made of different types of resin materials, such as acrylic, composite, ceramic, etc.

Orthopedic resin is a type of resin material that is used for orthopedic implants, such as screws, plates, rods, pins, etc. Orthopedic resin has to be biocompatible, meaning that it does not cause adverse reactions or infections in the body. Orthopedic resin also has to be stable, meaning that it does not degrade or corrode over time. Orthopedic resin can be made of different types of resin materials, such as polyetheretherketone (PEEK), polyethylene, polyurethane, etc.
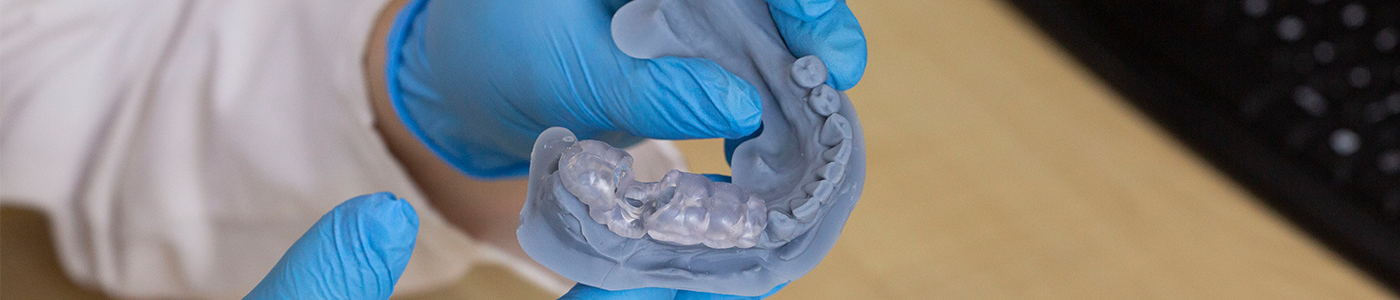
Surgical resin is a type of resin material that is used for surgical instruments, such as scalpels, scissors, forceps, etc. Surgical resin has to be sterile, meaning that it does not contain any harmful microorganisms or contaminants. Surgical resin also has to be sharp, smooth, and easy to handle. Surgical resin can be made of different types of resin materials, such as polycarbonate, polypropylene, polyamide, etc.
Hardness is a measure of how resistant a material is to indentation, scratching, or deformation. Hardness is usually measured by the Mohs scale, which ranges from 1 to 10, where 1 is the softest and 10 is the hardest. Hardness is an important property for resin materials, as it affects their durability, performance, and appearance.
The hardness of resin materials depends on their type, composition, and curing process. Generally, thermoset resins are harder than thermoplastic and elastomer resins, as they have higher cross-linking and rigidity. However, some thermoplastic and elastomer resins can also be hardened by adding fillers, additives, or modifiers.
Some examples of the hardest resin materials are:
Epoxy resin is one of the hardest thermoset resins, as it has high cross-linking and stability. Epoxy resin can have a hardness of up to 9 on the Mohs scale, depending on the type and amount of the hardener. Epoxy resin is used for various applications that require high strength, durability, and resistance, such as coatings, adhesives, composites, etc.
Polycarbonate resin is one of the hardest thermoplastic resins, as it has high molecular weight and crystallinity. Polycarbonate resin can have a hardness of up to 8 on the Mohs scale, depending on the type and amount of the filler. Polycarbonate resin is used for various applications that require high impact resistance, transparency, and heat resistance, such as lenses, helmets, shields, etc.
Silicone resin is one of the hardest elastomer resins, as it has high cross-linking and resilience. Silicone resin can have a hardness of up to 7 on the Mohs scale, depending on the type and amount of the catalyst or the hardener. Silicone resin is used for various applications that require high elasticity, flexibility, and temperature resistance, such as seals, gaskets, molds, etc.
When it comes to resin materials, their variety and wide range of applications is amazing. From polymers to synthetic resins, each material has its own unique properties and uses. Through this article, we explore the different types, performance characteristics, and applications of resin materials in various fields. Whether in construction, manufacturing or medical fields, resin materials show exciting potential and endless possibilities.
If you need resin 3D printing services, you can contact Richconn. We have rich experience and advanced technical equipment and are committed to providing excellent resin 3D printing services. We are well versed in the characteristics of resin materials and printing processes, and can accurately produce parts and models of various complex structures according to customer needs. Whether it's a personal project or commercial customization, we empower your designs and ideas with high quality and precision. When you work with us, you will receive the support of a professional team, the application of innovative technology, and the highest quality service experience. Richconn looks forward to bringing excellent solutions for resin 3D printing to your projects.
 Cutting Costs, Not Quality: Exploring the Best Cheap CNC Material OptionsDecember 4, 2023In today's competitive market, every business is constantly finding ways to cut costs without compromising the quality of their products or services. When it comes to CNC machining, one of the mos...view
Cutting Costs, Not Quality: Exploring the Best Cheap CNC Material OptionsDecember 4, 2023In today's competitive market, every business is constantly finding ways to cut costs without compromising the quality of their products or services. When it comes to CNC machining, one of the mos...view Galvanized vs. Galvannealed Steel: A ComparisonNovember 28, 2023Steel is one of the most widely used materials in various industries, such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. However, steel is also susceptible to corrosion and rust when exposed to moisture and oxygen.view
Galvanized vs. Galvannealed Steel: A ComparisonNovember 28, 2023Steel is one of the most widely used materials in various industries, such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. However, steel is also susceptible to corrosion and rust when exposed to moisture and oxygen.view What is Precision Grinding & Types, Materials, ProcessesNovember 27, 2023The so-called precision grinding process is to utilize fine-grained abrasive grains and micro-powder to process ferrous metals, hard and brittle materials, etc., in order to obtain high machining accuracy and low surface roughness values.view
What is Precision Grinding & Types, Materials, ProcessesNovember 27, 2023The so-called precision grinding process is to utilize fine-grained abrasive grains and micro-powder to process ferrous metals, hard and brittle materials, etc., in order to obtain high machining accuracy and low surface roughness values.view Choosing a Heat Resistant PlasticOctober 17, 2023If you've ever left a food container in the microwave for too long, you know that some plastics don't tolerate high temperatures very well. Depending on the type of container, you might be storing the food from the night before in polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC) or polyethylene (PE), none of which excel at heat resistance.view
Choosing a Heat Resistant PlasticOctober 17, 2023If you've ever left a food container in the microwave for too long, you know that some plastics don't tolerate high temperatures very well. Depending on the type of container, you might be storing the food from the night before in polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC) or polyethylene (PE), none of which excel at heat resistance.view Hot Rolled vs Cold Rolled: Which One Is Right for Your Project?February 26, 2024To optimize the properties of steel for specific applications, it is necessary to consider factors beyond its chemical composition. Hot rolling or cold rolling is a process employed to enhance the sha...view
Hot Rolled vs Cold Rolled: Which One Is Right for Your Project?February 26, 2024To optimize the properties of steel for specific applications, it is necessary to consider factors beyond its chemical composition. Hot rolling or cold rolling is a process employed to enhance the sha...view Unraveling the World of Machined Springs: Your Ultimate GuideNovember 9, 2023As a CNC machining service provider, we at Richconn understand the significance of precision engineering and how it's all about the details. In the realm of mechanical components, one topic that piques the curiosity of engineers, manufacturers, and professionals alike is -Machined Springs. In this comprehensive guide, I will walk you through the intricacies of Machined Springs, from the fundamentals to their applications, performance characteristics, manufacturing processes, and more.view
Unraveling the World of Machined Springs: Your Ultimate GuideNovember 9, 2023As a CNC machining service provider, we at Richconn understand the significance of precision engineering and how it's all about the details. In the realm of mechanical components, one topic that piques the curiosity of engineers, manufacturers, and professionals alike is -Machined Springs. In this comprehensive guide, I will walk you through the intricacies of Machined Springs, from the fundamentals to their applications, performance characteristics, manufacturing processes, and more.view