Carbon fiber has the performance advantages of high specific strength, high specific modulus, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, good electrical and thermal conductivity, etc., and is widely used in aerospace, military industry, marine equipment, high-end medical, rail transit, sports equipment and other fields. Carbon fiber composite materials can be divided into many types according to the different strength and modulus, mainly T series and M series, this article will introduce from the material characteristics, processing characteristics, processing and production, etc., if you are looking for a carbon fiber parts processor, start from us to solve all your questions in one stop: delivery, price, quality.
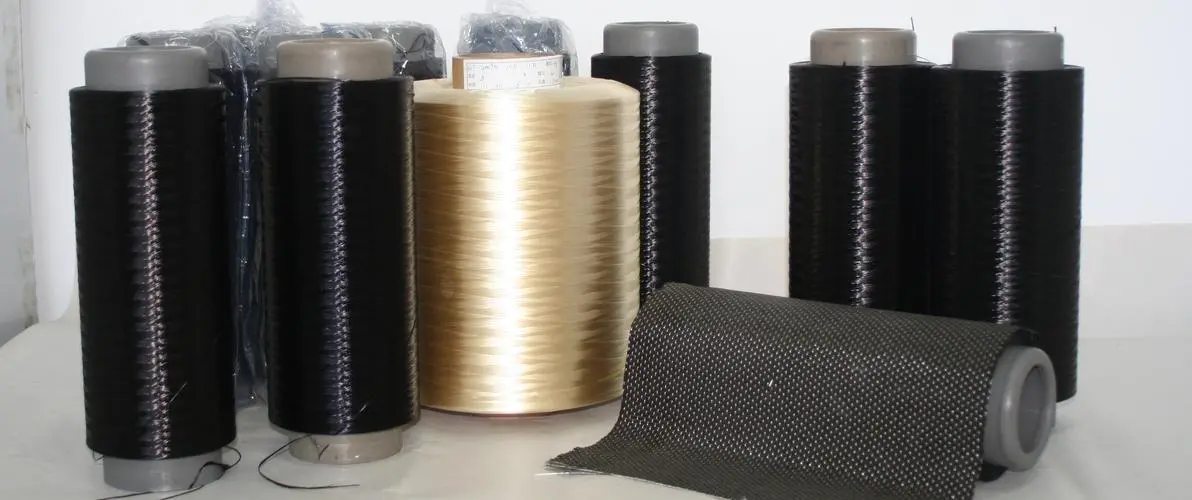

Carbon fiber is a kind of polymer fibrous material with a carbon content higher than 95% prepared by carbon-containing raw materials under specific conditions through high-temperature carbonization and other treatments. Carbon fiber is a novel non-metallic super-material, which is composed of flake graphite micro-crystallites stacked along the axial direction of fibers, and is obtained by carbonization and graphitization treatment. Carbon fiber and its composite materials have high specific strength and specific modulus, and carbon fiber has a small specific gravity, chemical resistance, heat resistance, thermal shock resistance and ablation resistance.
The raw materials of carbon fiber mainly include polyacrylonitrile, asphalt, viscose, lignin, phenolic and other organic fibers. According to the raw materials and manufacturing process used, precursor type, mechanical properties, etc., carbon fiber can be roughly divided into polyacrylonitrile-based (PAN) carbon fiber, asphalt-based (Pitch) carbon fiber, viscose-based carbon fiber and other fiber-based carbon fiber
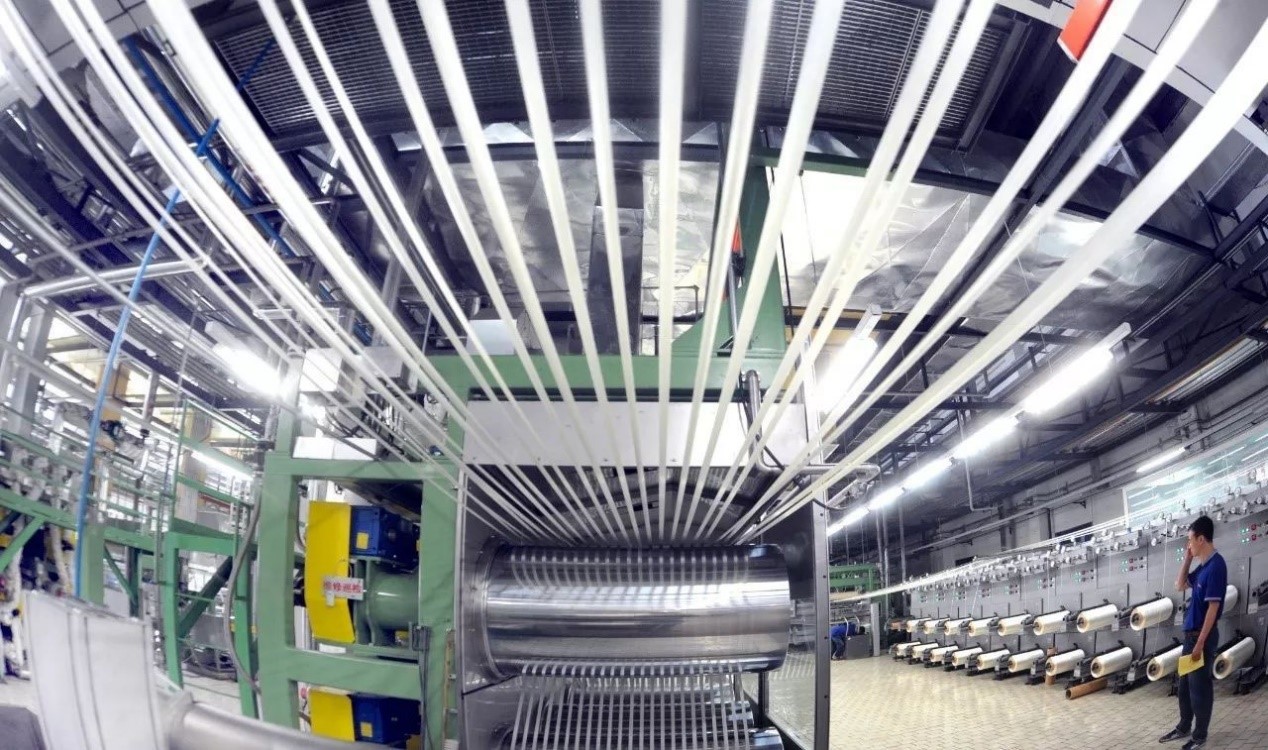

The main steps of the carbon fiber manufacturing process are divided into stabilization treatment (also known as non-melting treatment or pre-oxidation treatment), carbonization heat treatment, and graphitization heat treatment. Stabilization heat treatment is to make the pioneer wire non-melt to prevent melting or sticking in the subsequent high temperature treatment, carbonization heat treatment removes more than half of the non-carbon elements in the pioneer wire through high temperature, graphitization heat treatment turns carbon into graphite structure through higher temperature heating, so as to improve the performance of carbon fiber obtained in carbonization heat treatment.
The specific process mainly includes spinning, stabilization, carbonization, surface treatment, sizing, etc. Spinning is to mix the precursor with other materials to spin into fibers, and then these fibers are washed and stretched; Stabilization is the chemical change of carbon fiber before carbonization, by changing its linear atomic bonds to trapezoidal bonds to make it have higher thermal stability, heating the fibers to 200~300 °C in air for about 30min~2h. Carbonization is to heat the fiber to 1000~3000 °C in the absence of oxygen after it is thermally stabilized and keep it for a few minutes, the lack of oxygen prevents the fiber from burning at high heat, the fiber discharges its non-carbon atoms at high temperature, and the rest of the carbon atoms form tightly bonded carbon crystals, which are arranged parallel to the long axis of the carbon fiber. Surface treatment is to give the fibers after the carbonization process a smooth surface that does not bond well with epoxy resins and other materials used to make composite products. As a result, the surface is slightly oxidized. Oxidation gives the surface better chemical bonding properties, while also etching the surface to allow the chemicals to adhere better to the surface. Sizing is the process of wrapping the fibers to prevent them from being damaged when wound onto a spool or woven into a fabric. Sizing coating materials may include polyester, nylon, urethane or epoxy, among others.

According to the type of precursor used to make carbon fiber, it is divided into polyacrylonitrile, asphalt-based, viscose-based and other fiber-based carbon fibers.
According to the heat treatment temperature, it can be divided into two types: carbon fiber and graphite fiber
Carbon fiber can be divided into ordinary carbon fiber and high-performance carbon fiber according to its performance, and high-performance carbon fiber can be divided into high elastic modulus carbon fiber and high-strength carbon fiber.
Carbon fiber is an extremely fine filamentous fiber, and the diameter of carbon fiber is only 1/50 of a hair. The K number of carbon fiber cloth refers to the number of its monofilaments, and "K" represents the unit "thousand", for example, 1K means that each carbon fiber is composed of 1,000 monofilaments, and the higher the K number, the more monofilaments are contained in each strand. There are more 3K, 6K, and 12K on the market, and 3k represents 3,000 monofilament carbon fiber filaments in a bundle of carbon fiber, and 12k is 120,000 monofilament carbon fibers in carbon fiber.
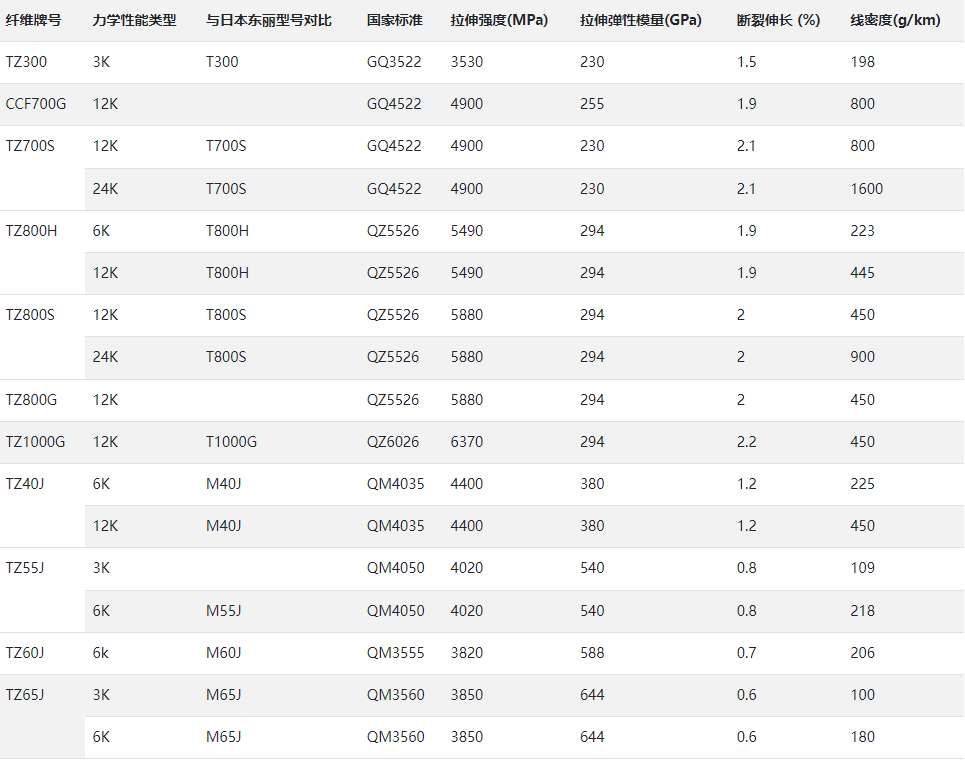
In addition to the K value, we should also pay attention to the carbon fiber strength T value. T represents the tensile strength of carbon fiber, which is divided into T300, T600, T700, T800, T1000, T1100, and the larger the T number, the higher the tensile strength. The most commonly used ones on the market are the T300 and T700.
T300 Series: A standard type of carbon fiber with good strength and stiffness, widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
T700 Series: High-performance carbon fiber with higher tensile strength and modulus for applications that require higher performance, such as aircraft components and sports equipment.
T800 Series: High-performance carbon fiber with increased strength and stiffness compared to the T700 series, commonly used in high-end aerospace and racing applications.
M40 series: High-modulus carbon fibers, mainly used in applications requiring extremely high modulus of elasticity, such as high-performance automotive braking systems.
M50 series: Carbon fibers with high tensile modulus and excellent fatigue properties for aerospace and sports equipment that require extreme high performance.
T-800H Series: Carbon fiber with improved thermal properties for applications in high temperature environments.
IM series: High-strength cross-linked carbon fibers used to enhance the properties of resin-based composites.
HM Series: High modulus carbon fiber with superior stiffness and tensile strength, commonly used in high-performance sports equipment and aerospace applications.
UHM series: Ultra-high modulus carbon fibers with an extremely high modulus of elasticity for applications that require very high material stiffness.
Toray Industries: A Japan-based chemical company and one of the world's largest carbon fiber manufacturers.
SGL Carbon: A German company that provides carbon fiber and composite solutions across a wide range of industries.
Honeywell (Hexcel Corporation): An American company focused on the manufacture of advanced composite materials, including carbon fiber.
ZOLTEK Companies, Inc.: An American company specializing in the production of carbon fiber, especially for industrial and infrastructure applications.
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation: A Japanese company involved in a variety of fields, including the manufacture of carbon fiber.
North Thin Ply Technology (NTPT): A Swiss company known for its unique thin layer stacking technology.
Taiwan Glass Industry Corp. (TGI): A Taiwanese company involved in the manufacture of carbon fibers and composite materials.
Rock West Composites: An American company focused on providing composite and carbon fiber products.
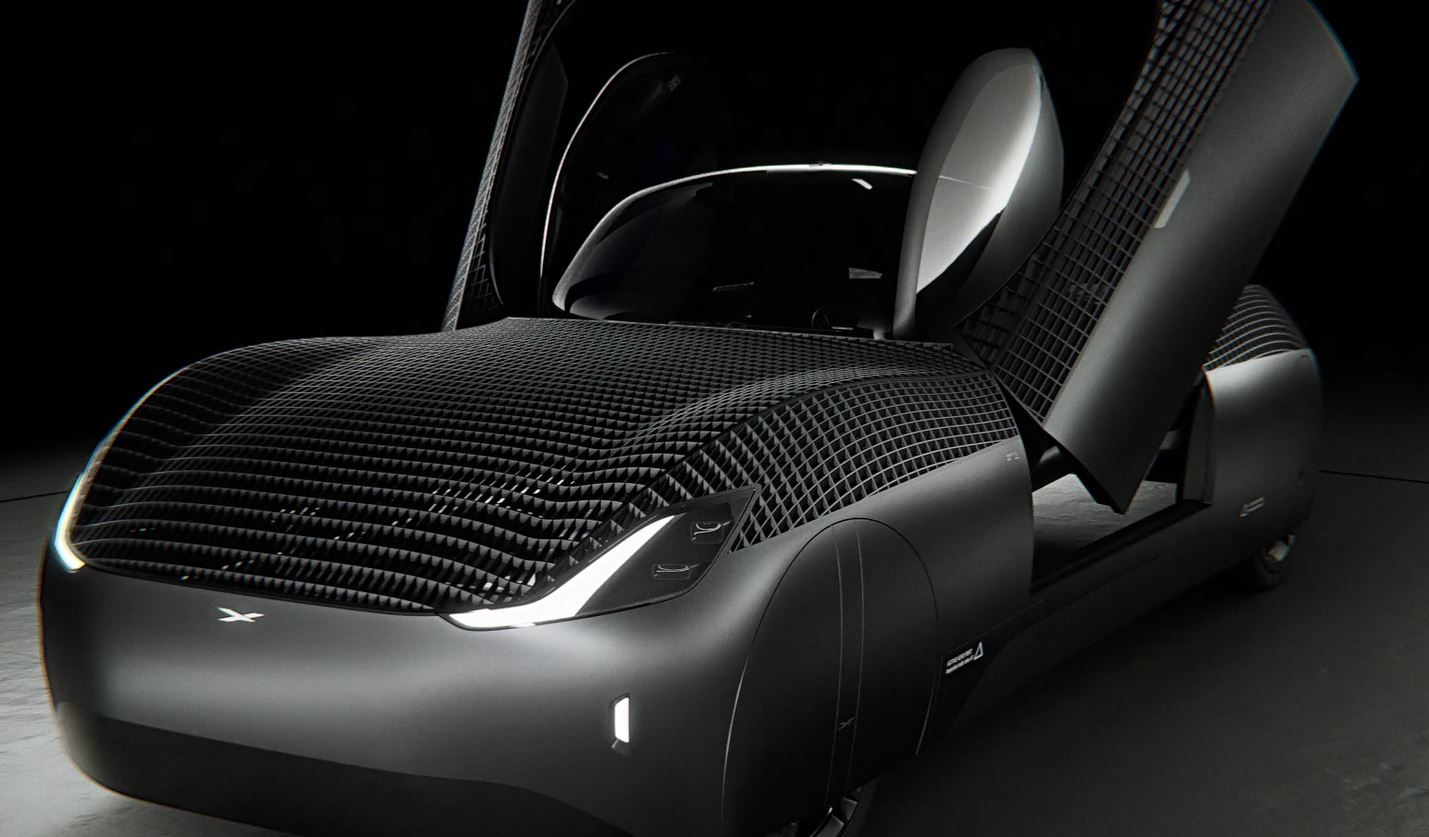
Automotive: Flying car frame: high-strength, lightweight, using T800/3K carbon fiber, using a single piece of high-strength carbon fiber spliced into an integral frame, so that the weight of the car is greatly reduced.

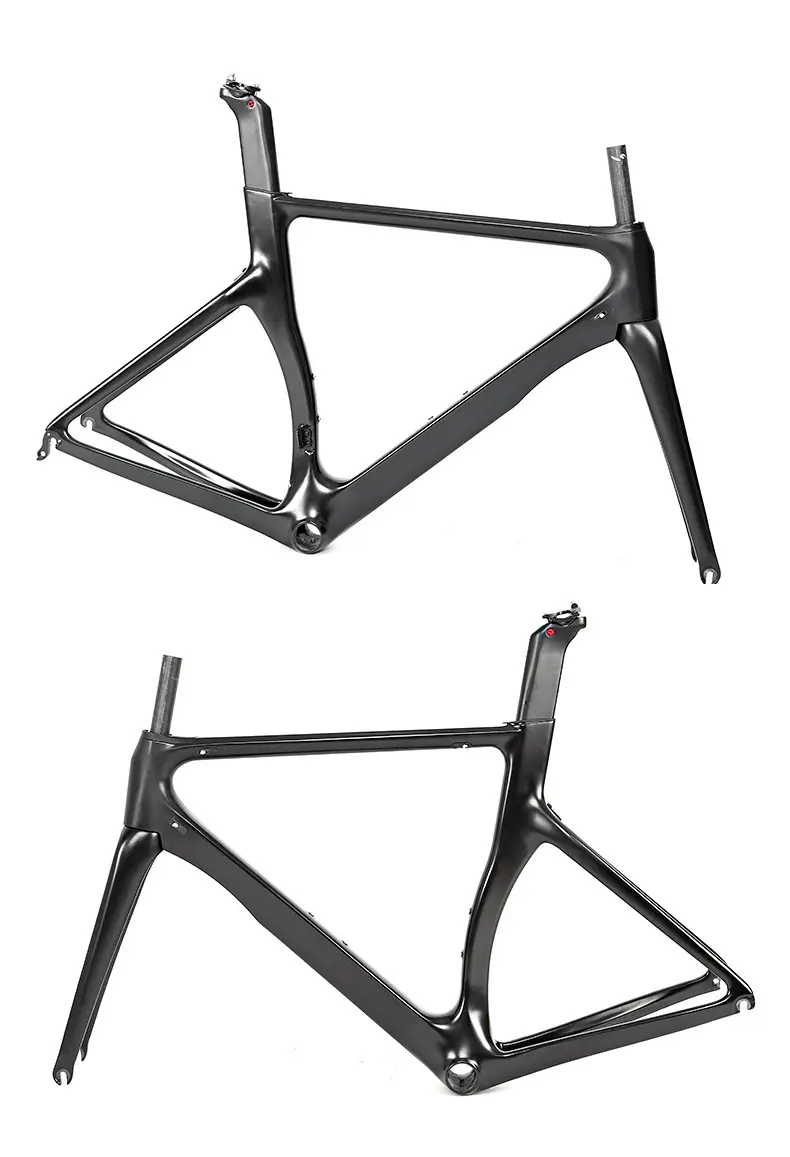
Bicycles: A carbon fiber bike is a type of bicycle that is made with carbon fiber composite materials, which are typically lightweight, high-strength, and have excellent corrosion resistance.

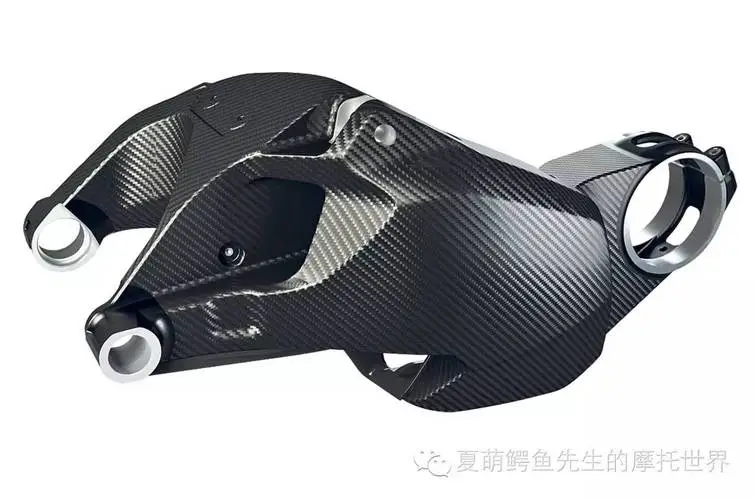
Motorcycles: At present, motorcycles generally use carbon fiber as their modified accessories to reduce weight and provide personalized services.

Electronics: Carbon fiber is a special fiber composed of carbon elements, its density is small, so the strength is much higher than that of metal, 5 times that of steel, and at the same time has the soft processability of textile fiber, so in some ways, it is the best substitute for metal.

Outdoor products: When outdoor activities, we usually choose some equipment, which requires several special products: strength, high and low temperature resistance, and light weight, which are excellent application scenarios of carbon fiber. Such as: tents, stands, crutches, car tents, etc.

Processing carbon fiber usually requires the use of some special machines and processes to ensure that the properties of the material are not compromised. Here are some common machines and equipment used for carbon fiber processing:
CNC cutting machine: It is used to make precise cutting of carbon fiber sheets or fabrics to meet design requirements.
CNC milling machine: For precise milling and machining of carbon fiber parts.
CNC lathes: Used for rotary machining of carbon fiber parts, usually used to manufacture shaft parts.
Laser cutting machine: It can be used to cut carbon fiber sheets or fabrics by laser to achieve high-precision and complex shape cutting.
Injection molding machine: Used to make carbon fiber reinforced plastic parts, where carbon fiber can be injected into the plastic matrix.
Composite Laminator: Used to press carbon fiber fabric with resin to form a composite material.
Vacuum packaging machine: It is used to create a vacuum environment in the manufacturing process of carbon fiber products to ensure that the resin is fully penetrated and the material is cured.
Grinding wheel grinder: Used to grind carbon fiber parts for more precise dimensions and surface quality.
CNC drilling machine: For precise hole machining on carbon fiber parts.
Laser engraving machine: Used for marking, engraving, or lettering on carbon fiber surfaces.
When using these machines for carbon fiber processing, proper process controls and precautions need to be taken to prevent damage to the fiber structure of carbon fiber and ensure the performance and quality of the final product. Fiber processing
As of December 2023, RICHCONN can undertake machining orders in various industries with years of hard work in the processing and manufacturing industry, with 200 machine tools/sets, 15 sets/sets of testing equipment, and can process large parts with a length of 2000mm and an accuracy of ±0.005mm, to small parts of 0.16±0.01, please contact us for more information.
 The Brief Introduction to 5 Axis CNC MachineAugust 22, 2023Over the past few years, CNC machining technology has advanced from basic machine tools to more complex ones. Nowadays one of the most cutting-edge techniques accessible is 5-axis CNC machining. It us...view
The Brief Introduction to 5 Axis CNC MachineAugust 22, 2023Over the past few years, CNC machining technology has advanced from basic machine tools to more complex ones. Nowadays one of the most cutting-edge techniques accessible is 5-axis CNC machining. It us...view Complete List of Machined Hardware Product TypesOctober 19, 2023Hardware: traditional hardware products, also known as "small hardware". Refers to gold, silver, copper, iron, tin five kinds of metal. Artificial processing can be made into knives, swords and other works of art or metal devices. In modern society, hardware is more extensive, such as hardware tools, hardware parts, daily-use hardware, construction hardware and security products. Most of the small hardware products are not final consumer goods.view
Complete List of Machined Hardware Product TypesOctober 19, 2023Hardware: traditional hardware products, also known as "small hardware". Refers to gold, silver, copper, iron, tin five kinds of metal. Artificial processing can be made into knives, swords and other works of art or metal devices. In modern society, hardware is more extensive, such as hardware tools, hardware parts, daily-use hardware, construction hardware and security products. Most of the small hardware products are not final consumer goods.view Better CNC Parts Through Fine tuning of TolerancesOctober 13, 2023Tolerances that are too tight can require rework, which in turn drives up costs. If tolerances are too loose, the part may not fit with the mating part. So to optimize your designs, know what tolerances are needed and when: Standard tolerances can improve quality, ensure fast repeatability and reduce manufacturing costs.view
Better CNC Parts Through Fine tuning of TolerancesOctober 13, 2023Tolerances that are too tight can require rework, which in turn drives up costs. If tolerances are too loose, the part may not fit with the mating part. So to optimize your designs, know what tolerances are needed and when: Standard tolerances can improve quality, ensure fast repeatability and reduce manufacturing costs.view All You Need to Know About the Significance and Methods of Limit Fit for CNC PartsJuly 23, 2024This article will explore the significance, methods, and processes of achieving limit fit for CNC parts in modern manufacturing, ensuring precision and quality.view
All You Need to Know About the Significance and Methods of Limit Fit for CNC PartsJuly 23, 2024This article will explore the significance, methods, and processes of achieving limit fit for CNC parts in modern manufacturing, ensuring precision and quality.view UNF Threads vs UNC Threads and What Are UNF Threads and UNC ThreadsNovember 17, 2023In the intricate world of CNC machining, understanding the nuances of UNF Threads and UNC Threads is paramount. These threading standards, Unified National Fine (UNF) and Unified National Coarse (UNC), serve as the bedrock of precision in mechanical engineering. Let's delve into the specifics, exploring their applications, differences, and the critical role they play in the realm of precision machining.view
UNF Threads vs UNC Threads and What Are UNF Threads and UNC ThreadsNovember 17, 2023In the intricate world of CNC machining, understanding the nuances of UNF Threads and UNC Threads is paramount. These threading standards, Unified National Fine (UNF) and Unified National Coarse (UNC), serve as the bedrock of precision in mechanical engineering. Let's delve into the specifics, exploring their applications, differences, and the critical role they play in the realm of precision machining.view What Are the Types of Metal Surface Finish?September 16, 2022Machining surface finishing is an important processing procedure in machining. Machining surface finish can play an important role in protecting and beautifying the workpiece. In machining, there are ...view
What Are the Types of Metal Surface Finish?September 16, 2022Machining surface finishing is an important processing procedure in machining. Machining surface finish can play an important role in protecting and beautifying the workpiece. In machining, there are ...view