Many CNC machines can be left unattended throughout the machining cycle, freeing the operator for other tasks. This benefit allows CNC users to provide several side effects, including reduced operator fatigue, errors due to operator error, and consistent and predictable machining times for each workpiece. Because the machine will run under program control, the skill level required of a CNC operator is also reduced compared to that of a machinist who produces a machinist with a conventional machine tool.
The most basic function of any CNC machine is automatic, precise, and consistent motion control. All forms of CNC machines have two or more directions of motion, called axes. These axes can be precisely and automatically positioned along the length of their travel.
Instead of manually turning cranks and handwheels in the manner required to cause motion on conventional machines, CNC machines allow motion to be actuated by servomotors under CNC control and guided by part programs. In general, motion types such as, rapid, linear and circular, axis movement, amount of motion and rate of motion or feed rate are programmable with almost all CNC machines.
CNC commands executed within the control are usually programmed to tell the drive motor to rotate a precise number of times. The rotation of the drive motor in turn rotates the ballscrew. The ball roller drives the spool. A feedback device on the opposite end of the roller allows the control to confirm that the commanded number of rotations has occurred.
Although having a rather crude analogy, the same basic linear motion can be found in an ordinary watch vise eye. As you rotate the vise crank, you rotate the lead screw, which in turn drives the movable jaws on the VISE. In contrast, the linear axes on a CNC machine are very precise. The number of revolutions of the axis drive motor precisely controls the amount of linear motion along the axis.

The CNC programmer must be aware of the programmable directions of motion (axes) available to the CNC machine. The names of the axes will be converted from one machine type to the next. They are always submitted via letter address. Common axis names are X, Y, Z, U, V and W for linear axes and A, B and C for rotary axes.
As mentioned above, programs consist of commands and the commands consist of words. Each word has a letter address and a numeric value. The letter address tells the word type.CNC control manufacturers do differ in how they determine word names (letter addresses) and their meanings. Beginning CNC programmers must refer to the maker's programming manual for the control to determine word names and meanings. Here is a short list of some word types and their general letter address specifications.
O-Program number (for program identification)
n-Serial number (for line identification)
G-Preparation function
X-X-axis designation
Y-Y-axis designation
Z-Z-axis designation
R-Radius designation
F-Feed effect designation
S-Spindle speed
H-Tool length offset designation
D-Tool radius offset designation
T-Tool designation
M-Miscellaneous Functions
Rotary axis offsets still require a letter address (usually A, B, or C) as well as the endpoint of the motion. However, the endpoint of the rotary axis motion is specified in degrees (not inches or millimeters).
While your particular CNC machine may have more types of motion depending on your application, let's focus on the three most common types found on almost all forms of CNC equipment. After a brief introduction to each type of motion, we'll show a sample program that emphasizes all three.
This motion type is used to command motion at the fastest rate of the machine. It is used to minimize unproductive time during a machining cycle. Common uses for rapid motion include positioning the tool to the cutting position, moving to clear fixtures and other obstacles, and generally, any non-cutting motion during the program.
This motion type allows the programmer to move in a completely straight line as discussed in the case we discussed during our discussion of linear interpolation. This motion type also allows the programmer to specify the rate of motion (feed rate) to be used during the motion. Linear motion can be used at any time with linear motion, including when drilling holes, turning diameters, faces, or tapers, and when milling straight surfaces.
This type of motion causes the machine to move in a circular path. As mentioned earlier during our demonstration of circular interpolation, this type of motion is used to generate radii during machining. All of the feed rate related points made during our discussion of linear motion still apply.
The continued development and innovation of CNC technology will continue to drive manufacturing forward, providing more opportunities and solutions for a variety of industries. We hope this article has helped you better understand the fundamentals of CNC motion control and its types.
When it comes to CNC technology and precision manufacturing, one company that is highly respected in the industry deserves a mention.Richconn, founded in 2008, is a precision manufacturing company dedicated to providing high-quality manufacturing services. They stand out for their superior technology and expertise, offering a range of solutions such as CNC machining services, sheet metal services, and plating services.
Richconn is not only experienced in CNC machining, but can also fulfill customers' sheet metal needs, as well as provide plating services to ensure products meet the highest standards of quality and performance. Whether you need customized metal parts or are looking to enhance the appearance and durability of your product, Richconn has the expertise to support you.
Richconn has been a trusted partner in the field of precision manufacturing and CNC machining. If you have any questions about their services or need more information, please feel free to contact Richconn, who will be happy to provide you with exceptional manufacturing solutions.Richconn's team of professionals will ensure that your project receives the best attention and treatment to meet your needs and expectations.
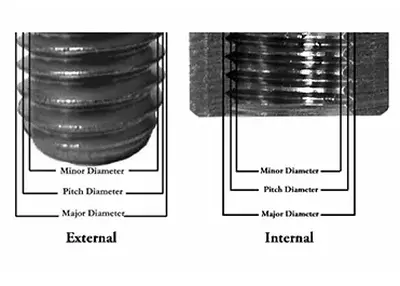 UNF Threads vs UNC Threads and What Are UNF Threads and UNC ThreadsNovember 17, 2023In the intricate world of CNC machining, understanding the nuances of UNF Threads and UNC Threads is paramount. These threading standards, Unified National Fine (UNF) and Unified National Coarse (UNC), serve as the bedrock of precision in mechanical engineering. Let's delve into the specifics, exploring their applications, differences, and the critical role they play in the realm of precision machining.view
UNF Threads vs UNC Threads and What Are UNF Threads and UNC ThreadsNovember 17, 2023In the intricate world of CNC machining, understanding the nuances of UNF Threads and UNC Threads is paramount. These threading standards, Unified National Fine (UNF) and Unified National Coarse (UNC), serve as the bedrock of precision in mechanical engineering. Let's delve into the specifics, exploring their applications, differences, and the critical role they play in the realm of precision machining.view What Is CNC Machining?April 4, 2023Definition of CNC MachiningCNC machining refers to the machining process conducted by a control system that controls the tools to perform various movements that meet the technical and processing requi...view
What Is CNC Machining?April 4, 2023Definition of CNC MachiningCNC machining refers to the machining process conducted by a control system that controls the tools to perform various movements that meet the technical and processing requi...view Exploring Nylon: A World of PossibilitiesSeptember 28, 2023Nylon's remarkable strength and versatility have made it a cornerstone of the textile industry. From silky stockings to rugged outdoor wear, nylon fibers have revolutionized our wardrobes.view
Exploring Nylon: A World of PossibilitiesSeptember 28, 2023Nylon's remarkable strength and versatility have made it a cornerstone of the textile industry. From silky stockings to rugged outdoor wear, nylon fibers have revolutionized our wardrobes.view Authoritative Guide to Tack Welding & Efficient Welding ProcessSeptember 19, 2023Welding is a long-standing process that remains essential in various industries. Manufacturers employ different types of welds depending on the project's requirements. Tack welding is particularly...view
Authoritative Guide to Tack Welding & Efficient Welding ProcessSeptember 19, 2023Welding is a long-standing process that remains essential in various industries. Manufacturers employ different types of welds depending on the project's requirements. Tack welding is particularly...view What Is High Carbon Steel? What Is the Difference Between High Carbon Steel Sk2, Sk4, Sk5, Sk7, Etc.?October 27, 2023High carbon steel is a type of steel with a carbon content between 0.6% and 1.7%, which contains much more carbon than ordinary carbon steel, and is therefore also caled carbon tool steel. High carbon steel has high hardness, high strength, low toughness, and is easy to quench and temper, so it is widely used in the manufacture of machine parts, tools and blades that require high strength and hardness.view
What Is High Carbon Steel? What Is the Difference Between High Carbon Steel Sk2, Sk4, Sk5, Sk7, Etc.?October 27, 2023High carbon steel is a type of steel with a carbon content between 0.6% and 1.7%, which contains much more carbon than ordinary carbon steel, and is therefore also caled carbon tool steel. High carbon steel has high hardness, high strength, low toughness, and is easy to quench and temper, so it is widely used in the manufacture of machine parts, tools and blades that require high strength and hardness.view Better CNC Parts Through Fine tuning of TolerancesOctober 13, 2023Tolerances that are too tight can require rework, which in turn drives up costs. If tolerances are too loose, the part may not fit with the mating part. So to optimize your designs, know what tolerances are needed and when: Standard tolerances can improve quality, ensure fast repeatability and reduce manufacturing costs.view
Better CNC Parts Through Fine tuning of TolerancesOctober 13, 2023Tolerances that are too tight can require rework, which in turn drives up costs. If tolerances are too loose, the part may not fit with the mating part. So to optimize your designs, know what tolerances are needed and when: Standard tolerances can improve quality, ensure fast repeatability and reduce manufacturing costs.view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru