In the contemporary world, machined parts are ubiquitous, and the reasons for this are evident. These components, offering precision and efficiency at affordable costs, are integral to the majority of machinery. However, what exactly defines CNC machine parts? And what attributes render them so vital?
This article delves into CNC machining and CNC machined parts, compiling comprehensive and up-to-date information on all aspects you should know. This article will offer expert insights into CNC machine part materials, tolerances, benefits, design considerations, and CNC machining services in general. Let's embark on this journey of discovery!
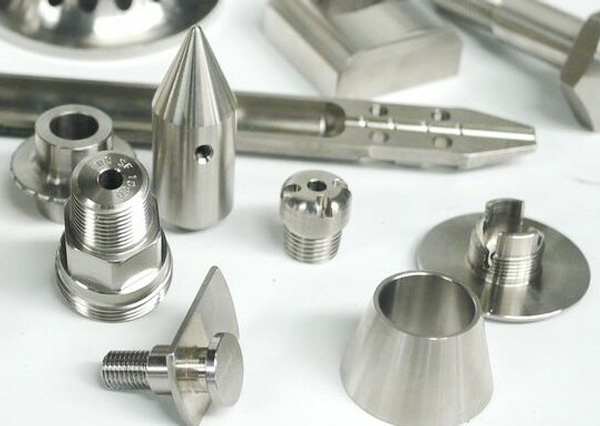

Machined parts are elements meticulously crafted through the machining process. So, what exactly is machining? It is a technique that utilizes subtractive cutting machines, including mills, lathes, and grinders, to fashion a desired part. Despite the distinct techniques employed by these machines, the ultimate objective remains the same: to eliminate material from a workpiece and fashion it into the desired shapes.
Machining can either be conducted manually or digitally. In manual machining, a highly skilled machinist manually operates cutting machines to shape components. Conversely, digital machining represents an automated cutting method utilizing Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines. This digital manufacturing process involves inputting pre-programmed instructions into the CNC machine, which then cuts parts precisely according to these specifications. The outcome? Exceptionally precise, uniform, and efficient machined parts.
With the availability of online CNC machining services, accessing CNC parts tailored to your specific business requirements has become straightforward. Nevertheless, manual machining and other manufacturing techniques, including molding, casting, and forging, still hold their own significance in the industrial landscape.
CNC machining is capable of processing a diverse range of materials, encompassing metals, plastics, and ceramics. However, not all machining materials possess identical properties. In selecting the appropriate material for your CNC machined part, it is crucial to thoroughly evaluate various factors, including cost, part weight, electrical conductivity, heat resistance, surface finish, and the intended application of the component.
Furthermore, the machinability of different materials varies significantly. Materials with extreme hardness can be challenging to cut, potentially causing damage to the cutting tool. Additionally, the manufacturing process may generate vibrations that significantly impact the precision and surface finish of the machined parts. Conversely, materials that are overly soft are susceptible to deformation under the cutting force, ultimately compromising the quality of the parts of a CNC machine.
A specialized CNC machining shop can provide expert guidance on the optimal materials for your specific project. In this section will discuss some of the commonly utilized materials in CNC machining.
Metal
Metals are among the most widely utilized materials in CNC machining services, offering a diverse range of industrial applications due to their electrical conductivity, high strength, and excellent mechanical properties. Each metal exhibits unique standout characteristics. For instance, stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, adaptability, and remarkable strength, while aluminum is prized for its lightweight nature, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
Common metals used in CNC machining services include aluminum, stainless steel, copper, titanium, magnesium, zinc, and mild steel. Additionally, metal alloys such as bronze may also be employed in the production of machined parts, prized for their appealing surface finish, malleability, and rust-resistant chemical properties.
Plastic
Another material frequently utilized in CNC machining is plastic, offering lightweight, versatility, and corrosion resistance. Common plastics employed in CNC machining services include Nylon, Acrylic, Polycarbonate, ABS, PVC, Polyethene, and Delrin. Due to their versatility, plastic components find widespread use in consumer electronics, medical equipment, and the automotive industry. Additionally, plastic parts are also employed in the manufacture of electrical insulation components.
Apart from metals and plastics, CNC machining centers also utilize ceramics and composite materials for part production. Composite materials are composed of two or more constituent materials with distinct properties, often incorporating a matrix material like fiberglass and epoxy resin.
Machined part tolerances refer to the permissible variations from the stated dimensions. The tolerances in CNC machine parts can be influenced by various factors, including the machining method employed, the material utilized, the intricacy of the design, and the associated cost considerations.
CNC machining excels in its ability to produce parts with precise tolerances, which is particularly beneficial for crucial dimensions like diameters, lengths, and hole sizes. Strict adherence to machining tolerances is essential for ensuring the functionality of the parts. However, tighter tolerances require more accurate CNC machining procedures, which may lead to increased production costs.
On the other hand, looser tolerances permit a less rigorous machining approach but may compromise the performance of the components. These relaxed specifications are typically used for prototypes and non-mechanical components.
Following the CNC machining process, we can apply surface treatments to machine parts to enhance their visual appearance and texture. The surface finish not only serves an aesthetic purpose but also fulfills functional requirements.
As-machined surfaces
It refers to those that are not subject to any treatment following the CNC machining process. They retain their natural surface finish and are typically used for internal parts, emphasizing functionality rather than aesthetics.
Bead-blasted Finishes
On the other hand, bead blasting utilizes abrasive media to achieve a matte surface finish on machined parts. The roughness of the resulting finish varies depending on the process parameters. However, it's worth noting that the bead-blasting process is not suitable for delicate parts as it can alter their geometry by removing material.
Anodization
After CNC machining, we may apply anodization to the component, a treatment commonly used for aluminum machined parts. This process creates a durable and corrosion-resistant finish that also enhances the wear resistance of the component.
Powder Coating
Another surface treatment option is powder coating, which involves applying powdered paint to the machined parts and baking them in an oven. This results in a wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant layer that outperforms traditional paint coatings. Additionally, powder coatings offer a range of vibrant colors, enabling the creation of visually appealing custom machined parts.
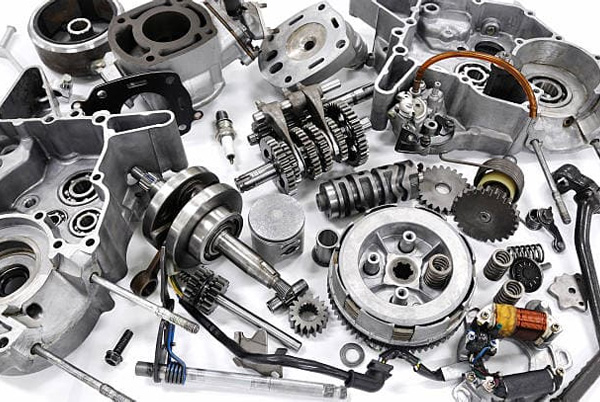

CNC machined parts possess numerous advantages over those produced through alternative manufacturing processes. The following section will delve into some of these key benefits.
1. No MOQ
One of the significant benefits of CNC machined parts is their flexibility in terms of order quantity, as there is no minimum order quantity (MOQ) requirement. This allows us to efficiently produce even small batches or individual custom parts at cost-effective rates.
Contrastingly, other manufacturing methods, such as molding, often involve expensive tooling processes that limit the cost-effectiveness of producing only a few custom parts.
Therefore, the CNC machining process is particularly suitable for businesses with varying quantity demands, customized designs, and prototyping needs. Now, let's move on to the next point.
2. prototypes
CNC machining stands out for its precision and efficiency, enabling us to swiftly produce high-quality prototypes with remarkable accuracy. These prototypes closely mimic the final product, facilitating efficient evaluation and design validation.
Moreover, the rapid prototyping process allows us to generate multiple variations of a part, facilitating thorough testing and validation. Based on the prototype that exhibits the best performance, we then proceed with the manufacture of CNC machined parts.
Contrastingly, other manufacturing methods, such as molding, often involve upfront tooling costs, limiting their cost-effectiveness for small-scale or customized production. CNC machining, on the other hand, with no minimum order quantity, is ideally suited for businesses seeking flexibility in quantity, customization, and prototyping needs. This brings me to the next crucial point.
3. design freedom
CNC machining offers unparalleled design flexibility, enabling us to fabricate precision parts with intricate details and complex geometries. This capability transforms imaginative concepts into reality, overcoming the challenges associated with traditional manufacturing methods. Additionally, the versatility of CNC machining services allows for the seamless creation of customized machined parts, meeting the unique needs of each project.
4. strength
When it comes to manufacturing parts, performance and durability are paramount considerations. CNC machined parts excel in both these aspects, offering superior strength and resilience compared to parts produced through other processes. This is due to the fact that CNC machining avoids the internal stresses commonly associated with other production methods.
Furthermore, machined parts are crafted from solid material blocks, ensuring their structural integrity and durability. This ensures that the parts can withstand rigorous use and last longer, making them a reliable choice for various applications.
1. Undercuts
Undercuts, which cannot be formed with standard cutting tools due to obstructed surfaces, are intricate features that come in two forms: T-slots and dovetails. To achieve these cuts, a specialized cutting tool is required. The width of an undercut typically falls between 3 and 40mm, with the depth not exceeding twice its width.
When dealing with undercuts on internal walls, it's crucial to consider the clearance needed for the cutting tool. As a general rule, the space between the machined wall and the internal wall should be at least four times the undercut depth.
To streamline the process and ensure cost-effectiveness, I advise adhering to standard sizes (whole millimeters) for undercut dimensions, as cutting tools are available in these standard sizes. If a design calls for a non-standard undercut, the manufacturer would have to fabricate a custom cutting tool, which can extend the lead time and inflate production costs. Therefore, if speed and cost are critical factors for your business, it's advisable to avoid such non-standard undercuts.
2. Scale
The capacity of a CNC machine to manufacture parts is determined by its work envelope, which differs based on the material type and the specific CNC machine used. Commonly, the maximum dimensions for milled parts are constrained to 400 x 250 x 150 mm, while turned parts can reach a maximum of ⌀ 500 mm x 1000 mm.
If you require the production of larger parts, it is feasible with larger CNC machines. It is advisable to consult with your manufacturing partners to obtain expert advice before embarking on a custom CNC machining process.
3. Cavities, holes, and threads
The dimensions of holes and cavities in a part vary based on the tools used. It is advisable to maintain a cavity depth that is four times its width to avoid excessive vibrations. Additionally, deeper cavities may result in rounded edges instead of sharp ones.
With CNC technology, threads can be cut down to M6. When designing threads, it's crucial to ensure that the thread length is at least 1.5 times its diameter, with a recommended length of three times the diameter. Lengths exceeding this recommendation are generally unnecessary as the initial teeth carry the majority of the load.
Holes are typically formed using drill bits or end mill tools. Given that drill bits are standardized in size, it's beneficial to align hole diameters with standard drill bit sizes. Furthermore, it's recommended to keep the maximum depth of a hole at four times its diameter.

CNC machining has revolutionized the industrial production of parts, offering numerous advantages including the elimination of minimum order quantities, accelerated prototyping, shortened lead times, and enhanced quality control. The availability of online CNC machining services has further facilitated the procurement of high-quality CNC parts with utmost convenience.
Richconn is your best choice offering these CNN machined parts, ranging from CNC machining aerospace parts to rotation custom motorcycle parts. Richconn prides itself on its extensive experience in the CNC machining industry, encompassing a diverse array of applications and industries. This expertise enables us to tackle a wide variety of projects with unparalleled precision and efficiency, earning us the trust of numerous clients globally.
 Types of Gears: An Overview of Various Mechanical GearsApril 26, 2024This article is about important information you need to know about gears, including types of gears, applications, production and advantages and disadvantages.view
Types of Gears: An Overview of Various Mechanical GearsApril 26, 2024This article is about important information you need to know about gears, including types of gears, applications, production and advantages and disadvantages.view Precautions for Stamping Dies 1July 11, 2023Spring compression and calculationIn a set of stamping dies, more elastic materials need to be used, including springs of different specifications, urethane, nitrogen springs, etc., and different elas...view
Precautions for Stamping Dies 1July 11, 2023Spring compression and calculationIn a set of stamping dies, more elastic materials need to be used, including springs of different specifications, urethane, nitrogen springs, etc., and different elas...view Unveiling the Wonders of Electrophoresis Metal Coating in Gel ElectrophoresisFebruary 29, 2024Gel electrophoresis, a foundational technique in the field of molecular biology, serves as a crucial tool for scientists to unravel the complexities of genetic material. At the heart of this precision...view
Unveiling the Wonders of Electrophoresis Metal Coating in Gel ElectrophoresisFebruary 29, 2024Gel electrophoresis, a foundational technique in the field of molecular biology, serves as a crucial tool for scientists to unravel the complexities of genetic material. At the heart of this precision...view Types of Casting | Which One Is Right for Your Project?December 7, 2023Compare the different types of casting, from sand casting to die casting. Learn about applications and safety measures. Choose the right casting solution!view
Types of Casting | Which One Is Right for Your Project?December 7, 2023Compare the different types of casting, from sand casting to die casting. Learn about applications and safety measures. Choose the right casting solution!view Titanium vs Stainless Steel: Choosing the Right Material for Your MachiningNovember 24, 2023Understand the differences between titanium and stainless steel and choose the best material for CNC machining.view
Titanium vs Stainless Steel: Choosing the Right Material for Your MachiningNovember 24, 2023Understand the differences between titanium and stainless steel and choose the best material for CNC machining.view Do You Know How Anodizing Works?November 4, 2022Anodizing, the process of forming an oxide film on aluminum products (anode) under the action of an applied current under the corresponding electrolyte and specific process conditions of metal or allo...view
Do You Know How Anodizing Works?November 4, 2022Anodizing, the process of forming an oxide film on aluminum products (anode) under the action of an applied current under the corresponding electrolyte and specific process conditions of metal or allo...view