In the realm of precision engineering, the term "cold machined parts" sparks curiosity and a quest for knowledge. As we delve into this intricate domain, my aim is to unravel the mysteries surrounding these components, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of their technology, applications, and performance.
In the fascinating world of engineering, "cool machined parts" stand as a testament to technological advancement. These components, crafted with precision in low-temperature environments, boast unique characteristics that set them apart from traditionally manufactured parts.
Intriguingly different from conventional machining, cold machining thrives in lower temperature settings, impacting the final product's performance. Let's explore how these conditions shape the essence of cold machined parts.
Cold machining involves the precision shaping of materials at temperatures below room temperature. This distinct approach is particularly advantageous for materials that exhibit enhanced properties when processed in a cold state. The characteristics of these components include heightened strength, improved corrosion resistance, and a fine-tuned balance between hardness and toughness.
Embarking on the journey of understanding, we'll dissect the fundamental principles of mechanical machining and the pivotal steps involved in cold machining.
Mechanical machining processes such as milling, turning, and grinding play a vital role in the creation of cold machined parts. Unlike traditional machining, the cold process introduces an additional layer of complexity. During milling, for example, the material is meticulously shaped with precision tools, ensuring the maintenance of low temperatures to harness the unique benefits associated with cold machining.
Delving deeper, we uncover the technical prowess and distinctive features that define cold machined parts, steering us towards a realm of balanced strength, resilience, and corrosion resistance.
Unraveling the intricacies, we explore the delicate equilibrium between strength and toughness, coupled with the remarkable corrosion resistance these parts exhibit in frigid conditions.
Cold machined parts, when subjected to low-temperature environments, showcase an exceptional balance between strength and toughness. This unique characteristic is especially crucial in applications where resilience to extreme conditions is paramount. For instance, in the aerospace industry, where components are exposed to varying temperatures during flight, the ability of cold machined parts to maintain structural integrity becomes a decisive factor.
Navigating the terrain of material science, we discern the types of materials suitable for cold machining and how material selection intricately shapes the performance of these parts.
Materials suitable for cold machining are often selected based on their response to low-temperature processes. Common choices include certain alloys and metals known for their malleability and durability in cold conditions. The selection process involves a meticulous evaluation of the material's thermal conductivity, strength, and the specific requirements of the end application.
To illustrate, a table detailing the thermal and mechanical properties of commonly used materials in cold machining can provide readers with a quick reference guide:
Table 1: Material Properties for Cold Machining
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy A | 150 | 600 | 450 |
| Stainless Steel | 16 | 700 | 500 |
| Aluminum | 250 | 300 | 200 |
This table serves as a valuable resource for engineers and manufacturers, aiding them in the meticulous selection of materials for cold machined parts.
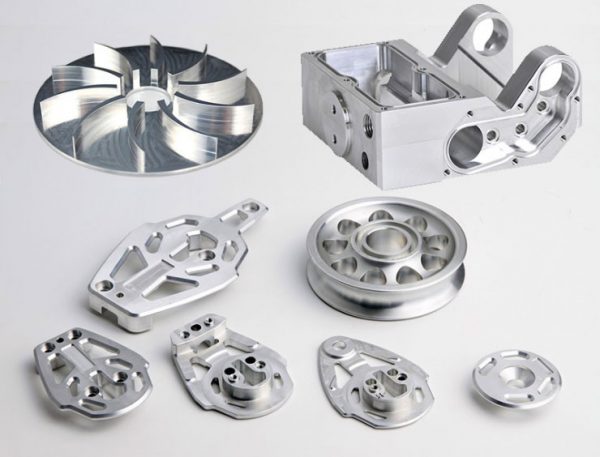

As we shift focus, we dive into the practical realms of application, exploring how cold machined parts find their purpose in diverse industries.
Witnessing their role in the automotive sector, we unravel the applications of cold machined parts and the rationale behind manufacturers' preference for these components.
Cold machined parts have revolutionized the automotive manufacturing landscape. The intricate components, crafted with precision, find applications in critical areas such as engine components, transmission systems, and suspension systems. The enhanced strength and durability of these parts contribute significantly to the overall performance and reliability of vehicles.
Soaring into the skies, we investigate the critical role played by cold machined parts in aerospace applications, accompanied by an exploration of the requisite technical standards.
The aerospace industry demands components that can withstand extreme conditions, and cold machined parts rise to the occasion. From aircraft engines to critical structural elements, the precision and durability of these components ensure the safety and efficiency of aerospace systems. Adhering to stringent technical standards, such as those set by the International Aerospace Quality Group (IAQG), becomes imperative in this high-stakes industry.
Navigating the intricacies of production, we scrutinize the methodologies of milling, turning, and grinding, unlocking the secrets behind these cold machining techniques.
Embarking on the realm of milling, we dissect the cold machining process, while simultaneously examining the impact of turning on the surface quality of these parts.
CNC Milling machining in Cold Machining: In the milling process, precise removal of material occurs as the workpiece is subjected to a rotating cutter. Cold milling introduces an additional layer of intricacy by maintaining a controlled low temperature throughout the operation. This ensures not only dimensional accuracy but also enhances the mechanical properties of the machined part.
CNC turning machining for Surface Quality: Turning, a fundamental cold machining technique, involves the rotation of a workpiece while a cutting tool shapes its surface. The low-temperature environment in cold turning contributes to superior surface finishes, a critical factor in applications where the visual and tactile qualities of the machined part are paramount.
Delving into precision, we explore the temperature control measures during grinding processes and unravel the symbiotic relationship between precision grinding and the quality of machined components.
Temperature Control in Grinding: Grinding, a process crucial for achieving tight tolerances and surface finishes, demands meticulous temperature control in cold machining. By incorporating advanced cooling systems and lubricants, manufacturers ensure that the material's temperature remains within the desired range, preventing thermal distortion and ensuring the dimensional stability of the machined part.
Precision Grinding and Quality Assurance: The marriage of precision grinding and cold machining results in components of unparalleled quality. The controlled temperature, coupled with precision tooling, allows for the creation of intricate geometries with tight tolerances. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the machined part but also ensures its functionality and longevity.
In the quest for excellence, we embark on a journey of comparing the performance of cold machined parts with their counterparts in both hot machining and traditional machining.
Unveiling a comparative analysis, we scrutinize the nuances of strength, hardness, and toughness, while simultaneously conducting a cost-benefit analysis.
Strength and Toughness: Cold machining's distinct advantage lies in its ability to impart enhanced strength and toughness to machined parts. The controlled temperature during processing contributes to refined microstructures, resulting in components capable of withstanding demanding operational conditions. In contrast, hot machining may compromise these properties due to the higher temperatures involved.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is integral to decision-making in precision engineering. While the initial investment in cold machining technology might be higher, the long-term benefits, including extended component lifespan and reduced maintenance costs, often outweigh the initial expenditures.
Positioning cold machining on the grand stage, we decipher its advantages over traditional machining methods, addressing potential drawbacks and proposing effective solutions.
Advantages of Cold Machining: Cold machining's advantages extend beyond improved material properties. The precision achievable in cold milling, turning, and grinding translates into components with minimal tolerances, reducing the need for additional finishing processes. Moreover, the environmental benefits, such as reduced energy consumption and material waste, contribute to the sustainability of cold machining practices.
Addressing Drawbacks: While cold machining excels in various aspects, it's crucial to acknowledge potential drawbacks, such as increased tool wear. However, advancements in tool materials and coatings are mitigating this issue, ensuring that the benefits of cold machining far outweigh its limitations.

In the world of precision engineering, adherence to industry standards and regulations is paramount. Let's navigate through the standards, ensuring a robust understanding of ISO certifications and compliance measures.
Demystifying the ISO standards, we explore their necessity, emphasizing their correlation with quality control and the role they play in certifying the excellence of cold machined parts.
Necessity of ISO Certification: ISO certification is a hallmark of quality assurance in precision engineering. For manufacturers of cold machined parts, obtaining ISO 9001 certification signifies a commitment to consistent quality and adherence to international standards. This certification instills confidence in clients and partners, assuring them of the reliability and durability of the produced components.
Correlation with Quality Control: ISO certification goes hand in hand with stringent quality control measures. Cool machining facilities with ISO certification implement rigorous quality management systems, encompassing everything from material inspection to final product testing. This meticulous approach ensures that each cold machined part meets or exceeds the specified requirements, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Navigating the regulatory landscape, we scrutinize safety standards, environmental requirements, and strategies to ensure compliance, thereby establishing a foundation for quality assurance.
Safety Standards and Compliance: The precision engineering sector operates within a framework of safety standards designed to protect both workers and end-users. Adhering to regulations such as Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines ensures a secure working environment during the manufacturing of cold machined parts. Compliance with safety standards also aligns with ethical and legal responsibilities, creating a foundation for sustainable business practices.
Environmental Requirements and Sustainability: Sustainability is a growing concern in the manufacturing industry. Cold machining, with its reduced energy consumption and minimal material waste, aligns well with environmental requirements. The implementation of eco-friendly practices, such as recycling coolant and responsibly disposing of machining byproducts, further strengthens the environmental credentials of cold machining facilities.
In the final leg of our exploration, we shift our focus to the practical aspects of procurement, understanding how to identify reliable suppliers and establish robust supply chain management practices.
Guiding your procurement journey, we unveil the key factors in selecting suppliers that align with your requirements, offering insights into evaluating their quality systems.
Supplier Selection Criteria: Choosing the right suppliers is paramount in ensuring the quality and reliability of cold machined parts. Key criteria include assessing their experience in cold machining, evaluating their infrastructure and technological capabilities, and understanding their commitment to quality control. A checklist for supplier evaluation might encompass:
Experience in Cold Machining: Assessing the supplier's experience in cold machining, including a track record of successful projects and testimonials from other clients in your industry.
Technological Capabilities: Ensuring that the supplier possesses advanced machinery and technology specifically designed for cold machining processes, contributing to precision and efficiency.
Quality Control Systems: Scrutinizing the supplier's quality management systems, with an emphasis on certifications such as ISO 9001. This ensures that their processes align with industry standards.
Evaluation Process: Establishing a systematic evaluation process aids in the selection of reliable suppliers. This involves conducting on-site visits to assess infrastructure, engaging in discussions about their technological capabilities, and reviewing their quality control documentation. By fostering open communication and transparent collaboration, a strong partnership between the manufacturer and the supplier can be forged.
Navigating the intricacies of supply chain dynamics, we explore strategies to mitigate risks, fostering beneficial collaborations with suppliers for a streamlined and efficient supply chain.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Supply chain management in cold machining necessitates a proactive approach to risk mitigation. Unforeseen events such as material shortages, production delays, or logistic challenges can impact the timely delivery of cold machined parts. Employing strategies such as maintaining strategic stock levels, diversifying suppliers, and implementing contingency plans ensures resilience in the face of uncertainties.
Collaborative Partnerships: Building collaborative partnerships with suppliers is the cornerstone of an effective supply chain. Open lines of communication, transparent information sharing, and mutually beneficial agreements contribute to a symbiotic relationship. Regular assessments of supplier performance, feedback mechanisms, and continuous improvement initiatives enhance the efficiency and reliability of the supply chain.
If you're in the market for reliable suppliers in the realm of cold machined parts, Richconn Precision is a noteworthy consideration. With a robust track record and a commitment to excellence, Richconn Precision aligns with the key criteria for selecting suppliers:
Experience in Cold Machining: Richconn Precision boasts a wealth of experience in cold machining, evident through successful projects and positive testimonials from various industries.
Technological Capabilities: Equipped with state-of-the-art machinery and cutting-edge technology specifically designed for cold machining processes, Richconn Precision ensures precision and efficiency in their manufacturing operations.
Quality Control Systems: Richconn precision machine shop places a strong emphasis on quality control, holding certifications such as ISO 9001. This underscores their commitment to maintaining high standards in their processes.
The evaluation process, including on-site visits and discussions about technological capabilities, is likely to reveal Richconn Precision's dedication to providing top-tier cold machined parts. By fostering transparent communication and collaborative partnerships, Richconn Precision stands out as a reliable and strategic supplier in the cold machining industry.
As we conclude our comprehensive exploration of cold machined parts, we have journeyed through the intricacies of technology, applications, manufacturing processes, performance evaluation, industry standards, and supply chain management. This multifaceted journey provides a holistic view of the world of precision engineering, specifically focusing on the unique attributes and challenges associated with cold machining.
The knowledge gained from this exploration equips engineers, manufacturers, and industry professionals with the insights needed to make informed decisions, from selecting the right materials and processes to establishing robust supply chain practices. Cold machined parts, with their enhanced performance characteristics, are positioned as integral components in industries requiring precision, durability, and reliability.
Embark on your own journey of exploration, leveraging the knowledge gained here to push the boundaries of what is possible in the realm of precision engineering. As technology advances and industries evolve, the secrets of cold machined parts continue to unfold, inviting further innovation and excellence. The call to action resonates: Explore, Understand, Implement, and Succeed in the dynamic world of cold machined parts.
 What Are Machined Rotors?November 8, 2023Welcome to the world of precision engineering, where the subtle details can make a world of difference. In the realm of CNC machining and automotive components, 'Machined Rotors' emerge as a pivotal player, quietly ensuring your safety and vehicle performance.view
What Are Machined Rotors?November 8, 2023Welcome to the world of precision engineering, where the subtle details can make a world of difference. In the realm of CNC machining and automotive components, 'Machined Rotors' emerge as a pivotal player, quietly ensuring your safety and vehicle performance.view Unlocking the Infinite Potential of CNC Milling MaterialsFebruary 29, 2024In the intricate tapestry of CNC milling materials, the careful selection of materials emerges as the linchpin, dictating the success and precision of every project.view
Unlocking the Infinite Potential of CNC Milling MaterialsFebruary 29, 2024In the intricate tapestry of CNC milling materials, the careful selection of materials emerges as the linchpin, dictating the success and precision of every project.view Aluminium Extrusion: A Versatile and Innovative Manufacturing ProcessNovember 30, 2023Aluminium extrusion is a process of forcing aluminium alloy material through a die to create a continuous shape or product. The material can be solid, liquid, or semi-solid, and it can be metal, plastic, ceramic, or food.view
Aluminium Extrusion: A Versatile and Innovative Manufacturing ProcessNovember 30, 2023Aluminium extrusion is a process of forcing aluminium alloy material through a die to create a continuous shape or product. The material can be solid, liquid, or semi-solid, and it can be metal, plastic, ceramic, or food.view Tig vs Mig Welding: Choosing Between Two Great WeldingNovember 16, 2023When comparing MIG and TIG welding, it is important to consider the factors involved, the pros and cons they have, and the applications they are suitable for.view
Tig vs Mig Welding: Choosing Between Two Great WeldingNovember 16, 2023When comparing MIG and TIG welding, it is important to consider the factors involved, the pros and cons they have, and the applications they are suitable for.view What Is a Shaft?October 30, 2023A shaft is basically a rotating part of any machine, having a circular cross-section, which is used to transmit power from one part to another or from a power generating machine to a power absorbing machine. To transmit power, one end of the shaft is connected to the power source and the other end is connected to the machine. Shafts can be solid or hollow as per requirement, hollow shafts help in reducing weight and provide advantages.view
What Is a Shaft?October 30, 2023A shaft is basically a rotating part of any machine, having a circular cross-section, which is used to transmit power from one part to another or from a power generating machine to a power absorbing machine. To transmit power, one end of the shaft is connected to the power source and the other end is connected to the machine. Shafts can be solid or hollow as per requirement, hollow shafts help in reducing weight and provide advantages.view Surface Treatment for CNC Machining PartsApril 4, 2023CNC machining can produce precision parts with strict tolerances and fine parts from various metal or plastic materials. Due to the influence of factors such as plastic deformation during chip separat...view
Surface Treatment for CNC Machining PartsApril 4, 2023CNC machining can produce precision parts with strict tolerances and fine parts from various metal or plastic materials. Due to the influence of factors such as plastic deformation during chip separat...view