Steel, is a generic term for iron-carbon alloys that contain between 0.02% and 2.11% carbon. When the carbon content is greater than 2.11%, it is referred to as pure iron. The chemical composition of steel can vary greatly, and steel containing only carbon is known as carbon or plain steel. During the smelting process, alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, manganese, silicon, titanium and molybdenum can be added to improve the properties of the steel. The main characteristic of stainless steel is its corrosion resistance, with a chromium content of at least 10.5% and a carbon content of no more than 1.2%.
Some people think that when the surface of stainless steel appears brown rust spots (points), stainless steel is no longer stainless, may be a problem with the quality of steel. This is actually a misunderstanding of stainless steel. In fact, stainless steel will rust under specific conditions.
Stainless steel has the ability to resist atmospheric oxidation, that is, stainless steel, but also has the ability to resist corrosion in the medium containing acids, alkalis and salts, that is, corrosion resistance. However, its corrosion resistance depends on the chemical composition of the steel, its crystal structure, the conditions of use and the type of environmental media. For example, in a dry, clean atmosphere, 304 exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, but if it is exposed to sea spray containing high levels of salt, it will quickly rust. As a result, not all types of stainless steel remain stainless under all circumstances.
Stainless steel relies on the very thin but strong chromium-rich oxide film (protective film) formed on its surface to prevent oxygen atoms from continuing to penetrate and oxidize, thus gaining resistance to corrosion. Once this film is destroyed for some reason, oxygen atoms in the air or liquid will continue to penetrate, resulting in metal surface rust.

There are three main factors that affect the rusting of stainless steel:
Alloying element content: Generally speaking, steel containing at least 10.5% chromium is less prone to rust. Higher chromium-nickel content will improve corrosion resistance, for example, the nickel content in 304 material is usually 8-10%, while the chromium content of 18-20% stainless steel is not easy to rust in general.
Production process: the smelting process of the production enterprise will also affect the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. The advanced smelting technology, equipment and process of large stainless steel plant can ensure stable and reliable product quality, thus reducing the possibility of rust.
External environment: dry climate and well-ventilated environment are not easy to rust, while humid and high pH environment increases the risk of rust. Even stainless steel made of 304 may rust in harsh environments.
Chemical: Pickling creams or sprays can be used to re-passivate rusted areas and form a new film of chromium oxide to restore corrosion resistance. After pickling, it is important to rinse thoroughly with water to remove all contaminants and residual acid. The surface is then re-polished and sealed using polishing equipment.
Mechanical Methods: Mechanical methods such as sandblasting, glass or ceramic particle blasting, brushing and polishing can be used to clean rust spots. After mechanical cleaning, it is recommended to re-polish and seal the surface using polishing equipment.
Whether stainless steel is magnetic or not is related to its crystal structure. Steel forms different organizational structures during solidification, including "ferrite", "austenite" and "martensite". Therefore, magnetic and non-magnetic is determined by the different organizational structure. Although some stainless steels are magnetic, this does not mean that they will rust. In fact, austenitic stainless steels have good corrosion resistance, but may also be slightly magnetic in some cases.
201: Stainless steel with manganese instead of nickel, suitable for cases, decorative tubes and some shallow drawn products.
202: low-nickel, high-manganese stainless steel, suitable for architectural decoration, highway guardrail, municipal engineering and so on.
304: general-purpose stainless steel, suitable for food, medical, industrial, chemical and home decoration.
304L: low carbon 304 stainless steel, suitable for corrosion resistance and formability equipment.
316: with added molybdenum, suitable for seawater equipment, chemical, food industry and paper making.
321: with high temperature properties, suitable for equipment in high temperature environments.
430: Suitable for household appliances and architectural decoration.
410: High hardness and good corrosion resistance, suitable for parts in some special environments.
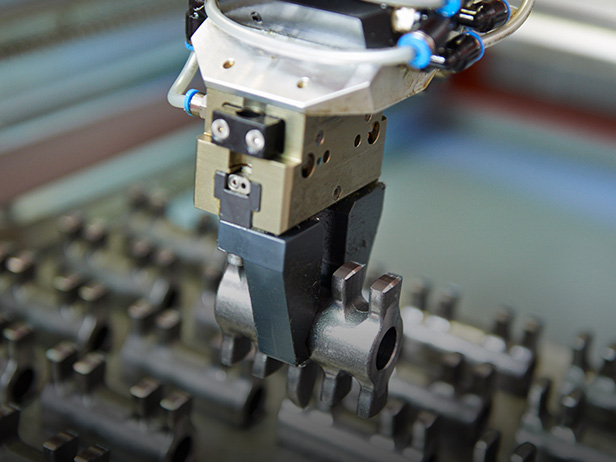
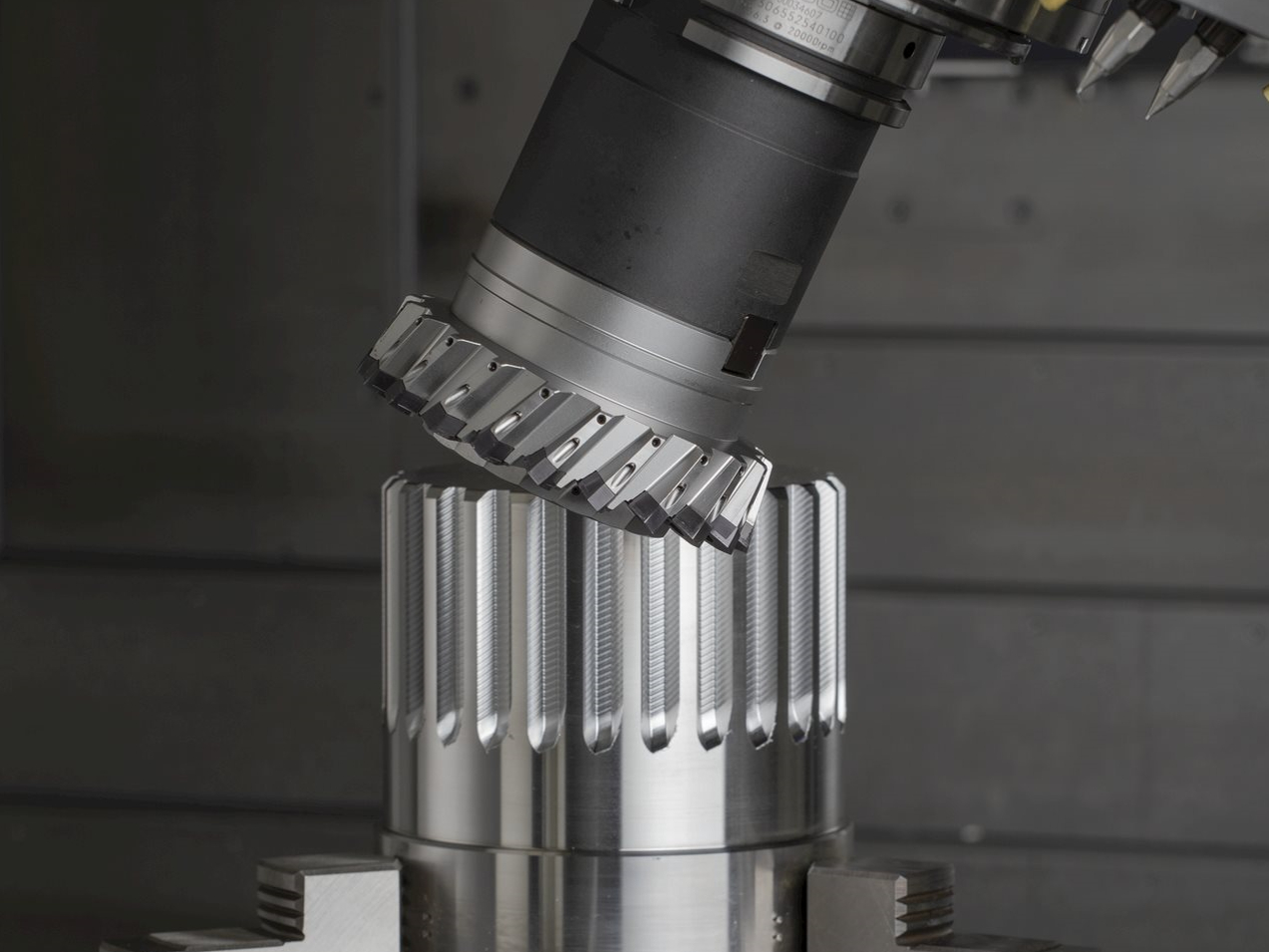
Stainless steel has a wide range of applications in CNC machining services, especially in CNC turning and CNC milling services.
Component Manufacturing: Stainless steel is a common material used in the manufacturing of various mechanical components, such as threaded shafts, bearing housings, bushings, etc.. Its corrosion and wear resistance make it ideal for manufacturing durable parts.
Threading: CNC lathes can be used to machine stainless steel threads, both internal and external, to meet a variety of engineering needs.
Pipe Fabrication: Stainless steel piping is commonly used in the chemical, food, and medical industries, and CNC lathes can be used to accurately cut, bend, and weld stainless steel piping to ensure its quality and tightness.
Custom Parts: CNC turning can be used to manufacture a variety of custom stainless steel parts, including jewelry, watches, and automotive parts for the retail industry.
Face Machining: CNC milling can be used to machine flat surfaces on stainless steel workpieces for high precision and flatness.
Assembly parts: Stainless steel is widely used to make assembly parts such as screws, nuts, washers and threaded pins. cnc milling machines can machine complex shapes and threads of these parts.
Engraving and Cutting: CNC milling machines can be used to engrave and cut stainless steel workpieces to produce decorative products such as plaques, engraved artwork and precision parts.
Mold Making: Stainless steel is commonly used in the manufacture of injection molds, die casting molds, and stamping molds, and CNC milling machines can be used to machine and repair these molds to ensure their accuracy and durability.
Stainless steel is used in a wide range of CNC machining services, and it is used to make a variety of different types of components, assembly parts, industrial equipment, and decorative products.CNC turning and CNC milling technologies offer highly accurate and efficient machining methods to meet the needs of stainless steel in a variety of industrial sectors.
| GRADE | TYPE | TRAITS | USES |
| 3CR12 | Ferritic | Useful corrosion resistance, particularly in wet abrasion environments. Readily welded and formed. | Tanks, flues, bins, chutes, rail wagons |
| 201 | Austenitic | Low nickel, high work hardening. | Cookware, hose clamps |
| 301 | Austenitic | Combination of strength and ductility to withstand severe forming methods. Corrosion resistance comparable to 302. | Rail cars, automotive components |
| 302 | Austenitic | Excellent corrosion resistance. High strength and hardness. | Food and drink, sanitary, cryogenic and pressure applications |
| 303 | Austenitic | Addition of sulfur or selenium gives it best machinability of all austenitic grades, but reduces corrosion resistance compared to 304. | Nuts and bolts, aircraft fittings and gears, bushings |
| 304 304L 304H | Austenitic | Slightly magnetic when cold worked. Excellent corrosion resistance but susceptible to pitting corrosion in warm chloride environments. Excellent toughness Accounts for 50% of all stainless steel produced. | Architecture, kitchens, food processing |
| 309S | Austenitic | Resistant to oxidation. | Heating, furnace parts |
| 316 316L 316H | Austenitic | Same mechanical and physical properties as 304 but more resistant to pitting corrosion, especially in warm chloride environments. Virtually non-magnetic. | Marine architectural components, food processing, hot water systems |
| 317L | Austenitic | Improved corrosion resistance over 316. 317L is a variation of 317 suitable for heavy-gauge welding. | Pulp and paper machinery, ink and dying processes, acetic acid distillation |
| 321 | Austenitic | Titanium-stabilized. | Aircraft, heat exchangers (up to intermediate temperatures) |
| 400 | Ferritic | Corrosion resistance comparable to 409, better surface finish | Caskets, applications requiring better finish than 409 |
| 409, Aluminized 409 | Ferritic | Resists atmospheric and automotive exhaust gas corrosion. Aluminized version adds salt and cosmetic corrosion resistance. | Auto exhaust systems, heat exchangers, furnace liners |
| 410, 410H | Martensitic | Resists dry atmospheres, freshwater, mild alkalis and acids, steam, and hot gases. Must harden for best heat and corrosion resistance. 410H has better hardenability. | Bolts, nuts, screws, pump parts and shafts, turbine parts, mine ladder rungs, cutlery, rulers, cold heading |
| 420, 420HC | Martensitic | Good resistance in hardened condition to atmosphere. Higher-carbon grade. HC offers better hardenability. | Cutlery, stainless steel hospital equipment, needle valves |
| 430, 430F | Ferritic | Good combination of corrosion resistance, formability, mechanical properties. 430F is suitable for high-speed machining, but corrosion resistance is lower. | Automotive trim, refrigerator doors, element supports, cold-headed fasteners |
| 431 | Martensitic | Excellent resistance to wide variety of corrosive media, approaching that of 304. High tensile, torque strength. | Pump and boat shafts, nuts, bolts, marine hardware |
| 434 | Ferritic | Molybdenum use improves pitting resistance over 430. | Automotive trim components |
| 435 Mod. | Ferritic | Improved formability and weldability. | Automotive trim |
| 436 | Ferritic | Controlled roping. | Automotive trim |
| 439 | Ferritic | Titanium-stabilized. 18% chrome alloy with low carbon content. Corrosion resistance to variety of oxidizing environments. Pitting corrosion resistance. | Nuclear, automotive, power generation, chemical processing, consumer appliances |
| 440 | Martensitic | High-carbon, moderate corrosion resistance, superior strength and hardness. | Knives, ball bearings, gauge blocks, dies |
| 444 | Ferritic | Resistant to oxidation, corrosion, and stress cracking. | Water heaters, engine components, solar panels |
| 904L | Austenitic | ‘Super austenitic’ grade with very high corrosion resistance, especially to strong acids and chlorides. | Sulphuric acid service |
| 2205 | Ferritic/ Austenitic | About 50% ferrite and 50% austenitic. High strength and hardness. Resistant to erosion, fatigue, stress corrosion cracking, and pitting and crevice corrosion. | Marine, chemical, and petrochemical industries |
| 41003 | Ferritic | Excellent weldability, toughness, and fabricating characteristics | Tubing for bus frames, hopper cars, chutes, storage tanks, shipping containers |
| UR52N | Ferritic/ Austenitic | ‘Super duplex’ grade with exceptional resistance to hot chlorides and sulfides. High in strength. | Marine, chemical, and petrochemical industries |
Stainless steel is an important material with a wide range of applications in various fields. Although it is known for its resistance to corrosion and wear, it does not mean that it is absolutely rust-free. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel is influenced by a number of factors, including the content of alloying elements, the production process and the external environment. Therefore, understanding the properties of stainless steel and proper handling is critical to its maintenance.
Stainless steel is also used in a wide range of CNC machining services, which provide high-quality and high-precision solutions for manufacturing a wide range of parts and products. Whether it is CNC turning services or CNC milling, these modern machining techniques offer more possibilities for the machining of stainless steel to meet the needs of different industries. As a result, the combination of stainless steel and CNC machining will continue to drive technology and engineering forward, providing a solid foundation for the success of a wide variety of projects, while also creating more opportunities for innovation and growth.
 What Are The Characteristics and Features of CNC Machining?June 21, 2022Process concentration, automation, high flexibility, and strong capabilities are the characteristics of CNC machining. The process rules of CNC machining and traditional machine tool machining are gen...view
What Are The Characteristics and Features of CNC Machining?June 21, 2022Process concentration, automation, high flexibility, and strong capabilities are the characteristics of CNC machining. The process rules of CNC machining and traditional machine tool machining are gen...view Experience Sharing on Design and Manufacturing of Metal Stamping DiesJuly 21, 2023Here, we will share some specific design and manufacturing experiences to provide our understanding of dies accumulated over the years. Through this article, we hope to give you a better understanding...view
Experience Sharing on Design and Manufacturing of Metal Stamping DiesJuly 21, 2023Here, we will share some specific design and manufacturing experiences to provide our understanding of dies accumulated over the years. Through this article, we hope to give you a better understanding...view Choosing the Optimal Material For CNC Machining.October 17, 2023If you find the vast selection of different materials for CNC machining confusing, this blog will tell you how to reduce that number to a manageable level.
Choosing the right material for CNC machining can make all the difference in getting a working part or prototype made at a reasonable price.view
Choosing the Optimal Material For CNC Machining.October 17, 2023If you find the vast selection of different materials for CNC machining confusing, this blog will tell you how to reduce that number to a manageable level.
Choosing the right material for CNC machining can make all the difference in getting a working part or prototype made at a reasonable price.view Plastics Solutions: Choosing the Right Materials for Your PartsOctober 18, 2023There are more than 85,000 commercial options for plastics listed in materials databases. Among them, there are 45 polymer families that can be roughly divided into two categories: Thermosets and Thermoplastics. We focus primarily on the latter category, offering hundreds of engineering thermoplastics through our Express Injection Molding service (see Figure 1). In addition to our in-stock plastics, we can handle many other plastics provided by our customers.view
Plastics Solutions: Choosing the Right Materials for Your PartsOctober 18, 2023There are more than 85,000 commercial options for plastics listed in materials databases. Among them, there are 45 polymer families that can be roughly divided into two categories: Thermosets and Thermoplastics. We focus primarily on the latter category, offering hundreds of engineering thermoplastics through our Express Injection Molding service (see Figure 1). In addition to our in-stock plastics, we can handle many other plastics provided by our customers.view How to Choose the Right CNC Machining Manufacturer?January 30, 2024Discover tips for selecting the CNC machining manufacturer. Learn about key criteria, including expertise, capabilities, lead times, warranty policies, etc.view
How to Choose the Right CNC Machining Manufacturer?January 30, 2024Discover tips for selecting the CNC machining manufacturer. Learn about key criteria, including expertise, capabilities, lead times, warranty policies, etc.view Application of 5-Axis Machining Center in High-Speed Blower Impeller ManufacturingMarch 24, 2023With the rapid development of technology, high-speed blowers have been widely used in various fields. In order to improve the performance and efficiency of the blowers, it is necessary to manufacture ...view
Application of 5-Axis Machining Center in High-Speed Blower Impeller ManufacturingMarch 24, 2023With the rapid development of technology, high-speed blowers have been widely used in various fields. In order to improve the performance and efficiency of the blowers, it is necessary to manufacture ...view