Steel comes in a variety of grades, sizes, shapes and finishes - the World Steel Association lists more than 3,500 different grades of steel, most with unique properties. The variety of steel grades means that steel can be used in a wide range of applications for foundations, appliances, vehicles, wind turbines and many more.
However, optimizing the properties of steel for each application involves more than just changing the chemical composition. The manufacturing process of the steel can also have a significant impact on the steel product - even if the grades and specifications are the same. One of the main differences between prefabricated steel products is the difference between hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel.
It is important to note that one of the main differences between hot rolled steel and cold rolled steel is the difference in process. "Hot rolling" refers to a process that utilizes heat. "Cold rolling" refers to a process that takes place at or near room temperature. Although these techniques affect overall performance and application, they should not be confused with the official specifications and grades of steel, which relate to metallurgical composition and performance levels. Different grades and specifications of steel can be hot or cold rolled, including basic carbon and other alloy steels. Knowing which to use can help avoid overspending on raw materials. It can also save time and money on additional processing. Understanding the differences between hot and cold steel is crucial to choosing one over the other.
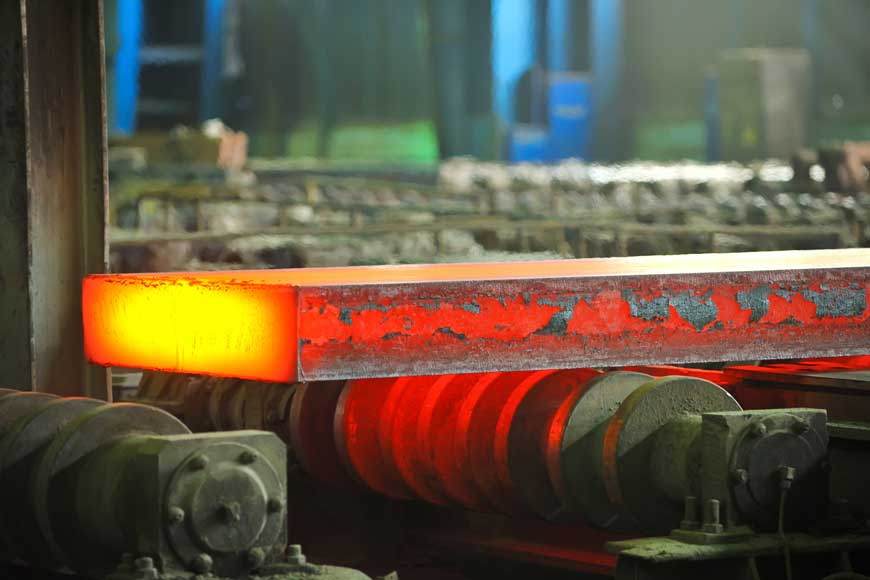

Hot rolled steel is steel that is rolled at extremely high temperatures above 1700°F, which relates to the recrystallization temperature of most steels. This makes the steel easier to form, which produces products that are easier to process.
To process hot rolled steel, manufacturers start with a large shaped metal called billet. The billet is heated and sent for cutting, where it is flattened into a large coil. It is held at high temperatures and passed through a series of rolls to reach its final size. The white-hot strand is pushed through the rolls at high speed. For sheet metal, the rolled steel is spun into coils and cooled. For forms such as bars or other plates, the material is skeletonized and packed.
The steel shrinks slightly as it cools. Since hot rolled steel cools after processing, it is less suitable for precision applications because of the lighter control of its final shape. Hot rolled steel is typically used in applications that require less precise detailed dimensions. Railroad tracks and construction projects typically use hot rolled steel.
Scaly surface - cooling retention from extreme temperatures.
Slightly rounded edges and corners on bar and plate products (due to shrinkage and less precise finishing) .
Slight distortion from cooling may result in a slight trapezoidal shape rather than perfectly squared corners.
Hot rolled steel usually requires less machining than cold rolled steel, which makes it cheaper to process. Because hot rolled steel can be cooled under, it is essentially normalized - meaning it may not have internal stresses from quenching or process hardening.
Hot rolled steel is ideal where dimensional tolerances are less important than overall material strength and surface finish is not a critical issue. If surface finish is a concern, oxidized skin can be removed by grinding, sandblasting, or acid bath pickling.
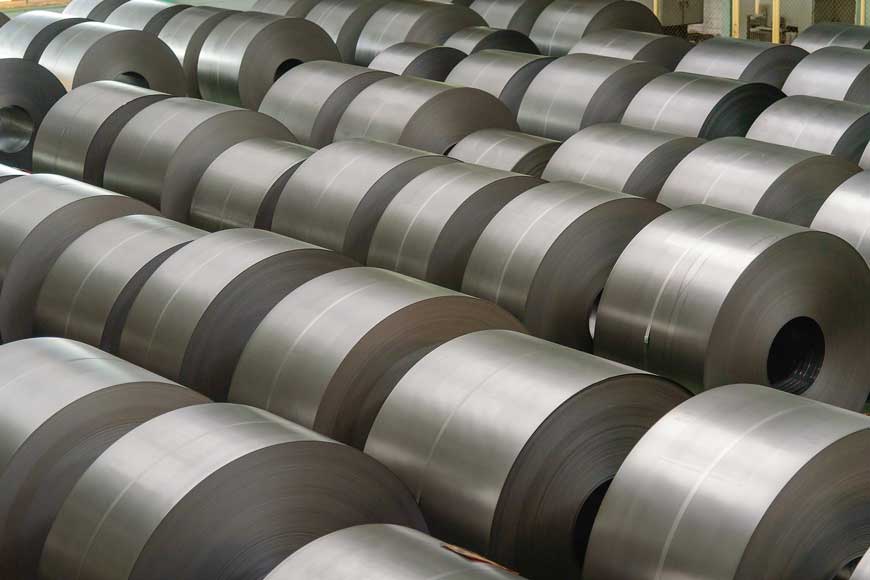

Cold rolled steel is essentially hot rolled steel that has been further processed. After hot rolling the cooled steel, it is re-rolled next to ensure more accurate dimensions and better surface quality.
A better, more finished surface with smaller tolerances .
Smooth surface, usually greasy to the touch.
Bars usually have well-defined angles.
Tubes with better uniform concentricity and straightness.
Cold rolled steel has better surface properties than hot rolled steel, so it is not surprising that it is often used for technically more precise applications or for aesthetic purposes. However, cold finished products are more expensive due to the additional processing required.
In terms of physical properties, cold rolled steel is usually harder and stronger than standard hot rolled steel. Because the metal is formed at a lower temperature, the steel's hardness, tensile fracture resistance, and resistance to deformation are all increased by work hardening.
However, these additional treatments create internal stresses within the material. If the stresses are not removed prior to cutting, grinding or welding, unpredictable warping may result.
 What Is a CMM Machine: Components, Uses, and BenefitsMarch 15, 2024Here is a thorough introduction to CMM machines from components, uses to benefits. Let’s have a deeper look and choose the best CMM service for your projects.view
What Is a CMM Machine: Components, Uses, and BenefitsMarch 15, 2024Here is a thorough introduction to CMM machines from components, uses to benefits. Let’s have a deeper look and choose the best CMM service for your projects.view Machined Castings - Your Comprehensive GuideNovember 7, 2023Are you looking to delve into the fascinating world of machined castings? Are you curious about how these essential components are made, their diverse applications, and the key factors to consider when choosing a supplier?view
Machined Castings - Your Comprehensive GuideNovember 7, 2023Are you looking to delve into the fascinating world of machined castings? Are you curious about how these essential components are made, their diverse applications, and the key factors to consider when choosing a supplier?view How to Measure Surface Roughness?August 2, 2023In order to ensure the optimal quality of parts, the surface of components after manufacturing applications must be maintained within the desired range of roughness. Surface treatment plays a critical...view
How to Measure Surface Roughness?August 2, 2023In order to ensure the optimal quality of parts, the surface of components after manufacturing applications must be maintained within the desired range of roughness. Surface treatment plays a critical...view Titanium vs Stainless Steel: Choosing the Right Material for Your MachiningNovember 24, 2023Understand the differences between titanium and stainless steel and choose the best material for CNC machining.view
Titanium vs Stainless Steel: Choosing the Right Material for Your MachiningNovember 24, 2023Understand the differences between titanium and stainless steel and choose the best material for CNC machining.view How Many Fasteners Are Needed in the Construction Machinery Sector?October 27, 2023Fasteners as commonly used parts, you should not be unfamiliar, today Richconn from the classification of fasteners, the identification and inspection of threads, bolts, screws and studs of the material requirements, heat treatment requirements and mechanical performance requirements, the types of steel bolts and the construction of the four aspects of the introduction.view
How Many Fasteners Are Needed in the Construction Machinery Sector?October 27, 2023Fasteners as commonly used parts, you should not be unfamiliar, today Richconn from the classification of fasteners, the identification and inspection of threads, bolts, screws and studs of the material requirements, heat treatment requirements and mechanical performance requirements, the types of steel bolts and the construction of the four aspects of the introduction.view Define Polished: Process, Benefits & ApplicationsAugust 31, 2023Have you ever imagined transforming a raw piece of stainless steel into a shining masterpiece? When we say something is polished, we are describing a transformation from a rough and lackl...view
Define Polished: Process, Benefits & ApplicationsAugust 31, 2023Have you ever imagined transforming a raw piece of stainless steel into a shining masterpiece? When we say something is polished, we are describing a transformation from a rough and lackl...view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru