Copper is renowned for its versatility and resilience. It is not merely a metal but a cornerstone in various industries. This essential element boasts an array of properties that make it ideal for countless applications, from intricate electronics to robust building materials. Today, we delve into the question of what is copper, exploring its key characteristics and potential for CNC machining.
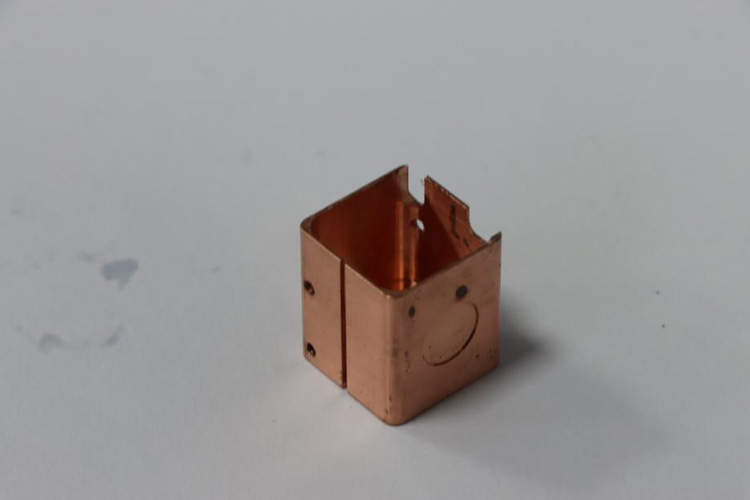
Copper, a reddish-brown element praised for its exceptional conductivity, malleability, and durability. Copper is an example of a metal that shines in electronics, construction, and beyond, shaping our world from wires to roofs. As we navigate through the fundamental properties of copper, it becomes apparent that this versatile metal holds a rich tapestry of characteristics.
Copper, with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29, is a versatile transition metal characterized by its metallic nature and distinctive reddish-brown color. Remarkably, copper excels in high electrical conductivity, ductility, corrosion resistance, and more. Its recyclability and sustainable attributes further enhance its attractiveness, rendering copper an essential material across construction, plumbing, electronics, and diverse industrial sectors.
A common misconception is that copper itself is an alloy. However, copper (Cu) is a pure element found on the periodic table. It readily blends with other metals to form numerous alloys, with brass being one of the most well-known examples. Brass is indeed an alloy of copper and zinc, though the term "zinc and copper alloy" is also technically accurate.
Therefore, the alloy of copper and zinc emphasizes copper as the base metal, followed by the additional element (zinc) that modifies its properties. However, copper is not an alloy itself, even though it forms numerous alloys.
One feature of copper is its resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Unlike iron, which readily succumbs to rust, copper showcases a unique chemical resilience. A common inquiry arises: Does copper rust?
The answer is a resounding no. Copper does not undergo the typical rusting process observed in metals like iron. Instead, it develops a protective patina over time. It's a chemical shield forged by the interaction of copper with oxygen and atmospheric elements. This patina acts as a barrier, slowing down the oxidation process and safeguarding the underlying metal from further degradation.
Copper's chemical properties also allow it to be purified in some cases. Electrolysis of copper involves the decomposition of copper ions through the application of an electric current. In this process, copper electrodes are immersed in a copper sulfate solution, serving as the electrolyte. This method allows for the purification of copper, eliminating impurities through the separation of copper ions and the creation of a more refined and high-quality metal. The electrolysis of copper is a fundamental technique used in various industries to produce pure copper for manufacturing purposes.
Copper's physical attributes are characterized by malleability and ductility. The copper yield strength, indicating the stress it can endure before experiencing permanent deformation, stands at approximately 30-60 MPa. Additionally, copper exhibits a commendable copper tensile strength, with the ability to withstand a maximum stress of around 170-220 MPa before breaking.
Here's a helpful table summarizing the yield and the tensile strength of copper, along with some comparisons:
Property | Copper | Steel | Aluminum |
Yield Strength (MPa) | 30-60 | 250-310 | 80-120 |
Tensile Strength (MPa) | 170-220 | 400-600 | 200-300 |
* Yield Strength: This indicates the maximum stress an object can withstand before experiencing permanent deformation (essentially, "denting").
* Tensile Strength: This represents the maximum stress an object can bear before breaking.
Copper excels not only in its physical characteristics but also in its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity.
To answer the question of what is coppers melting point? The melting point of copper is approximately 1,984 degrees Fahrenheit (1,085 degrees Celsius). This high melting point renders copper suitable for applications involving elevated temperatures, such as metallurgical processes and electrical components.
Copper is also renowned for its exceptional electrical conductivity. With a conductivity rating of approximately 58 x 10^6 S/m, it stands as one of the most efficient conductors among metals. Compared to aluminum, another common conductor, copper boasts nearly twice the electrical conductivity, making it the preferred choice for most high-performance applications. This property makes copper an indispensable material in electrical wiring, electronic components, and various power transmission systems.
In addition to its electrical prowess, copper excels in thermal conductivity. It efficiently transfers heat, making it a preferred material for heat sinks, radiators, and other applications where thermal management is crucial. The thermal conductivity of copper is approximately 398 W/(m·K), showcasing its efficiency in dissipating heat.
Unlike permanent magnets, copper's magnetic properties arise from its interactions with electric current in a specific context: an electrochemical cell. The key question then arises – is copper a cathode or anode? The answer is like many things in science, depends on the specific circumstances.
Cathode: In most common setups, copper acts as a cathode. This means it attracts positively charged ions (cations) during the electrochemical process. In batteries, for example, copper ions in the electrolyte move towards the copper electrode and gain electrons, becoming neutral copper atoms. This electron flow generates the current that powers the battery.
Anode: However, under certain conditions, copper can also act as an anode. This typically occurs when exposed to highly oxidizing environments or specific chemical solutions. In this scenario, copper loses electrons, becoming positively charged copper ions and contributing to the flow of current in the opposite direction.
In cathode scenarios, copper's potential aligns well with the electron-rich environment, readily attracting cations and gaining electrons. Conversely, in specific oxidizing situations, copper's potential can shift, making it prone to losing electrons and acting as an anode.
Compared to many common metals, copper ranks among the more expensive ones. The current (as of January 2024) spot price for copper sits around $3.79 per pound. This price can fluctuate based on market dynamics, supply and demand, and the specific form of copper (e.g., ingots, sheets, wires). Is copper expensive? Why the higher price? Several factors contribute to copper's cost:
Limited Resources: Copper is a finite resource. This scarcity contributes to its higher value compared to more abundant metals like iron or aluminum.
Production Costs: Extracting and refining copper can be a complex and energy-intensive process, involving mining, crushing, smelting, and refining. These expenses are reflected in the final cost of the metal.
High Demand: Copper's versatility and essential role in various industries, from electronics to construction, create a constant and robust demand, further influencing its price.
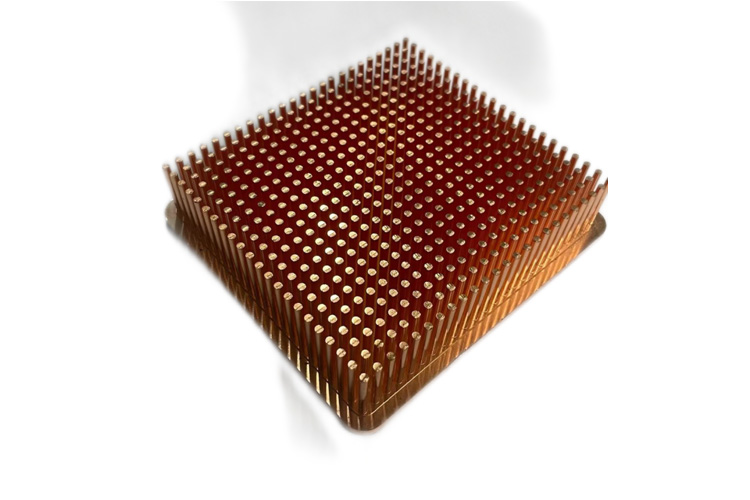
Copper contains exceptional properties, but its true versatility unfolds in the diverse range of material options available for CNC machining. CNC machinists have access to a variety of copper material options, each option possesses a unique blend of characteristics, tailoring its suitability for specific applications.
1. Electrolytic Tough Pitch (ETP) Copper:
Conductivity Champion:
Reigns supreme in electrical conductivity, ideal for components requiring optimal current flow such as busbars, connectors, and intricate circuitry.
Machining Maestro:
Exhibits excellent workability, allowing for precise shaping and fabrication of complex geometries.
Application All-Star:
Versatile performer suited for intricate electrical contacts and heat sinks in high-performance electronics.
2. Free-Cutting Copper:
Machining Mastermind:
Shines in CNC machining with superior chip breakability, reduced friction, and efficient cutting, making it suitable for intricate parts.
Conductivity Compromise:
Sacrifices a slight degree of electrical conductivity compared to ETP copper, but the machining advantages often outweigh this trade-off.
Application Ally:
Ideal for intricate heat sinks, decorative architectural elements, and complex machined components where ease of fabrication is crucial.
3. Phosphorized Copper:
Strength Standout:
Boasts enhanced strength and resistance to hydrogen embrittlement due to the infusion of phosphorus.
Conductivity Considerations:
Exhibits slightly lower conductivity compared to ETP copper, similar to free-cutting options.
Application Expert:
Beneficial for high-pressure applications like hydraulic components and pressurized vessels requiring superior mechanical strength.
Note: This is just a glimpse into the diversity of copper materials for CNC machining. Beyond these options, numerous other alloys and modified forms cater to specific demands.
Wanna get more CNC machining tips for free? Contact Richconn instantly!
Copper coating is a process that bestows various substrates with a thin layer of copper, introducing a new dimension of utility and aesthetics.
1. Strengthening the Shield
One of the primary benefits of copper coating lies in its capacity to enhance corrosion resistance. By forming a protective barrier against environmental elements, copper plating shields underlying materials from rust, oxidation, and degradation. This extension of component lifespan is particularly valuable in harsh environments, such as marine applications, chemical processing, and construction.
2. Conductivity Channel
By depositing a highly conductive layer on non-conductive or less conductive substrates, electrical flow can be optimized. This makes copper plating ideal for enhancing the performance of heat sinks, electrical connectors, and various electronic components.
3. Aesthetic Allure
Beyond functionality, copper plating introduces a touch of decorative appeal. The warm reddish-brown hue, developing a mesmerizing patina over time, adds a unique elegance to diverse objects.
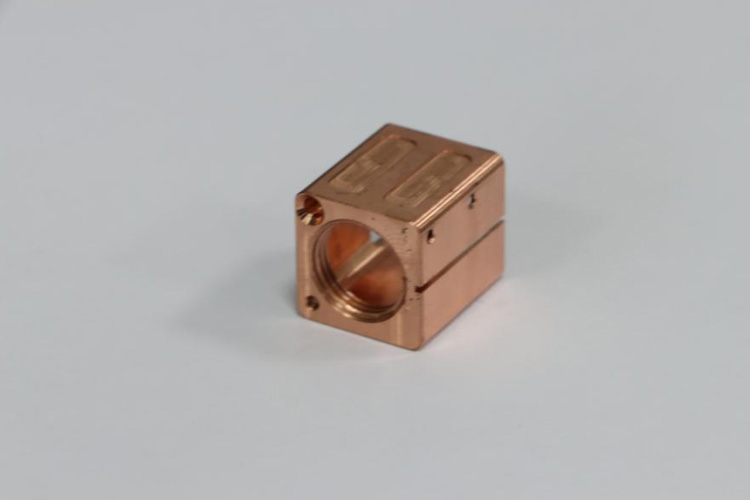

While copper's intrinsic properties often shine in lighter applications, some situations demand increased weight for optimal performance or stability. CNC machinists have an array of techniques at their disposal to ensure copper creations meet the desired weight criteria:
1. Material Matters:
The most straightforward approach is utilizing thicker copper material. Selecting a higher gauge or thicker sheet metal directly increases the final weight without compromising the desired properties of pure copper.
2. Filling the Void:
For hollow sections within a copper part, strategically filling them with denser materials offers a targeted weight increase. Tungsten, lead, or steel inserts can be strategically integrated to achieve the desired mass distribution without altering the overall design or functionality.
3. A Mixed Metal:
Combining copper with heavier metals through composite structures or cladding is another effective strategy. Brazing or welding steel, lead, or tungsten plates onto the copper base can significantly increase the overall weight while maintaining specific conductivity or aesthetic qualities where needed.
4. Specialized Techniques:
These are just a few avenues for manipulating copper's weight. Specialized techniques like electroforming can create intricate, lightweight copper structures with strategic internal reinforcements for targeted mass distribution. Additionally, advanced composite materials incorporating copper fibers offer unique possibilities for combining strength, conductivity, and precise weight control.
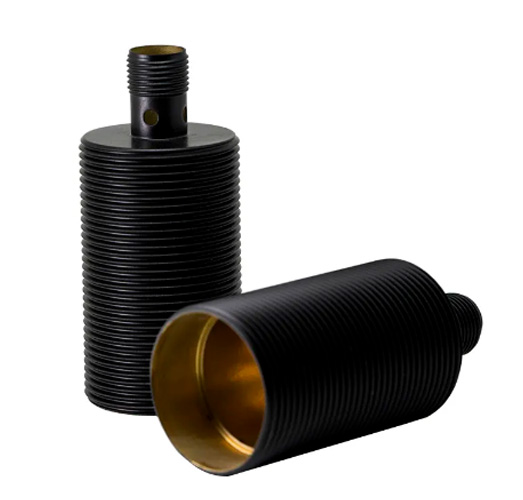

Copper's unique blend of properties – high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, ductility, and corrosion resistance – has propelled it to become a crucial material in a vast array of scientific and technological applications.
1. Electrical and Electronic Applications:
Electrical wiring: Due to its exceptional conductivity, copper forms the backbone of electrical wiring in buildings, appliances, and circuitry.
Electromagnets: Copper coils in electromagnets generate powerful magnetic fields, vital for motors, generators, and various electromagnetic devices.
Transformers: Copper windings within transformers efficiently transfer electrical energy at different voltage levels, powering homes, industries, and grids.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs): Copper traces on PCBs carry electrical signals, forming intricate pathways within electronic devices.
2. Thermal Management:
Heat sinks: Copper's high thermal conductivity enables efficient heat dissipation from electronic components, preventing overheating and ensuring stable operation.
Heat exchangers: In various industries, copper pipes and fittings facilitate efficient heat transfer, crucial for processes like refrigeration and power generation.
Building materials: Copper roofs and cladding provide excellent thermal insulation and weather resistance, contributing to energy efficiency in buildings.
3. Construction and Infrastructure:
Plumbing systems: Copper pipes offer superior corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of installation, making them ideal for water supply and distribution.
Roofing and cladding: Copper's longevity, weather resistance, and distinctive patina enhance the aesthetics and lifespan of architectural elements.
Building hardware: Copper nails, screws, and other hardware resist corrosion and offer superior holding power in construction applications.
4. Industrial Applications:
Chemical processing: Copper's resistance to certain chemicals makes it valuable for equipment and piping in chemical plants.
Marine applications: Copper's corrosion resistance and anti-fouling properties make it suitable for boat hulls, propellers, and other marine components.
Heat exchangers: In refineries and power plants, copper heat exchangers facilitate the efficient transfer of heat in complex industrial processes.
5. Scientific and Medical Applications:
Medical equipment: Copper's antimicrobial properties make it suitable for surgical instruments, catheters, and other medical devices.
Scientific instruments: Copper components enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of scientific instruments like electromagnets and X-ray detectors.
When your project demands the exceptional properties of copper, crafted with precision and expertise, consider seeking the services of a trusted CNC machining provider like Richconn. With their advanced technology, skilled machinists, and commitment to quality, they can transform your copper concept into a tangible reality, whether it's a high-performance heat sink, a delicate architectural element, or an intricate electronic component. Don't hesitate to inquire!
 Spray painting, powder spraying, electrophoresis: three common surface treatment methodsMarch 6, 2024Spray painting is a common way of surface treatment, its principle is to use air pressure to spray paint from the nozzle, forming tiny droplets, that and evenly attached to the surface of the painted object.view
Spray painting, powder spraying, electrophoresis: three common surface treatment methodsMarch 6, 2024Spray painting is a common way of surface treatment, its principle is to use air pressure to spray paint from the nozzle, forming tiny droplets, that and evenly attached to the surface of the painted object.view Richconn 2023 Chinese New Year Holiday NoticeDecember 2, 2022November 29, 2022Chinese New Year is approaching! We would like to remind you that Richconn will be on holiday to celebrate our Chinese New Year. For your convenience in arranging your project, please...view
Richconn 2023 Chinese New Year Holiday NoticeDecember 2, 2022November 29, 2022Chinese New Year is approaching! We would like to remind you that Richconn will be on holiday to celebrate our Chinese New Year. For your convenience in arranging your project, please...view The Purpose and Importance of Metal Surface FinishApril 4, 2023Nowadays, metal surface finish technology is applied in many fields, which brings about innovation in metal surface finish and oil stain cleaning technology. Metal surface finish pretreatment is an in...view
The Purpose and Importance of Metal Surface FinishApril 4, 2023Nowadays, metal surface finish technology is applied in many fields, which brings about innovation in metal surface finish and oil stain cleaning technology. Metal surface finish pretreatment is an in...view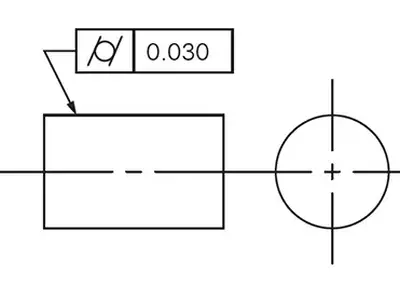 Unlocking Precision: Mastering Cylindricity for Engineering ExcellenceNovember 21, 2023In the intricate world of engineering, precision reigns supreme. Enter the realm of cylindricity - a fundamental attribute dictating the perfection of cylindrical forms. Here, I guide you through an explorative journey, unveiling the essence of cylindricity, its nuanced applications in GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing), and the crucial methods to measure and comprehend this vital parameter.view
Unlocking Precision: Mastering Cylindricity for Engineering ExcellenceNovember 21, 2023In the intricate world of engineering, precision reigns supreme. Enter the realm of cylindricity - a fundamental attribute dictating the perfection of cylindrical forms. Here, I guide you through an explorative journey, unveiling the essence of cylindricity, its nuanced applications in GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing), and the crucial methods to measure and comprehend this vital parameter.view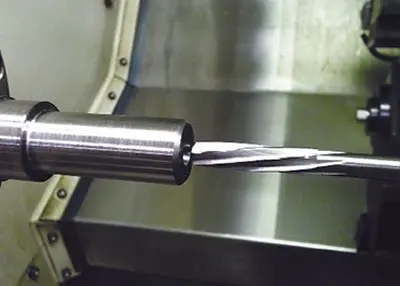 Turning Cylindrical PartsOctober 16, 2023In the past, everything was simple: round parts were turned on lathes, while non-round parts were machined on mills. With the advent of CNC machining centers that effortlessly insert round part features, the dividing line between the two machining processes became blurred.view
Turning Cylindrical PartsOctober 16, 2023In the past, everything was simple: round parts were turned on lathes, while non-round parts were machined on mills. With the advent of CNC machining centers that effortlessly insert round part features, the dividing line between the two machining processes became blurred.view What Is a CMM Machine: Components, Uses, and BenefitsMarch 15, 2024Here is a thorough introduction to CMM machines from components, uses to benefits. Let’s have a deeper look and choose the best CMM service for your projects.view
What Is a CMM Machine: Components, Uses, and BenefitsMarch 15, 2024Here is a thorough introduction to CMM machines from components, uses to benefits. Let’s have a deeper look and choose the best CMM service for your projects.view