Powder bed fusion (PBF) is a type of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, that uses a heat source, such as a laser or an electron beam, to melt and fuse material powder together to create solid parts. Unlike conventional manufacturing methods that remove material from a larger piece, PBF builds parts layer by layer from the bottom up, adding material only where it is needed. This allows for greater design freedom, material efficiency, and customization. PBF can produce parts with complex geometries, high strength, and high accuracy, making it suitable for various applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and dental.
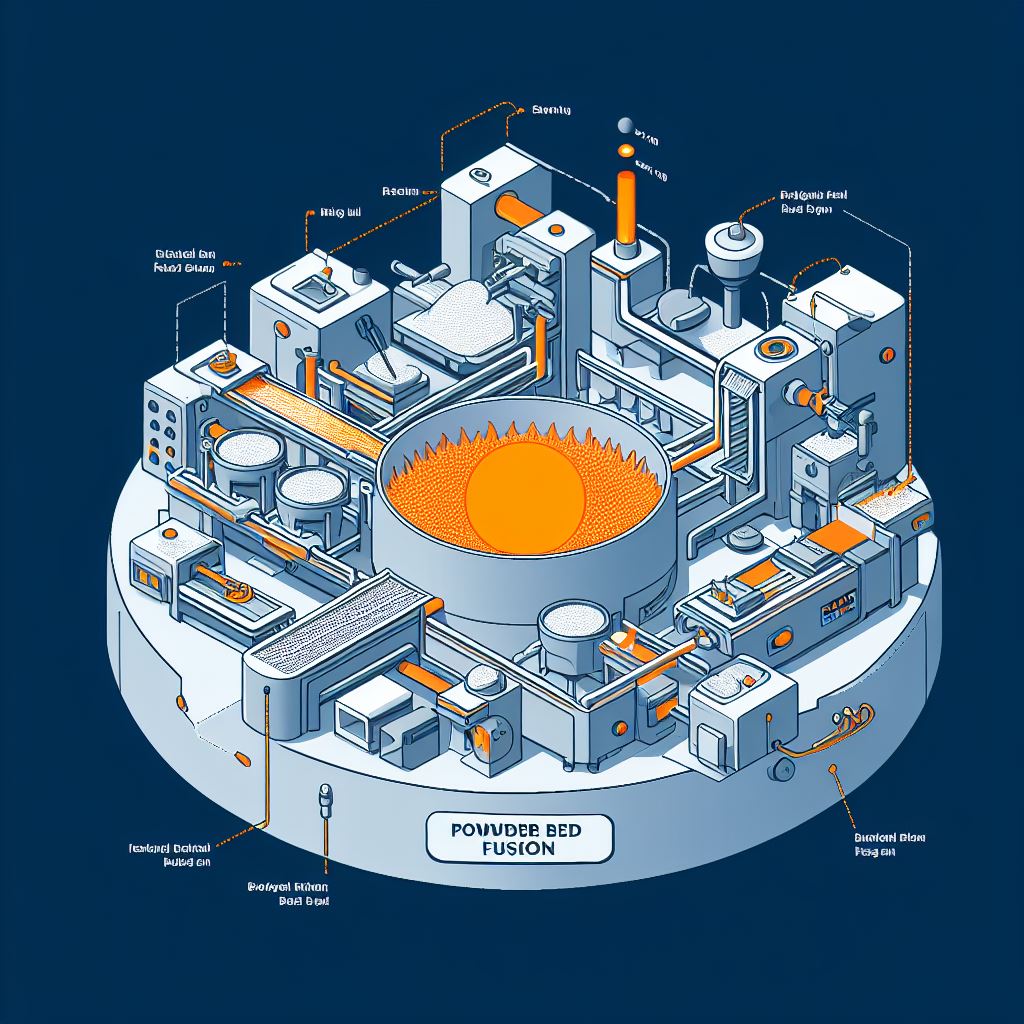
The PBF process starts with a digital 3D model of the part, which is sliced into thin layers by a software program. Each layer represents a cross-section of the part, and defines the shape and size of the material to be melted and fused. The sliced model is then sent to the PBF machine, which consists of a powder bed, a heat source, and a recoating system.
The powder bed is a platform where the part is built, and it contains a thin layer of powdered material, such as metal, plastic, or ceramic. The heat source is either a laser or an electron beam, which scans the cross-section of the part on the powder bed, melting and fusing the powder particles together. The recoating system is a mechanism that spreads a new layer of powder over the previous layer, after the heat source has completed its scan. The process is repeated until the part is finished, and the part is then removed from the powder bed and cleaned.
There are several variants of PBF, which differ in the type of heat source and the type of material used. The most common types are:
SLS uses a laser to sinter, or partially melt, powdered polymer materials, such as nylon, polyamide, or polystyrene. The sintered material forms a solid part, while the unsintered material acts as a support structure. SLS parts have good mechanical properties, but may have a rough surface finish and a porous structure. SLS is mainly used for producing functional prototypes, end-use parts, and complex shapes that are difficult to manufacture by other methods.
SLM uses a laser to fully melt powdered metal materials, such as aluminum, titanium, steel, or nickel. The melted material forms a solid part, while the unmelted material is removed. SLM parts have high strength, density, and accuracy, but may require post-processing to improve the surface finish and reduce the residual stress. SLM is mainly used for producing high-performance parts, such as aerospace components, medical implants, and dental crowns.
DMLS is similar to SLM, but it uses a lower laser power and a higher scanning speed, resulting in a partial melting of the powdered metal materials. The partially melted material forms a solid part, while the unmelted material is removed. DMLS parts have good mechanical properties, but may have a lower density and a higher porosity than SLM parts. DMLS is mainly used for producing metal parts that require a balance between strength and ductility, such as engine parts, tooling, and molds.
EBM uses an electron beam to fully melt powdered metal materials, such as titanium, cobalt-chrome, or tantalum. The electron beam has a higher energy and a larger spot size than the laser, allowing for a faster and deeper melting of the material. The process takes place in a vacuum chamber, which prevents oxidation and contamination of the material. EBM parts have high strength, density, and accuracy, but may have a rough surface finish and a coarse microstructure. is mainly used for producing parts that require high temperature and corrosion resistance, such as aerospace components, medical implants, and turbine blades.
MJF uses an inkjet array to apply fusing and detailing agents to powdered polymer materials, such as nylon or polypropylene. The fusing agent binds the material together, while the detailing agent controls the melting and cooling of the material . The agents are then activated by a heating lamp, which fuses the material into a solid part. MJF parts have good mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish, and can be produced in various colors and textures. MJF is mainly used for producing functional prototypes, end-use parts, and complex shapes that require high detail and resolution.
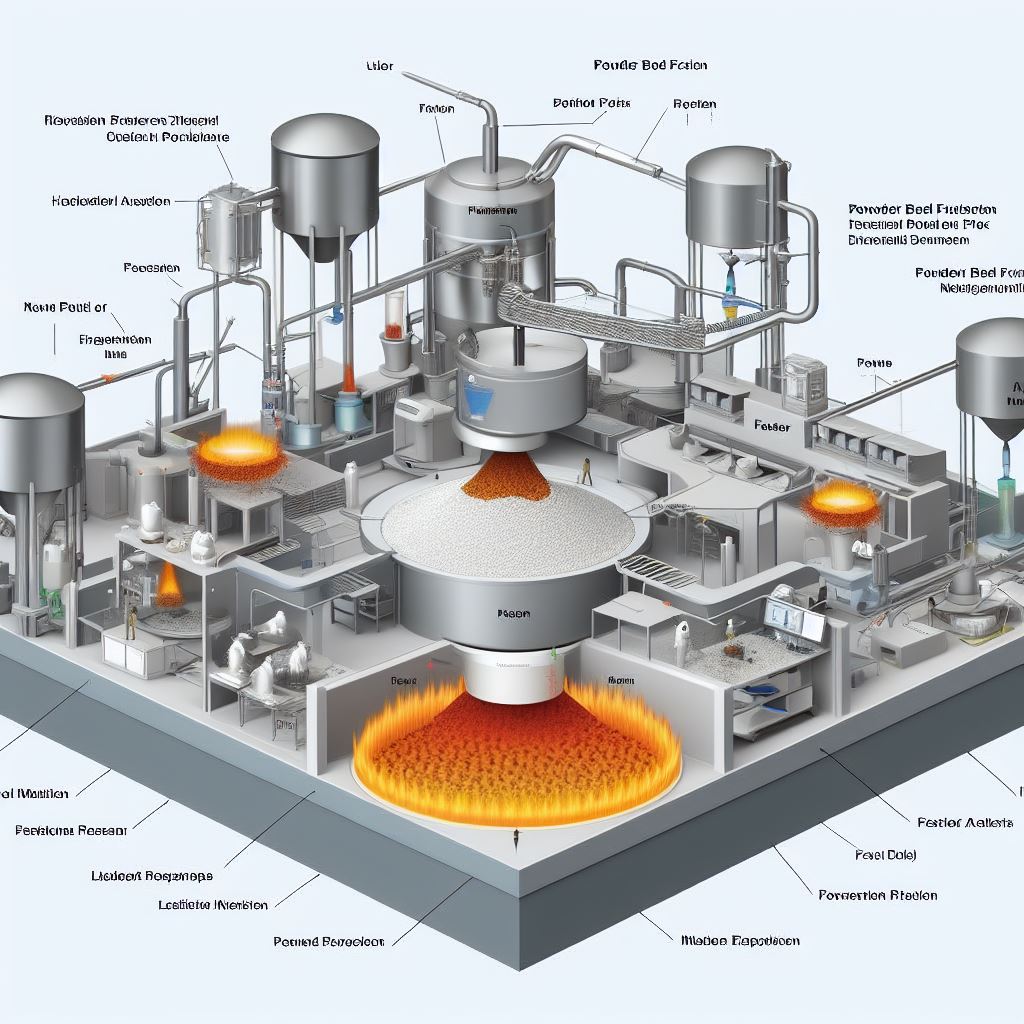
PBF offers several advantages over other manufacturing methods, such as:
• Design freedom: PBF can produce parts with complex geometries, internal features, and intricate details, that are impossible or costly to produce by other methods. PBF can also produce parts with varying material properties, such as density, porosity, or color, by controlling the heat source and the material composition.
• Material efficiency: PBF uses only the material that is needed to create the part, reducing the material waste and the environmental impact. The unused material can also be recycled and reused for future builds, further increasing the material efficiency.
• Customization: PBF can produce parts that are tailored to the specific needs and preferences of the customer, such as personalized designs, shapes, sizes, and functions. PBF can also produce parts on-demand, reducing the inventory and the lead time.
However, PBF also has some disadvantages, such as:
• Cost: PBF machines are expensive to purchase and operate, as they require high power, maintenance, and skilled operators. The material cost is also high, especially for metal powders, which are scarce and difficult to produce. The post-processing cost may also be significant, as some parts may require additional steps, such as heat treatment, surface finishing, or support removal.
• Quality: PBF parts may suffer from some quality issues, such as distortion, cracking, porosity, or surface roughness, due to the high temperature gradients, residual stress, and thermal cycling involved in the process. The quality may also vary depending on the machine parameters, the material properties, and the part geometry, requiring careful optimization and calibration.
• Safety: PBF involves high temperatures, high voltages, and high-energy beams, which pose potential hazards to the operators and the environment. The material powders may also be flammable, explosive, or toxic, requiring proper handling, storage, and disposal.
Powder bed fusion is a type of additive manufacturing that uses a heat source to melt and fuse material powder together to create solid parts. PBF can produce parts with complex geometries, high strength, and high accuracy, making it suitable for various applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and dental. PBF has several variants, such as SLS, SLM, DMLS, EBM, and MJF, which differ in the type of heat source and the type of material used. PBF offers several advantages over other manufacturing methods, such as design freedom, material efficiency, and customization, but also has some disadvantages, such as cost, quality, and safety.
If you are looking for a reliable and professional service for your powder bed fusion needs, I recommend you to check out Richconn's 3D printing service. Richconn is a leading company that offers high-quality and cost-effective 3D printing solutions for various materials, including metal, plastic, and ceramic. Richconn has a team of experienced and skilled engineers and technicians who can handle any design and specification you may have. Richconn also has a fast turnaround time and a strict quality control system that ensures your satisfaction and success. To To learn more about Richconn's 3D printing service, please visit their website or contact them today.
 The Top 7 CAD/CAM Software for CNC ProjectsMarch 18, 2024CAD/CAM software for CNC projects is a specialized tool used to design and control the machining of parts. Here are the top 7 CAD/CAM software for your choice.view
The Top 7 CAD/CAM Software for CNC ProjectsMarch 18, 2024CAD/CAM software for CNC projects is a specialized tool used to design and control the machining of parts. Here are the top 7 CAD/CAM software for your choice.view Aerospace CNC Machining: A Comprehensive GuideNovember 6, 2023Aerospace CNC machining plays a pivotal role in the aviation and aerospace industry. It's the technology that enables the precision manufacturing of critical components. In this guide, I'll walk you through the importance, applications, key steps, material and process selection, quality standards, and the process of finding a reliable aerospace CNC machining service, with a special recommendation for Richconn's services.view
Aerospace CNC Machining: A Comprehensive GuideNovember 6, 2023Aerospace CNC machining plays a pivotal role in the aviation and aerospace industry. It's the technology that enables the precision manufacturing of critical components. In this guide, I'll walk you through the importance, applications, key steps, material and process selection, quality standards, and the process of finding a reliable aerospace CNC machining service, with a special recommendation for Richconn's services.view What is a CNC machine? The Precision Way to Modern ManufacturingSeptember 21, 2023CNC machine stands for Computer Numerical Control, which is a manufacturing process that controls the movement of a tool or machine through a computer program.view
What is a CNC machine? The Precision Way to Modern ManufacturingSeptember 21, 2023CNC machine stands for Computer Numerical Control, which is a manufacturing process that controls the movement of a tool or machine through a computer program.view Choosing the Optimal Material For CNC Machining.October 17, 2023If you find the vast selection of different materials for CNC machining confusing, this blog will tell you how to reduce that number to a manageable level.
Choosing the right material for CNC machining can make all the difference in getting a working part or prototype made at a reasonable price.view
Choosing the Optimal Material For CNC Machining.October 17, 2023If you find the vast selection of different materials for CNC machining confusing, this blog will tell you how to reduce that number to a manageable level.
Choosing the right material for CNC machining can make all the difference in getting a working part or prototype made at a reasonable price.view Brass vs Bronze or Brass vs Copper: Which Is Better for Your Project?October 7, 2023This article introduces the difference between brass and bronze and copper, which can help you and your project find the right choice of these metals.view
Brass vs Bronze or Brass vs Copper: Which Is Better for Your Project?October 7, 2023This article introduces the difference between brass and bronze and copper, which can help you and your project find the right choice of these metals.view Unveiling the Power of Galvanized Materials: Your Ultimate GuideSeptember 28, 2023Have you ever wondered about the remarkable process that transforms ordinary steel into a corrosion-resistant wonder material? Look no further, as we embark on an enlightening journey to understand the world of galvanization.view
Unveiling the Power of Galvanized Materials: Your Ultimate GuideSeptember 28, 2023Have you ever wondered about the remarkable process that transforms ordinary steel into a corrosion-resistant wonder material? Look no further, as we embark on an enlightening journey to understand the world of galvanization.view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru