In this era of rapid change, mechanical equipment is developing rapidly, the degree of automation and intelligence in production is continuously improving, and the performance indicators of mechanical parts are also facing increasingly higher requirements. As an indispensable and important component of mechanical equipment, the performance of roller products directly affects the operating efficiency and product quality of the entire machine. Taking the paper machine as an example, roller products are used for conveying raw materials, compressing and forming, guiding operations, etc. Their strength, uniformity and durability are crucial to the quality of paper. In a device or component, roller products often account for a relatively high proportion of the cost compared to other parts due to their special purpose and quantity.
When your production is in trouble and you urgently need high-performance roller products to ensure the normal operation of the paper machine and keep the production chain unblocked, you need to take a look at this article - the roller products introduced here can fully meet your personalized needs. We have advanced centrifugal casting production lines and machining equipment to help achieve lightweight and high strength. At the same time, we closely follow the industry development dynamics, continue to develop new products, improve performance and realize personalized customization. The roller products we produce are suitable for various working conditions. The main types are: transmission roller, guide roller, press roller, embossing roller, etc. The common materials are alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, rubber, polyurethane, etc. We provide rubber roller grinding, roller plating, roller welding and other services. At the same time, we have a strong design and manufacturing team, which can provide solutions and customized services for non-standard roller products.
Our products have been widely used in paper-making, printing, textile, plastic, cable, and other industries. We look forward to cooperating with you to provide high-quality and efficient roller solutions and services. If you have any needs, please feel free to contact us.
There are many types of roller products, widely used, and they are indispensable key components of mechanical equipment. Here is a comprehensive interpretation of the classification, characteristics, functions and applications of roller products. After reading the following passage, you will have a simple understanding of "what are roller products".
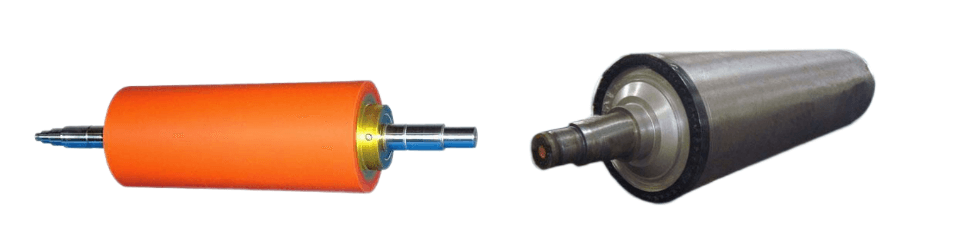
<Picture: Rubber roller and metal roller>
Rubber rollers have certain elasticity and are mainly used for medium and low speed transmission. Metal rollers have high hardness and are used for high speed transmission.
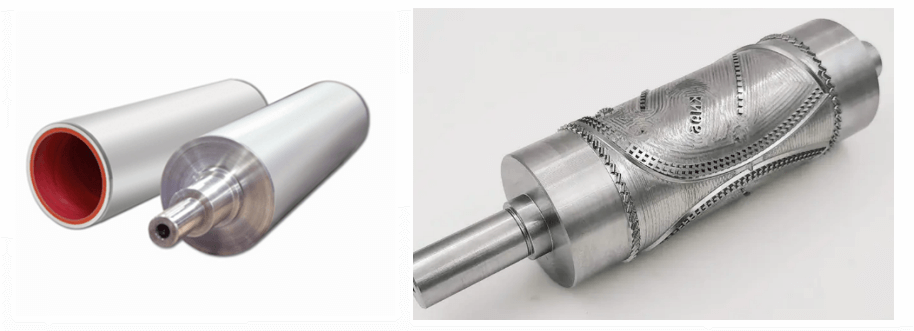
<Picture: Smooth embossing roller and patterned embossing roller>
The smooth embossing roller produces flat embossing, and the patterned embossing roller can produce various patterned embossing.
Idle rollers achieve high speed or slow conveying; embossing rollers press out specific shapes on the material surface; deflection rollers change the material conveying direction; support rollers provide support.
The driving roller and the driven roller achieve the transmission of power and motion through mutual meshing or friction, and the surface of the driven roller cooperates with the nip to drive the material motion. The driving roller drives the driven roller to rotate at high speed. The two rollers are supported by bearings but also allow a certain relative motion. The outer surface of the driven roller is mechanically processed or molded into a smooth, concave-convex patterned or toothed shape to produce conveying, embossing or pulling effects.
Conveying systems of paper making machines and printing presses; filament orientation of textile machines; orientation and embossing of packaging machinery; transmission systems of rubber machinery, etc., are widely used in machinery and electronics industries. The performance selection of roller products directly affects machine efficiency and product quality. Gaining an in-depth understanding of different types, characteristics and functions of rollers helps optimize production processes and improve product quality.
The above briefly introduced some information about rollers. More detailed introductions will follow. We hope that through our analysis, we can help you properly select and use roller products.
Roller products are classified in depth from five angles to help customers quickly understand and choose suitable products:
a. Idler roller: used for conveying and transmission to achieve high-speed or slow conveying function.
b. Pressure roller: used to emboss patterns or press shapes on the material surface to achieve embossing function.
c. Deflection roller: used to change the conveying direction of the material to achieve deflection function.
d. Counterweight roller: provides pressure to strengthen embossing and achieve pressure providing function.
a. Rubber roller: elastic, used for medium and low speed transmission, rubber types include silicone, acrylic rubber, nitrile rubber, etc.
b. Metal roller: high hardness, used for high speed transmission, metals mainly include cast iron, forged steel, etc.
c. Silver roller: with electroplated silver layer, used for food grade transmission, the base material is mainly 304 stainless steel.
d. Ceramic roller: smooth surface, high temperature resistant, used for high temperature conveying.
e. Polyethylene roller: chemically stable, low density, used for light low speed conveying.
a. Smooth roller: smooth surface without pattern.
b. Patterned roller: surface with certain patterns such as rough surface, corrugated surface, etc.
c. Embossing roller: surface with irregular embossing die which can press out different shapes.
a. Micro roller: diameter less than 50mm, used for conveying and guiding small structures.
b. Small roller: diameter 50-200mm, used for conveying small materials.
c. Medium roller: diameter 200-500mm, commonly used in flexible packaging machinery.
d. Large roller: diameter over 500mm, used for conveying and embossing large materials.
a. Hollow roller: used for light transmission, small shaft diameter.
b. Solid roller: large shaft diameter, used for heavy duty transmission and high speed transmission.
c. Adjustable center roller: adjustable center shaft structure used for precisely adjusting tension.
d. Inlaid roller: shaft embedded inside roller shell, shaft end exposed.
e. Welded roller: shaft and roller shell are connected by welding.
f. Combined roller: shaft is segmented for easy transportation and installation.
In summary, this briefly introduced some classification information to help you quickly understand the product types and characteristics and choose the optimal product according to the specific application.
1. Hollow structure: The inside of the roller shell is a hollow structure, and both ends are closed with end caps. The hollow shaft has a smaller diameter, generally used for light load and low speed occasions, lower cost but also lower strength.
2. Solid structure: The inside of the roller shell is filled with a solid shaft of the same material as the shell. The solid shaft has a larger diameter, has higher strength and rigidity, used for medium-high speed and heavy load working conditions.
3. Adjustable structure: The inside of the roller shell is a hollow structure, but adjustable devices are installed at both ends. By adjusting the adjustable devices, the center distance of the roller shaft can be accurately adjusted. It is mainly used in occasions where there are high requirements for tension, such as expansion rollers.
4. Shaft structure: Shaft pads are connected at both ends, and the shaft is connected through the shaft pads. The shaft can be easily disassembled and assembled, mainly used in occasions where the shaft needs to be frequently disassembled and assembled, but the axial positioning accuracy is poor.
5. Roller bearing structure: Roller bearings are installed at both ends, the shaft pads are connected to the shaft, the roller shell is supported by bearings, the shaft can be easily disassembled and assembled, while ensuring higher axial accuracy and stability, commonly used in high speed occasions.
6. Sliding bearing structure: Sliding bearings are installed at both ends, the shaft pads are connected to the shaft, the roller shell is supported by bearings, which can reduce the axial space of the bearings to a certain extent, but the accuracy is lower than that of roller bearings, used for medium and low speed occasions.
7. Inserted shaft structure: The roller shell has shaft pads at both ends, and the shaft is directly inserted into the shaft pads, simple and convenient, but the axial positioning accuracy is poor, only suitable for ordinary low-requirement occasions.
8. Integral structure: The roller shell and shaft are integrally manufactured, the structure is simple and compact, but the shaft cannot be disassembled, only suitable for occasions where disassembly of the shaft is not required and the bearing space is large. In summary, different structure forms can be selected according to different use conditions to obtain better working performance. At the same time, the structural design is also related to the service life of roller products.
The commonly used materials for roller products mainly include:
1. Rubber materials:
Silicone rubber: resistant to high temperature and abrasion, Shore hardness HRC70-90, used for high-speed heavy-duty transmission.
Acrylic rubber: good elasticity, resistant to chemicals, Shore hardness HRC60-90, medium speed transmission.
Nitrile rubber: oil and high temperature resistant, Shore hardness HRC70-95, high speed transmission.
Natural rubber: most elastic, Shore hardness HRC40-70, low speed light load transmission.
2. Metal materials:
Cast iron: poor toughness, hardness HB180-300, heavy load low speed occasions.
10# forged steel: hardness HB230-320, high strength, medium and high speed transmission.
20MnCr5 steel: hardness HB300-380, high strength, high speed and heavy duty occasions.
40Cr steel: hardness HB360-440, high strength and high hardness, high speed and high temperature occasions.
Aluminum alloy: such as 6061, 6063 series, density is only 2.7g/cm3, 1/3 of steel, so using aluminum alloy material can greatly reduce the weight of the roller.
Steel: ordinary carbon steel or alloy steel, density about 7.8g/cm
Rollers that need to withstand large loads will usually choose steel.
3. Stainless steel materials:
304 stainless steel: good corrosion resistance, hardness HB190-240, food grade transmission.
316L stainless steel: corrosion resistant, hardness HB190-235, acid-resistant food grade transmission.
4.Silver alloy plating layer:
Silver/stainless steel: the silver surface layer has antimicrobial properties, the base material is 304 or 316L stainless steel, food grade transmission.
Silver/carbon steel: the silver surface layer has antimicrobial properties, the base material is 45# or 50# carbon steel, food grade medium and low speed transmission.
5. Ceramic materials:
Silicon nitride ceramic: high temperature, acid, alkali and wear resistant, hardness HRA88-93, used for high temperature and corrosion applications.
Alumina ceramic: high temperature and wear resistant, hardness HRA88-92, used for high temperature transmission.
The above are the main materials and their characteristics commonly used for roller products. Suitable materials can be selected to manufacture roller products according to working conditions.
Here are some special materials used in roller products:
1. Titanium alloy: density 4.5g/cm3, high strength, corrosion resistant, but high cost. Used for lightweight rollers in special occasions.
2. Composite materials: such as aluminum-based composite materials, composed of an aluminum-based matrix and a reinforcing phase (usually SiC particles), density 3-3.7g/cm3, high strength, used for high-speed lightweight rollers. Therefore, overall, if weight is an important design consideration, aluminum alloy is a better lightweight material choice.
3. Aluminum-based composite materials:
Al-SiC: aluminum matrix reinforced with SiC particles, density 3-3.7g/cm3, high strength. Such as 6061/SiC, 7075/SiC, etc.
Al-C: aluminum matrix reinforced with carbon fibers, density 2.6-2.9g/cm3, high strength and rigidity. Such as 6061/C, 7075/C, etc.
Al-B4C: aluminum matrix reinforced with tungsten boride particles, good high temperature performance and wear resistance.
4. Magnesium-based composite materials:
Mg-C: magnesium matrix reinforced with carbon fibers, density 1.8g/cm3, high strength, can be used for high-speed lightweight rollers.
Mg-SiC: magnesium matrix reinforced with SiC particles, density 2.2g/cm3.
5. Titanium-based composite materials: Ti-6Al-4V reinforcing phase is SiC, density 4.4g/cm3, high strength and toughness, corrosion resistant. Used for marine lightweight rollers.
6. Zirconium-based composite materials: Zr-2.5Nb reinforcing phase is SiC, density 5.6g/cm3, suitable for nuclear power lightweight rollers. In summary, the most widely used lightweight roller composite materials are aluminum-based composite materials, and carbon fiber reinforced aluminum-based composite materials are currently the best performing options. But the cost is relatively high, mainly used for high-speed rolling mill rolls and other occasions with higher requirements.
7. But strength and cost factors also need to be considered, and suitable materials should be selected according to specific working conditions.
Hope the above information is helpful. If you have any other questions, please feel free to ask.
The main surface treatment methods for roller products include:
1. Electroplating: is the electrodeposition of a layer of metal or alloy thin film on the surface of the roller body. Common ones include:
Silver plating: has antibacterial and corrosion resistance effects, used for food grade transmission rollers.
Chrome plating: has corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance effects, used for general transmission rollers.
Nickel plating: similar to chrome plating, slightly worse corrosion resistance.
2. Electro-spark doping: Melting a layer of the roller body surface by electric spark to improve the surface quality, mainly to:
Remove surface defects and oxide films, improve surface quality, Ra up to 0.2μm.
Increase surface hardness, hardened layer depth 0.2-0.5mm, hardness HV800-1000.
Improve wear resistance, can increase 3-8 times.
3. Wire spraying: High-pressure spraying wire material (usually stainless steel wire) onto the roller body surface to improve surface quality, to:
Increase surface hardness, hardened layer depth 0.1-0.3mm, hardness HV550-650.
Increase surface roughness, Ra about 1.6-3.2μm, enhance gripping.
Increase wear resistance, can increase 2-5 times.
4. Diffusion hardening: Forming a hardened layer of a certain depth on the surface of the roller body. Commonly used are:
Nitriding treatment: can obtain a hardened layer of 0.3-0.8mm, hardness HV800-1200, wear resistance increased more than 10 times.
High frequency induction hardening: can obtain a hardened layer of 0.5-3mm, hardness HV500-650, wear resistance increased 3-8 times. Cyaniding: can obtain a hardened layer of 0.2-0.8mm, hardness HV700-1000, wear resistance increased 5-10 times.
Surface treatment can significantly improve the performance of roller products and prolong service life. We can provide electroplating, nitriding, high-frequency induction hardening, spraying and other surface treatment services according to customer needs. Please contact us for more details.
Surface carburizing: Carburizing is a kind of surface strengthening treatment. It diffuses carbon atoms on the surface or below the surface of steel to increase surface hardness and wear resistance. Carburizing can increase the surface hardness of roller products to:
HRC60-67: Low carburizing or selective carburizing, carburizing depth about 0.5-1mm, mainly to increase surface hardness and wear resistance.
HRC50-58: Medium carburizing, carburizing depth 1-3mm, both increasing surface hardness and strengthening quenched and tempered zone, with better overall performance.
HRC42-48: Deep carburizing, carburizing depth over 3mm, although the surface hardness decreases, the quenched and tempered zone is strengthened, suitable for heavy load transmission.
Generally speaking, the deeper the carburizing depth, the higher the surface hardness, but the hardness gradually decreases below the surface. Carburizing treatment requires the selection of appropriate carburizing temperature and holding time. Commonly used processes are:
Gas carburizing: Using high-temperature gas medium (usually a mixture of propane and butane gas) for carburizing at 900-1000°C, processing period 6-72 hours.
Liquid carburizing: Using liquid medium (molten salt mixture of sodium carbide and potassium) for carburizing at 850-950°C, processing period 2-6 hours.
Solid carburizing: Using powdered activated carbon for carburizing at 925-980°C, processing period 10-24 hours.
Quenching after carburizing: High temperature quenching (800-860°C) after carburizing to quickly increase surface hardness (about HRC60), then low temperature tempering (150-300°C) to reduce residual internal stress. • Chrome molybdenum carburizing: hardened layer 0.5-2mm, hardness HRC58-62, wear resistance increased 5-15 times. • Directional solidification: hardened layer 0.3-3mm thick obtained by directional solidification, hardness HV900-1500, extremely high wear resistance.
Plating or spraying composite coatings: Coating special coatings on the roller body surface to achieve corrosion resistance, wear resistance, anti-sticking and other properties. The above are the common surface treatment methods and characteristics of roller products. Suitable surface treatment techniques can be selected according to working conditions.
5. Ceramic coating:
Ceramic materials have extremely high hardness, high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. Spraying ceramic coatings can significantly improve the hardness and service life of roller products.
Commonly used ceramic coating materials include:
Silicon nitride ceramics: Silicon nitride is an excellent high temperature ceramic material with high temperature resistance (working temperature up to 1000°C or higher), corrosion resistance and wear resistance. The hardness can reach HRA88-93. After spraying silicon nitride ceramic coating, the hardness and service life of roller products can be increased 3-5 times.
Alumina ceramics: Alumina ceramics are also excellent high temperature ceramics with extreme hardness (HRA88-92) and high temperature resistance (working temperature above 900°C). After spraying, the hardness and service life of roller products can be significantly improved (3-4 times).
Silicon carbide ceramics: Silicon carbide ceramics not only have extremely high hardness (above HRA90) and good mechanical strength, but also excellent high temperature resistance (working temperature up to 1200°C) and corrosion resistance. The sprayed layer can increase the hardness of roller products by more than 5 times and the service life by 4-6 times.
The main process flow of ceramic coating spraying is:
Surface pretreatment of roller body: polishing, dust removal, chemical cleaning to enhance adhesion.
Spray ceramic coating: use plasma spraying or high velocity flame spraying to spray ceramic powder on the pretreated roller body surface to form a 0.3-3mm thick ceramic coating.
Heat treatment: sintering and vitrification to enhance the densification and hardness of the ceramic coating.
Machining: polishing and grinding the surface of the ceramic coating to achieve the desired smoothness and accuracy.
In summary, the technology of ceramic coating spraying is a very effective surface strengthening method, which can greatly improve the hardness, high temperature resistance and service life of roller products. It is very suitable for roller products working under high speed, heavy load and high temperature conditions.
The common processing techniques for roller products mainly include:
1. Rolling: Heat the steel ingot to the appropriate temperature and roll it into a roller shell through the rolling mill. It has high density and mechanical properties, often used for large heavy-duty roller products. The rolling precision is generally IT7-IT8.
2. Casting: The molten steel is poured and cooled in the mold to form. Used for small and medium-sized roller products, the casting precision IT9-IT12 is poor.
3. Forging: Heat the steel ingot and forge it into shape with a forging press. Higher density and mechanical properties but slower forming speed, used for small and medium-sized high-strength roller products. Forging precision is IT7-IT10.
4. Machining: Use CNC lathes, grinding machines and other machine tools to process steel into shape. High precision up to IT5 or above, but poor metallic properties and low production efficiency, only suitable for small batch production.
5. Welding: Assemble multiple steel plates or forgings into shape by welding, used for ultra-large roller products, but the weld joint will produce anisotropy and residual stress, low precision.
6. Heat treatment: Heat treat the roller shell by annealing, quenching and tempering to obtain the corresponding structure and properties. The quenching hardness is usually HRC40-65, mainly to improve wear resistance and service life.
7. Precision machining: Precision machining the roller shell by grinding, polishing, welding joint finishing, etc. to improve its surface quality and precision. Ordinary precision machining precision can reach IT7, high precision machining precision can reach IT4-IT6.
8. Dynamic balance: Perform dynamic balance detection and finishing on high-speed roller products to reduce vibration and noise during rotation and improve operational stability.
9. Surface treatment: Implement various surface treatments on the roller shell, such as electroplating, chemical oxidation, anodizing, and spraying technology, to obtain the corresponding surface properties such as hardness, wear resistance and corrosion resistance. In summary, according to the requirements of different roller products, one or more of the above processes can be adopted to obtain the desired mechanical properties and surface properties to meet the actual usage requirements. At the same time, the fineness of the process flow also determines the high or low quality of roller products.
1. Rolling rollers: Used for various rolling production lines such as sheet rolling mills, tube rolling mills, forging rolling mills, etc., to transmit and reduce high power. They have high requirements for precision and dynamic balance.
2. Transmission rollers: Used for various transmission equipment such as conveyors, roller kilns, printing presses, etc. to continuously transmit belts or materials. They have certain requirements for surface quality.
3. Press rollers: Used for various calendering production lines such as paper machines to squeeze and control the thickness of materials. They have high requirements for spindle parallelism.
4. Guide rollers: Used for various conveyors and production lines to turn and correct belts or materials. They have high requirements for axial tolerance.
5. Expansion rollers: Used for printing presses, spray lines, etc. The internal expansion system controls slight axial changes to control tension or other parameters. They have high requirements for structure and control systems.
6. Isolation rollers: Used for various printing presses, coating lines, etc. to support and isolate belts. Reduce mutual interference. They have high requirements for axial positioning accuracy.
7. Orientation rollers: Used for various production lines to orient and turn belts. They have high requirements for surface gripping and axial positioning accuracy.
8. Support rollers: Used for various conveyors and mechanical equipment to support belts or other parts. They have certain requirements for axial tolerance.
9. Elastic rollers: Contain elastic elements internally to play a shock absorption role, often used in high-speed occasions or transmission equipment for conveying fragile materials. They have high requirements for structural design.
10. Anode rollers: The surface has an anodic oxide coating, used for rolling profiles, etc., to prevent sticking and hardening. They have high requirements for surface treatment.
In addition to the above roles, roller products also have drive rollers, iche rollers, tapered rollers, expansion rollers, etc. They are widely used in various industries and are indispensable important parts of mechanical transmission.
Q1: Roller products are basic components widely used in mechanical equipment and transmission systems, mainly including various rollers, bearings, clamps, etc., serving as support, steering, transmission, etc. Common roller products include conveyor rollers, support rollers, press rollers, guide rollers, etc.
Q2: Common materials for roller products include:
Carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel and other steel materials for general working conditions;
High chromium steel, steel backing composite materials, rubber and other wear-resistant materials for high-speed or heavy-duty wear-resistant products;
Plastic wheels, PVC, centrifugal cast iron and other non-metallic materials for special requirements such as wear resistance, noise reduction, conductivity, etc.
Q3: Common surface treatment processes for roller products include:
Spraying and powder coating: spraying different coatings to meet appearance or usage requirements;
Electroplating: chromium plating, nickel plating, etc., to improve surface hardness and corrosion resistance;
Heat treatment: surface quenching, surface hardening, etc., to improve surface hardness and wear resistance;
Polishing: mechanical polishing or polishing the surface to improve surface roughness and appearance;
Anodizing: forming an oxide film on the surface to improve appearance and corrosion resistance, etc.
Q4: Please refer to the above content: Packaging and Transportation.
Q5: The IP rating indicates the protection level of the product. For roller products, it is related to the requirements for dust and water protection. A higher IP rating indicates greater protection against environmental factors. Roller products choose the appropriate IP rating according to the severity of the operating environment, and choose the corresponding dust and water packaging to meet the product requirements in that environment.
1. Rolling rollers: Used for various rolling production lines such as sheet rolling mills, tube rolling mills, forging rolling mills, etc., to transmit and reduce high power. They have high requirements for precision and dynamic balance.
2. Transmission rollers: Used for various transmission equipment such as conveyors, roller kilns, printing presses, etc. to continuously transmit belts or materials. They have certain requirements for surface quality.
3. Press rollers: Used for various calendering production lines such as paper machines to squeeze and control the thickness of materials. They have high requirements for spindle parallelism.
4. Guide rollers: Used for various conveyors and production lines to turn and correct belts or materials. They have high requirements for axial tolerance.
5. Expansion rollers: Used for printing presses, spray lines, etc. The internal expansion system controls slight axial changes to control tension or other parameters. They have high requirements for structure and control systems.
6. Isolation rollers: Used for various printing presses, coating lines, etc. to support and isolate belts. Reduce mutual interference. They have high requirements for axial positioning accuracy.
7. Orientation rollers: Used for various production lines to orient and turn belts. They have high requirements for surface gripping and axial positioning accuracy.
8. Support rollers: Used for various conveyors and mechanical equipment to support belts or other parts. They have certain requirements for axial tolerance.
9. Elastic rollers: Contain elastic elements internally to play a shock absorption role, often used in high-speed occasions or transmission equipment for conveying fragile materials. They have high requirements for structural design.
10. Anode rollers: The surface has an anodic oxide coating, used for rolling profiles, etc., to prevent sticking and hardening. They have high requirements for surface treatment. In addition to the above roles, roller products also have drive rollers, iche rollers, tapered rollers, expansion rollers, etc. They are widely used in various industries and are indispensable important parts of mechanical transmission.
We are a professional company engaged in the research and development and production of roller products for nearly 20 years. Over the past 20 years, we have always adhered to the tenet of "quality first and customer first", continuously developed new products, improved production processes, and improved product performance. From material selection and cutting to precision machining and strict surface treatment, each process is carefully designed and strictly controlled. We provide a wide range of roller products with complete specifications, covering mining machinery, metallurgical equipment, conveying machinery, food machinery, medical equipment and other industries.
Over the years, we have accumulated rich technical experience and extensive customer resources. We are not only familiar with the detailed technical specifications of roller products in various industries, but also can provide personalized design and customization according to the specific use environment and conditions of customers. Our products are sold well at home and abroad and are well recognized and trusted by customers. In the new century, new opportunities and new challenges. We will continue to commit to the research and development and innovation of roller products, continuously improve product performance and quality, and provide customers with higher quality products and more thoughtful services. We believe that with strong technical strength and rich industry experience, we can bring greater value and new surprises to our customers!
 Custom Machined Metal Parts: Precision at Your FingertipsNovember 9, 2023Do you crave perfection in your machinery? Are you seeking the ideal metal components for your projects? You've come to the right place! Welcome to Richconn, your reliable partner for custom machined metal parts. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the world of precision engineering, from understanding the basics to choosing the right materials, processes, and designs.view
Custom Machined Metal Parts: Precision at Your FingertipsNovember 9, 2023Do you crave perfection in your machinery? Are you seeking the ideal metal components for your projects? You've come to the right place! Welcome to Richconn, your reliable partner for custom machined metal parts. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the world of precision engineering, from understanding the basics to choosing the right materials, processes, and designs.view What Is Mechanical Rack: Picking the Best for Your Custom PartsMay 22, 2024Delve into the world of equipment racks with this comprehensive article. Learn about their structure, design principles, materials, manufacturing processes, installation, commissioning, and more.view
What Is Mechanical Rack: Picking the Best for Your Custom PartsMay 22, 2024Delve into the world of equipment racks with this comprehensive article. Learn about their structure, design principles, materials, manufacturing processes, installation, commissioning, and more.view Experience Sharing on Design and Manufacturing of Metal Stamping DiesJuly 21, 2023Here, we will share some specific design and manufacturing experiences to provide our understanding of dies accumulated over the years. Through this article, we hope to give you a better understanding...view
Experience Sharing on Design and Manufacturing of Metal Stamping DiesJuly 21, 2023Here, we will share some specific design and manufacturing experiences to provide our understanding of dies accumulated over the years. Through this article, we hope to give you a better understanding...view The Beginner's Guide to the 3D Printing ProcessMay 5, 2024This article explains what 3D printing is, the materials it uses, its advantages, processes and techniques, applications, and more. Read on and get the best custom 3D printing services.view
The Beginner's Guide to the 3D Printing ProcessMay 5, 2024This article explains what 3D printing is, the materials it uses, its advantages, processes and techniques, applications, and more. Read on and get the best custom 3D printing services.view Machining on a Dime: Creating High-Quality Products with Cheap CNC MaterialsDecember 4, 2023In today's fast-paced world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to reduce costs without compromising on quality. This is particularly true for manufacturers who heavily rely on CNC machining t...view
Machining on a Dime: Creating High-Quality Products with Cheap CNC MaterialsDecember 4, 2023In today's fast-paced world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to reduce costs without compromising on quality. This is particularly true for manufacturers who heavily rely on CNC machining t...view In-depth Understanding of Five-axis CNC Service ProcessingOctober 24, 2022When it comes to cnc machining services, you will definitely think of 5-axis CNC machining. Choosing the right machining solution will lead to a successful production. CNC machining is a procedure use...view
In-depth Understanding of Five-axis CNC Service ProcessingOctober 24, 2022When it comes to cnc machining services, you will definitely think of 5-axis CNC machining. Choosing the right machining solution will lead to a successful production. CNC machining is a procedure use...view