Have you ever wondered how your laptop, smartphone, or gaming console can run so fast without overheating? The answer is heat sinks. Heat sinks are devices that help to cool down electronic components by transferring heat away from them. They are essential for ensuring the reliability and performance of many modern devices.
To understand how heat sinks work, we need to first understand the basic concept of heat transfer and thermal resistance. Heat transfer is the process of moving heat from a hotter object to a colder object. Thermal resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for heat to flow through a material or a system. The lower the thermal resistance, the easier it is for heat to flow.
Heat sinks work by increasing the surface area and enhancing the heat dissipation of electronic components. They are usually made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metals or ceramics, which can transfer heat efficiently. They also have fins or pins that extend from the base, which create more contact with the surrounding air or liquid. This way, heat sinks can reduce the temperature difference and the thermal resistance between the electronic component and the environment.
There are three main modes of heat transfer that heat sinks can use: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the direct transfer of heat through physical contact. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of fluids, such as air or water. Radiation is the transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves, such as infrared or visible light. Heat sinks can use one or more of these modes depending on the design and the application.
There are two main categories of heat sinks: passive and active.
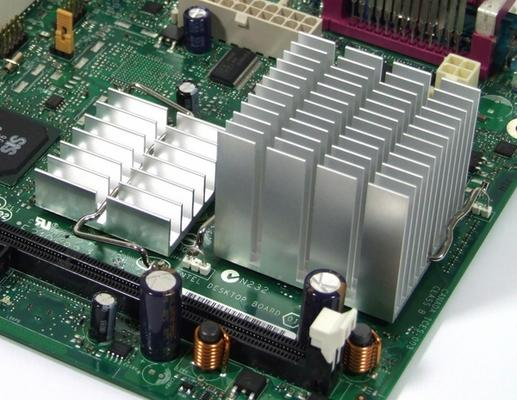

Passive heat sinks do not have any moving parts or external power sources. They rely on natural convection and radiation to dissipate heat.
Passive heat sinks are simpler, cheaper, and more reliable than active heat sinks. They are suitable for applications that do not generate too much heat or have limited space or power availability. However, passive heat sinks have lower cooling capacity and efficiency than active heat sinks. They can also suffer from thermal runaway, which is a condition where the heat sink temperature rises uncontrollably due to insufficient heat dissipation.
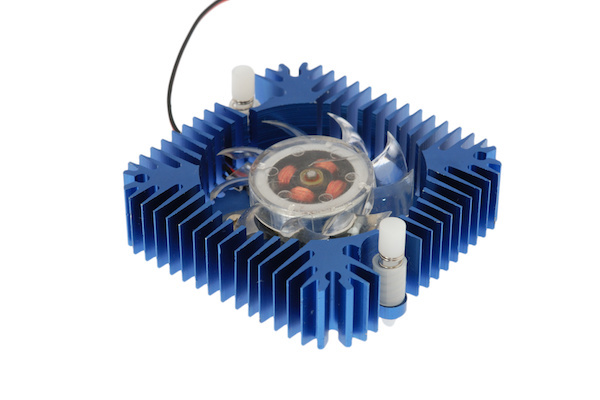
Active heat sinks have fans, pumps, or other devices that enhance the airflow or liquid flow around the heat sink. They require external power sources and can generate more noise and vibration.
Active heat sinks are more complex, expensive, and less reliable than passive heat sinks. They are suitable for applications that generate a lot of heat or have high performance or reliability requirements. Active heat sinks can provide better cooling performance and control than passive heat sinks. They can also prevent thermal runaway by adjusting the fan speed or pump flow according to the heat load.
Some examples of passive and active heat sinks are:
Passive heat sinks: aluminum or copper fins, heat pipes, thermoelectric coolers, etc.
Active heat sinks: fan-cooled heat sinks, liquid-cooled heat sinks, phase-change heat sinks, etc.
The design of a heat sink depends on many factors, such as the heat source, the environment, the material, the shape, the size, the orientation, etc. The goal of heat sink design is to optimize the heat transfer and minimize the thermal resistance while meeting the constraints and requirements of the application.
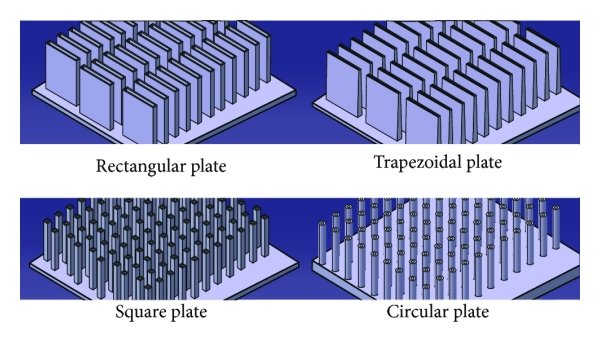
One of the most important aspects of heat sink design is the fin design. Fins are the protrusions that extend from the base of the heat sink and increase the surface area for heat dissipation. There are many types of fin designs, such as straight, pin, flared, etc. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of heat transfer, pressure drop, weight, cost, etc.
Some guidelines and tips for choosing the best heat sink fin design are:
Straight fins are the simplest and most common type of fins. They are easy to manufacture and have low pressure drop. However, they have low heat transfer coefficient and high thermal resistance at the tip of the fins due to boundary layer effects.
Pin fins are cylindrical or rectangular fins that are arranged in a staggered or aligned pattern. They have high heat transfer coefficient and low thermal resistance due to the turbulence created by the pins. However, they have high pressure drop and high weight due to the large number of pins.
Flared fins are fins that have a larger cross-sectional area at the tip than at the base. They have higher heat transfer coefficient and lower thermal resistance than straight fins due to the increased surface area and reduced boundary layer effects. However, they have higher pressure drop and higher cost due to the complex shape and manufacturing process.
Richconn, a precision machining company, is known for its superior heat sink design and machining capabilities. With advanced technical equipment and a professional team, the company is committed to providing customers with efficient and innovative heat dissipation solutions. In terms of heat sink design, Richconn pays attention to details, giving full consideration to material selection, structural optimization and thermal conductivity to ensure that the heat sinks perform excellently in various application scenarios. As for processing, the company adopts advanced manufacturing processes, including aluminum alloy extrusion and copper-aluminum composite welding, to ensure product quality and stability. Through continuous innovation and technological enhancement, Richconn's radiator design and processing capability not only meets customer needs, but also maintains a leading position in market competition.
 A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing CNC Machining ToolsJuly 19, 2023Description:Discover how to select suitable CNC machining tools through this comprehensive guide. Explore key considerations for choosing CNC machining tools, different tool types, and expert advice t...view
A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing CNC Machining ToolsJuly 19, 2023Description:Discover how to select suitable CNC machining tools through this comprehensive guide. Explore key considerations for choosing CNC machining tools, different tool types, and expert advice t...view Unveiling the World of Helical Machined Springs: A Comprehensive ExplorationNovember 15, 2023Embarking on a journey through the intricate world of helical machined springs is more than just an exploration of engineering marvels – it's a pathway to unlocking innovation, efficiency, and reliability in diverse industries. In this article, I'll guide you through the essential aspects of helical machined springs, from their fundamental workings to practical applications and market trends.view
Unveiling the World of Helical Machined Springs: A Comprehensive ExplorationNovember 15, 2023Embarking on a journey through the intricate world of helical machined springs is more than just an exploration of engineering marvels – it's a pathway to unlocking innovation, efficiency, and reliability in diverse industries. In this article, I'll guide you through the essential aspects of helical machined springs, from their fundamental workings to practical applications and market trends.view The Top 7 CAD/CAM Software for CNC ProjectsMarch 18, 2024CAD/CAM software for CNC projects is a specialized tool used to design and control the machining of parts. Here are the top 7 CAD/CAM software for your choice.view
The Top 7 CAD/CAM Software for CNC ProjectsMarch 18, 2024CAD/CAM software for CNC projects is a specialized tool used to design and control the machining of parts. Here are the top 7 CAD/CAM software for your choice.view Sheet Metal Bending: Comprehensive Insights from Processes to EconomicsJuly 25, 2024Sheet metal bending holds a significant place in manufacturing. Let’s discover its diverse processes, unique methods, safety aspects, and cost analysis in this comprehensive exploration.view
Sheet Metal Bending: Comprehensive Insights from Processes to EconomicsJuly 25, 2024Sheet metal bending holds a significant place in manufacturing. Let’s discover its diverse processes, unique methods, safety aspects, and cost analysis in this comprehensive exploration.view Gear Processing Process (7 Steps Make You Feel Simple)May 30, 2022One of the gear processing methods is the forming method, which is the method of cutting the tooth shape by using the forming milling cutter which is completely consistent with the shape of the tooth ...view
Gear Processing Process (7 Steps Make You Feel Simple)May 30, 2022One of the gear processing methods is the forming method, which is the method of cutting the tooth shape by using the forming milling cutter which is completely consistent with the shape of the tooth ...view Basic of Gear Manufacturing: A Guide to Learn about Gear Production ProcessesAugust 29, 2023There is no single process for manufacturing gear because several processes are required based on the type and application. The gears need to be in absolutely perfect condition to adapt to strenuous c...view
Basic of Gear Manufacturing: A Guide to Learn about Gear Production ProcessesAugust 29, 2023There is no single process for manufacturing gear because several processes are required based on the type and application. The gears need to be in absolutely perfect condition to adapt to strenuous c...view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru