Extrusion is a process of forcing a material through a die or a nozzle to create a continuous shape or product. The material can be solid, liquid, or semi-solid, and it can be metal, plastic, ceramic, or food. The die or the nozzle is a tool that has a hole or an opening of the desired cross-section, such as round, square, or complex. The material is pushed through the die or the nozzle by a ram, a screw, or a piston, and it emerges from the other end as a long and uniform product that has the same cross-section as the die or the nozzle.
The extrusion process is based on the principle of plastic deformation, which means that the material changes its shape permanently under a certain amount of pressure and temperature. The material is subjected to compressive and shear forces that cause it to flow and conform to the shape of the die or the nozzle. The extrusion process can produce products with various lengths, diameters, and wall thicknesses, depending on the size and shape of the die or the nozzle.
• It can create very complex cross-sections that are difficult or impossible to produce by other methods, such as casting, forging, or machining.
• It can work with materials that are brittle or have low ductility, such as ceramics or glass, because the material encounters only compressive and shear stresses, and not tensile stresses that can cause cracking or fracture.
• It can create products with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy, because the material flows smoothly and uniformly through the die or the nozzle, and there is no need for further machining or polishing.
• It can create products with varying material properties, such as density, porosity, or color, by controlling the pressure, temperature, and composition of the material during the extrusion process.
• It can create products with high strength and durability, because the material undergoes a favorable grain structure and orientation that aligns with the direction of the material flow.
• It can reduce the material waste and the environmental impact, because the material is used only where it is needed, and the excess or unused material can be recycled and reused for future extrusion processes.
• Metal industry: Extrusion is used to produce metal products, such as rods, bars, tubes, pipes, wires, cables, profiles, and sheets, from materials such as aluminum, copper, steel, brass, and titanium. These products are used for various purposes, such as structural, electrical, mechanical, and decorative.
• Plastic industry: Extrusion is used to produce plastic products, such as films, sheets, tubes, pipes, hoses, profiles, and fibers, from materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and nylon. These products are used for various purposes, such as packaging, insulation, medical, and textile.
• Ceramic industry: Extrusion is used to produce ceramic products, such as tubes, rods, wires, and fibers, from materials such as clay, porcelain, and alumina. These products are used for various purposes, such as electrical, thermal, optical, and biomedical.
• Food industry: Extrusion is used to produce food products, such as pasta, noodles, snacks, cereals, and pet food, from materials such as flour, starch, corn, and rice. These products are used for various purposes, such as nutrition, convenience, and taste.
There are several types of extrusion, which differ in the direction of the material flow, the temperature of the material, and the shape of the die or the nozzle. Each type of extrusion has its own advantages and disadvantages, and may be suitable for different materials and products.
The direction of the material flow refers to the relative movement of the material and the die or the nozzle during the extrusion process. There are three main types of extrusion based on the direction of the material flow: direct, indirect, and hydrostatic extrusion.
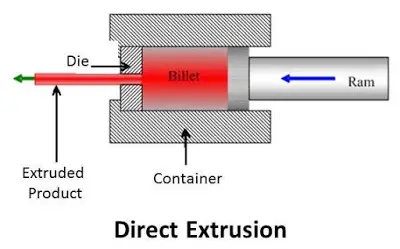
Direct extrusion, also known as forward extrusion, is the most common type of extrusion, where the material moves in the same direction as the ram, and the die or the nozzle is fixed at the opposite end of the extruder. The material is pushed through the die or the nozzle by the ram, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Direct extrusion is simple and economical, but it also has some drawbacks, such as high friction, high temperature, and high pressure, which can affect the quality and efficiency of the extrusion process. The following image shows a schematic diagram of the direct extrusion process.
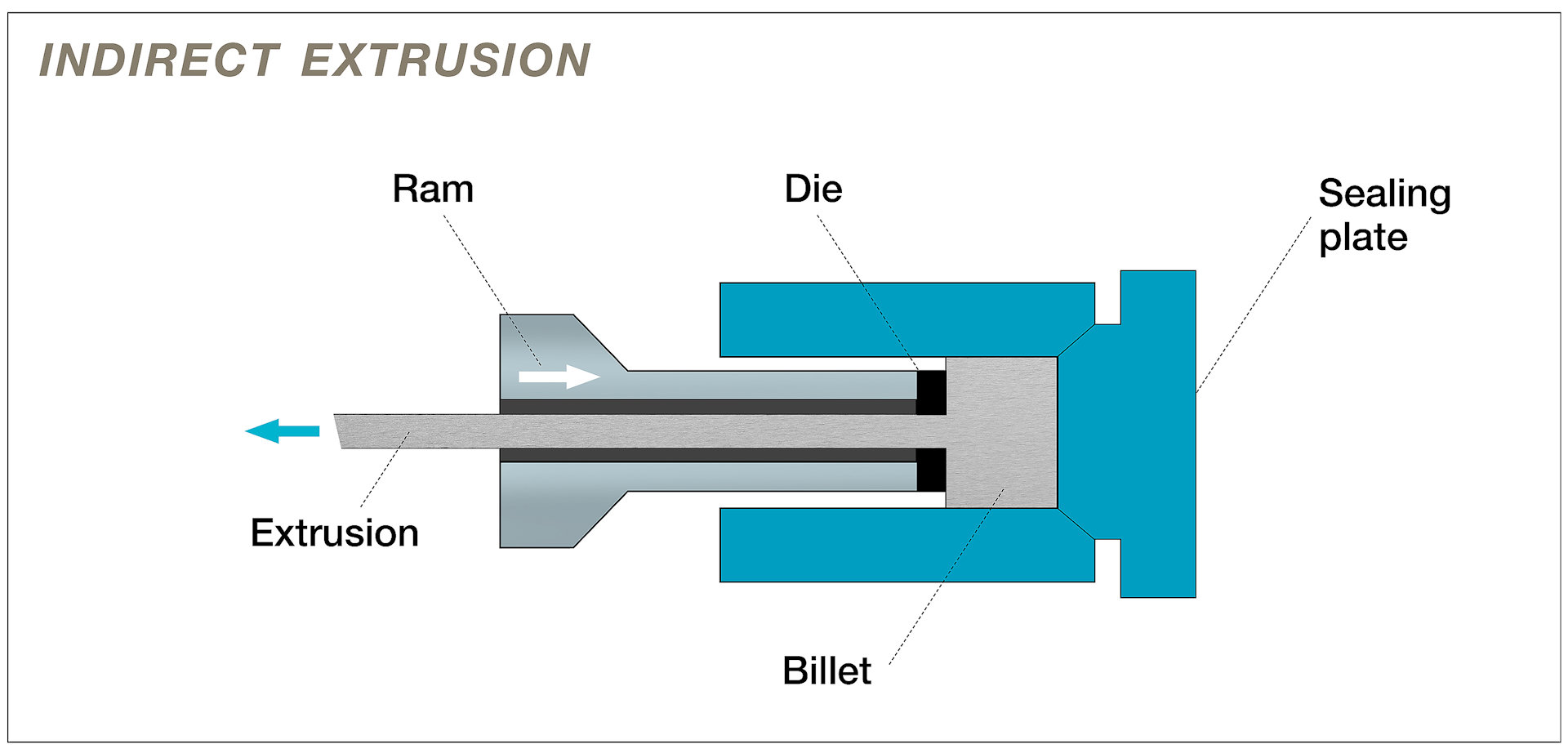
Indirect extrusion, also known as backward extrusion, is the opposite of direct extrusion, where the material moves in the opposite direction as the ram, and the die or the nozzle is attached to the ram. The material is pushed back by the ram, and it flows around the die or the nozzle, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Indirect extrusion has some advantages over direct extrusion, such as lower friction, lower temperature, and lower pressure, which can improve the quality and efficiency of the extrusion process. However, indirect extrusion also has some limitations, such as the need for a hollow ram, a larger extruder, and a more complex die or nozzle design. The following image shows a schematic diagram of the indirect extrusion process.
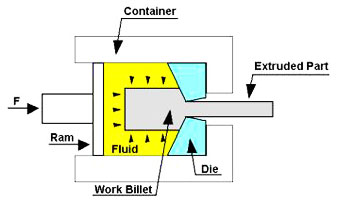
Hydrostatic extrusion, also known as liquid extrusion, is a special type of extrusion, where the material is surrounded by a pressurized fluid, such as oil or water, during the extrusion process. The fluid acts as a lubricant and a cushion, reducing the friction and the stress on the material and the extruder. The material can be pushed through the die or the nozzle by the ram, the fluid, or both, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Hydrostatic extrusion has some benefits over direct and indirect extrusion, such as higher extrusion ratio, higher extrusion speed, and higher material ductility, which can enable the extrusion of difficult materials and complex shapes. However, hydrostatic extrusion also has some drawbacks, such as the need for a sealed extruder, a high-pressure fluid system, and a high-cost and high-maintenance equipment. The following image shows a schematic diagram of the hydrostatic extrusion process.
The temperature of the material refers to the degree of heating or cooling of the material during the extrusion process. The temperature of the material affects the viscosity, the flow, and the properties of the material. There are three main types of extrusion based on the temperature of the material: hot, warm, and cold extrusion.
Hot extrusion is the type of extrusion where the material is heated above its recrystallization temperature, which is the temperature at which the material can restore its original structure and properties after being deformed. The material is heated by an external source, such as a furnace or an induction coil, before being fed into the extruder. The material is then pushed through the die or the nozzle by the ram, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Hot extrusion has some advantages, such as lower extrusion force, lower extrusion ratio, and higher material ductility, which can enable the extrusion of large and complex shapes. However, hot extrusion also has some disadvantages, such as high energy consumption, high oxidation, and high grain growth, which can affect the quality and the performance of the extrusion process and the product.
Warm extrusion is the type of extrusion where the material is heated below its recrystallization temperature, but above its room temperature. The material is heated by an external source, such as a furnace or an induction coil, or by an internal source, such as friction or deformation, before or during the extrusion process. The material is then pushed through the die or the nozzle by the ram, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Warm extrusion has some benefits over hot and cold extrusion, such as lower extrusion force, lower extrusion temperature, and lower material hardening, which can improve the quality and the efficiency of the extrusion process and the product.
Cold extrusion is the type of extrusion where the material is not heated, or heated below its room temperature. The material is fed into the extruder at its ambient temperature, and it is then pushed through the die or the nozzle by the ram, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Cold extrusion has some advantages, such as high extrusion speed, high surface finish, and high dimensional accuracy, which can enhance the performance and the appearance of the product. However, cold extrusion also has some drawbacks, such as high extrusion force, high extrusion ratio, and high material hardening, which can limit the extrusion of large and complex shapes.
The following image shows a comparison chart of the different types of extrusion based on the temperature of the material.
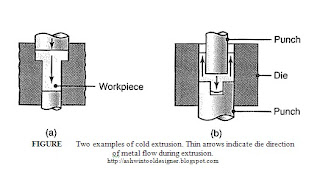
The shape of the die or the nozzle refers to the cross-sectional profile of the hole or the opening that the material passes through during the extrusion process. The shape of the die or the nozzle determines the shape and the size of the product that is produced by the extrusion process. There are three main types of extrusion based on the shape of the die or the nozzle: solid, hollow, and profile extrusion.
Solid extrusion is the type of extrusion where the die or the nozzle has a solid cross-sectional profile, such as round, square, or hexagonal. The material is pushed through the die or the nozzle by the ram, and it emerges from the other end as a solid product that has the same cross-section as the die or the nozzle. Solid extrusion is simple and common, and it can produce products with various diameters and lengths, depending on the size of the die or the nozzle. Solid extrusion is mainly used for producing metal products, such as rods, bars, and wires, from materials such as aluminum, copper, steel, and brass.
Hollow extrusion is the type of extrusion where the die or the nozzle has a hollow cross-sectional profile, such as circular, rectangular, or oval. The material is pushed through the die or the nozzle by the ram, and it emerges from the other end as a hollow product that has the same cross-section as the die or the nozzle. Hollow extrusion is more complex and challenging than solid extrusion, as it requires a mandrel, which is a rod or a tube that supports the inner wall of the product and prevents it from collapsing. Hollow extrusion can produce products with various diameters, wall thicknesses, and lengths, depending on the size of the die, the nozzle, and the mandrel. Hollow extrusion is mainly used for producing metal products, such as tubes, pipes, and hoses, from materials such as aluminum, copper, steel, and titanium.
Profile extrusion is the type of extrusion where the die or the nozzle has a complex and irregular cross-sectional profile, such as T-shaped, L-shaped, or U-shaped. The material is pushed through the die or the nozzle by the ram, and it emerges from the other end as a profile product that has the same cross-section as the die or the nozzle. Profile extrusion is the most difficult and versatile type of extrusion, as it can produce products with various shapes and sizes, depending on the design of the die or the nozzle. Profile extrusion is mainly used for producing plastic products, such as films, sheets, and profiles, from materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and nylon.
Extrusion is a manufacturing process that uses a heat source to melt and fuse material powder together to create solid parts. Extrusion can produce parts with complex geometries, high strength, and high accuracy, making it suitable for various applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and dental. Extrusion has several types, such as direct, indirect, hydrostatic, hot, warm, cold, solid, hollow, and profile extrusion, which differ in the direction of the material flow, the temperature of the material, and the shape of the die or the nozzle. Extrusion offers several advantages over other manufacturing methods, such as design freedom, material efficiency, and customization, but also has some disadvantages, such as cost, quality, and safety.
If you are looking for a reliable and professional service for your extrusion needs, I recommend you to check out Richconn's CNC machining service. Richconn is a leading company that offers high-quality and cost-effective CNC machining solutions for various materials, including metal, plastic, and ceramic. Richconn has a team of experienced and skilled engineers and technicians who can handle any design and specification you may have.
 MIG Welding vs. TIG Welding: Choosing the Right Welding MethodSeptember 25, 2023MIG vs. TIG welding: Master the art, choose wisely. Explore techniques, applications, and trends for welding success.view
MIG Welding vs. TIG Welding: Choosing the Right Welding MethodSeptember 25, 2023MIG vs. TIG welding: Master the art, choose wisely. Explore techniques, applications, and trends for welding success.view What Is Reaming & Reamer And Their DifferencesSeptember 26, 2023Reaming is an important process in CNC machining services, and its main purpose is to join parts or components so that they can rotate or oscillate relative to each other and move at a specific angle or direction.view
What Is Reaming & Reamer And Their DifferencesSeptember 26, 2023Reaming is an important process in CNC machining services, and its main purpose is to join parts or components so that they can rotate or oscillate relative to each other and move at a specific angle or direction.view What kind of process is suitable for machining different types of parts?October 31, 2023Machining is a widely used manufacturing process and is one of the common machining methods used in the manufacturing industry for making different types of parts. Different types of parts require dif...view
What kind of process is suitable for machining different types of parts?October 31, 2023Machining is a widely used manufacturing process and is one of the common machining methods used in the manufacturing industry for making different types of parts. Different types of parts require dif...view Waterborne Aluminum Powder Coating on(Nylon+Fiberglass )Composite Materials: The Innovative Path to the FutureAugust 8, 2023Waterborne aluminum powder coating on nylon+fiberglass composite materials is an ingenious technology that combines nylon and fiberglass to give a unique metallic appearance. This innovative coating t...view
Waterborne Aluminum Powder Coating on(Nylon+Fiberglass )Composite Materials: The Innovative Path to the FutureAugust 8, 2023Waterborne aluminum powder coating on nylon+fiberglass composite materials is an ingenious technology that combines nylon and fiberglass to give a unique metallic appearance. This innovative coating t...view The Basics For the Right ThreadOctober 16, 2023At Richconn, you can easily add threaded holes to your CNC machined parts. Adding by turning gives you many additional threading options. There are two types when it comes to threading: Internal threads and external threads.view
The Basics For the Right ThreadOctober 16, 2023At Richconn, you can easily add threaded holes to your CNC machined parts. Adding by turning gives you many additional threading options. There are two types when it comes to threading: Internal threads and external threads.view Laser Etching: Guide and Comprehensive ContentOctober 8, 2023Laser Etching is a high-precision processing technique widely used to create fine patterns, markings, and engravings on a variety of materials. It utilizes the high energy of a laser beam to gradually remove the surface of a material to create depth, patterns or text.view
Laser Etching: Guide and Comprehensive ContentOctober 8, 2023Laser Etching is a high-precision processing technique widely used to create fine patterns, markings, and engravings on a variety of materials. It utilizes the high energy of a laser beam to gradually remove the surface of a material to create depth, patterns or text.view