3D printing technology has evolved tremendously over the past few decades and has seen the emergence of a variety of different types of 3D printers. These different types of 3D printers differ in terms of working principles, materials, application areas and costs. In this paper, we will discuss the different types of 3D printers, as well as their characteristics and application areas.

FDM is one of the most common and widely used 3D printing technologies. It works by expelling plastic filaments (usually ABS or PLA) through a nozzle and then stacking them layer by layer to create objects. Here are some of the features of FDM 3D printers:
Low cost: FDM 3D printers are usually relatively inexpensive, making them suitable for individuals and small businesses.
Easy to use: they are easy to operate and maintain, making them a popular choice for beginners.
Multiple material options: FDM printers can use a variety of different types of plastic materials, including soft TPU and hard PETG.
Wide range of applications: FDM printers can be used to create prototypes, toys, housewares, parts and small batch production.
Limitations: Relatively poor surface quality, not suitable for applications requiring high precision.
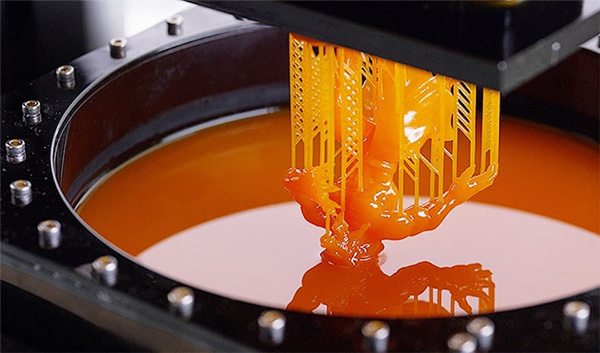
SLA is a light-curing 3D printing technology that uses a UV laser or beam of light to harden a liquid photosensitive resin into a solid. Here are some of the features of SLA 3D printers:
High precision: SLA printers usually have high precision and excellent surface quality for making complex parts and models.
Faster molding speed: SLA prints faster compared to other technologies.
Liquid Resin: SLA uses liquid resin as the raw material, so there are more material choices, including clear, soft, and heat-resistant resins.
Higher cost: SLA printers are usually more expensive and relatively complicated to maintain.
Application areas: SLA is suitable for high-precision fields such as jewelry, dentistry, engineering models, and medical devices.
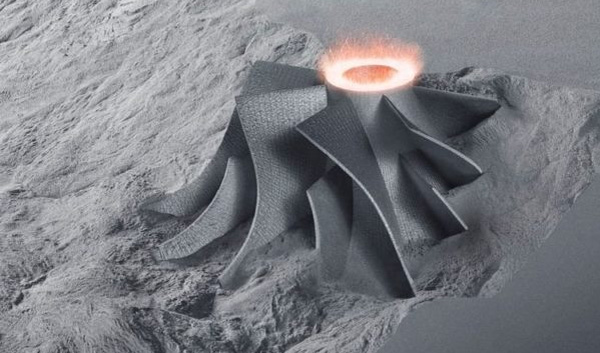
SLS is a 3D printing technology that uses a laser to sinter layers of powdered material into solid objects. Here are some of the features of SLS 3D printers:
Material Versatility: SLS can use a wide variety of powder materials, including nylon, metals, ceramics, and more.
No support structure required: Since the powder supports the printed object during the printing process, there is no need for a support structure, reducing post-processing work.
High Temperature Requirements: SLS printers typically require high temperature working environments, so specialized equipment is needed.
Wide range of applications: SLS is suitable for the manufacture of complex functional parts, tools, prototypes and medical implants.
Higher cost: SLS printers are relatively expensive, suitable for large manufacturing enterprises and research and development organizations.
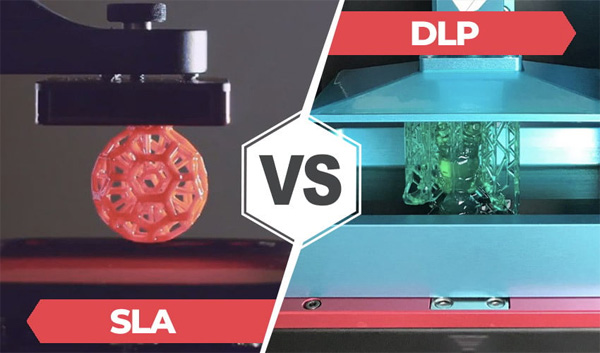
DLP is a light-curing technology similar to SLA, but it uses a digital projector to illuminate an entire layer of light. Here are some of the features of DLP 3D printers:
High speed printing: DLP printers usually print faster because they can irradiate the entire layer at the same time.
Good surface quality: DLP printers usually have excellent surface quality for applications that require high resolution.
Limited material options: Compared to SLA, DLP has relatively limited material options.
Areas of application: DLP is suitable for use in areas such as jewelry, dentistry, visual arts and consumer goods manufacturing.
Binder Jetting is a 3D printing technology that uses a nozzle to spray adhesive onto a layer of powder, and then repeats the process layer by layer until the print is complete. Here are some of the features of Binder Jetting 3D printers:
Multiple material options: Binder Jetting can work with a wide range of powder materials, including metals, ceramics, plastics, and more.
Faster speeds: Binder Jetting prints faster compared to other powder technologies.
Low cost: This technology is typically less expensive and suitable for mass production.
Lower precision: Compared to SLA and SLS, Binder Jetting is relatively less precise.
Application areas: Binder Jetting is suitable for manufacturing parts, tools, models and metal parts.
Metal 3D printing technology uses metal powder or wire as raw material to create metal parts. Here are some of the features of Metal 3D Printing:
High Strength and Heat Resistance: Metal 3D Printing can be used to create high strength, heat and corrosion resistant parts.
Variety of metal materials: metal 3D printing can use a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, titanium, nickel alloys, and more.
High cost: Metal 3D printers are relatively expensive and have expensive material costs.
Application areas: Metal 3D printing is suitable for aerospace, automotive, medical, energy and defense.
Ceramic 3D printing technology uses ceramic powder or ceramic paste as raw material to create ceramic parts. Here are some of the features of ceramic 3D printing:
High temperature and corrosion resistance: Ceramic 3D printing can be used to create parts for high temperature environments and chemical resistant parts.
Biocompatible: ceramic 3D printing materials are often biocompatible for medical devices and biomedical applications.
Higher cost: Ceramic 3D printers and materials are typically more expensive.
Application areas: ceramic 3D printing is suitable for manufacturing ceramic parts, biomedical instruments and artwork and other fields.
Large Format 3D Printers are specifically designed to print large objects and are often used in the fields of architecture, aerospace, automotive and art. Here are some of the features of large format 3D printing:
Printing large size objects: these printers can build large models, prototypes, sculptures, etc.
Slow build speed: Due to the large size of the object, the printing speed is slow.
Areas of application: large size 3D printing is suitable for construction, automotive parts, art installations and other areas where large parts are required.
Bioprinting is a 3D printing technology specialized in creating biological materials and cells for biomedical and life science research. Here are some of the features of bioprinting
Tissue engineering: Bioprinting can be used to create artificial tissues, organs and cell culture substrates.
Biocompatibility: This technique uses biocompatible materials to ensure the stability and health of biomaterials.
High precision: Bioprinting usually requires high precision to mimic the tissue structure within a living organism.
Application areas: Bioprinting is suitable for medical, life science research and tissue engineering.
Multi-material 3D printing technology allows the use of many different types of materials in the same object, thus realizing more functions. Here are some of the features of multi-material 3D printing:
Material Versatility: This technology allows the use of different materials such as plastics, metals, electronic components, etc. in the same printing process.
Versatility: multi-material 3D printing allows the creation of objects with multiple functions, such as electronic devices, sensors, and medical devices.
High precision: This technology usually requires high precision to ensure accurate stacking of different materials.
Areas of application: Multi-material 3D printing is suitable for electronics, machinery, medical and scientific research.
3D printing technology has evolved rapidly and a number of different types of 3D printers have emerged, each with their own characteristics and application areas. Choosing the right type of 3D printer for your needs depends on your project requirements, budget and material needs. Whether you are an individual user, an engineer, a doctor or a manufacturer, there are different types of 3D printing technology from which you can find the right solution for you.
Choosing the right 3D printer for beginners is an important decision, as it will affect your process and experience of learning to 3D print. Beginners usually want to find a 3D printer that is easy to use, affordable, reliable and not too complicated.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM technology is one of the best 3D printing technologies for beginners. Here's why FDM printers are a good choice for beginners:
Low cost to start: FDM printers are usually relatively inexpensive, which is an attractive factor for beginners. You can start learning 3D printing at a low cost.
Ease of use: FDM printers are great for beginners because they usually have an intuitive user interface and easy to follow instructions. Many FDM printers come with easy-to-use software that makes preparing and printing models much simpler.
Multiple material options: FDM printers can work with a variety of different types of plastic materials, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and more. This means you can choose the right material for your project's requirements.
Large community support: Because of the popularity of FDM technology, there are tons of online resources, communities, and tutorials available for beginners to refer to and learn from.
Safety: FDM is usually safer compared to other 3D printing technologies because it uses melted plastic rather than photosensitive resins or metal powders.
Wide range of applications: FDM printers are suitable for a wide range of applications such as making prototypes, toys, home furnishings, parts and small batch production.
However, there are some limitations to FDM printing for beginners. Chief among them is the relatively low printing accuracy and inferior surface quality to some other technologies. In addition, some complex geometries may require support structures that require subsequent manual processing.
II. Stereolithography (SLA) / Light Curing
SLA technology can also be suitable for beginners, but it is usually suited for those who have higher demands for high precision and excellent surface quality. Here are the reasons why SLA printers are suitable for beginners:
High precision and excellent surface quality: SLA printers are usually capable of very high precision, making them suitable for projects that require a high level of detail and smooth surfaces.
No need for support structures: Unlike FDM, SLA printers usually do not require support structures, so post-processing requirements are lower.
Material Versatility: SLA printers use liquid resin as the raw material, so a wide range of different resins can be selected, including clear, soft and high temperature resins.
Learning curve: Although SLA printing technology is superior in terms of accuracy, it may take more time to get used to its operation and post-processing techniques.
Areas of application: SLA is suitable for high precision applications such as jewelry, dentistry, engineering models, and medical devices.
However, SLA printers are usually expensive and resin materials are relatively expensive. In addition, special safety measures are required to protect eyes and skin due to the use of UV light sources.
III. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) / Selective Laser Sintering
SLS technology is an advanced 3D printing technique that is usually less suitable for beginners. Here is some information about SLS printers:
Material Versatility: SLS printers can use a wide range of powder materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and more. This allows for flexibility in material selection.
High Precision: SLS technology is typically highly accurate and suitable for manufacturing complex functional parts.
High Temperature Requirements: SLS printers need to work in high temperature environments and therefore require special equipment and operating environments.
Higher cost: SLS printers are usually more expensive and are not suitable for beginners or individual users with limited budgets.
Application areas: SLS is suitable for the manufacture of parts, tools, prototypes and medical implants and other fields.
Fourth, digital light processing (DLP) / Digital Light Processing
DLP technology, similar to SLA, is a light-curing technology that is usually used to manufacture high-precision models and parts. Here is some information about DLP printers:
High speed printing: DLP printers usually print faster because they can irradiate an entire layer at the same time.
High precision and surface quality: DLP technology typically enables high precision and excellent surface quality for applications that require high resolution.
Limited material choices: Compared to SLA, DLP has relatively limited material choices.
Learning curve: The operation of DLP printers can take some time to get used to, especially when working with complex models.
Areas of application: DLP is suitable for use in areas such as jewelry, dentistry, visual arts and consumer goods manufacturing.
For beginners, FDM technology is usually the best choice because of its low cost, ease of use and extensive community support. However, if you have a higher demand for high precision and excellent surface quality, then SLA and DLP technologies are also good choices, although they can be a bit more expensive and complex. Above all, whichever type of 3D printer you choose, be prepared to learn and explore, as 3D printing is a creative and fun field that can offer you endless possibilities.
The cheapest type of 3D printing is usually a printer based on Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or fused deposition modeling technology. Here are some reasons why FDM technology is usually more affordable:
Low-cost printers and materials: FDM printers are usually relatively inexpensive for individual users and beginners. In addition, the printing materials used in FDM, such as PLA (polylactide) and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene copolymer), are relatively inexpensive. This reduces initial investment and running costs.
Low energy consumption: FDM printers typically use thermal nozzles to melt plastic filaments and deposit them into layers. Compared to other 3D printing technologies, such as laser sintering or light curing, FDM consumes less energy and therefore saves on electricity costs.
Wide market: Due to the wide popularity of FDM technology, there are many different brands and models of FDM printers available in the market, which increases competition and helps to reduce prices.
Low Maintenance Costs: FDM printers are usually easy to maintain as they do not have complex laser systems or liquid photosensitive resins, parts that can require expensive repairs.
Open source community: there are many open source FDM printer designs and groups that share information and designs, allowing people to build their own 3D printers, further reducing costs.
It is important to note that while FDM technology is one of the cheapest types of 3D printing, it may not be as good as some of the other high-end technologies, such as light curing (SLA) or selective laser sintering (SLS), in terms of print accuracy and surface quality. Therefore, if you need higher precision and quality prints, you may want to consider other types of 3D printing technology, even though they are usually more expensive. However, for many home users, schools, and small businesses, FDM technology offers an affordable entry option for most basic 3D printing needs.
When you're looking for a high-quality, reliable processing partner for 3D printing services, Richconn is your go-to choice!
EXCELLENT QUALITY: Richconn has advanced 3D printing technology and an experienced team to ensure your project is made with exceptional quality.
VARIETY OF MATERIALS: we offer a wide selection of materials including PLA, ABS, PETG, metal, ceramic, and more to meet a variety of project needs.
CUSTOMIZED SOLUTIONS: Whether you need rapid prototyping, low volume production or custom parts, we can provide you with the best solution.
Rapid Delivery: We support your project with efficient production processes and prompt delivery times to ensure your project is completed on time.
Reasonable Pricing: we offer competitive pricing so that you can get high quality 3D printing services at a reasonable cost.
Customer Satisfaction: we are centered on customer satisfaction and strive to exceed expectations to ensure you are satisfied with our services.
Whether you are trying 3D printing for the first time or looking for a trusted partner for your 3D printing needs, Richconn will provide you with the best solution. Contact us and let's realize your ideas and projects together!
 Machinist Tools: What They Are, How to Use ThemDecember 1, 2023Machinist tools are a variety of products that are used to shape, cut, grind, shear, and form metal into a desired part. They are essential for metalworking and machining, which are the processes of creating metal products or components by removing metal chips in the workpiece.view
Machinist Tools: What They Are, How to Use ThemDecember 1, 2023Machinist tools are a variety of products that are used to shape, cut, grind, shear, and form metal into a desired part. They are essential for metalworking and machining, which are the processes of creating metal products or components by removing metal chips in the workpiece.view A Comprehensive Copper Analysis for CNC MachiningJanuary 12, 2024Here are various properties of copper - from its elemental essence, physical prowess, thermal and electrical properties, to applications in CNC machining.view
A Comprehensive Copper Analysis for CNC MachiningJanuary 12, 2024Here are various properties of copper - from its elemental essence, physical prowess, thermal and electrical properties, to applications in CNC machining.view Waterborne Aluminum Powder Coating on(Nylon+Fiberglass )Composite Materials: The Innovative Path to the FutureAugust 8, 2023Waterborne aluminum powder coating on nylon+fiberglass composite materials is an ingenious technology that combines nylon and fiberglass to give a unique metallic appearance. This innovative coating t...view
Waterborne Aluminum Powder Coating on(Nylon+Fiberglass )Composite Materials: The Innovative Path to the FutureAugust 8, 2023Waterborne aluminum powder coating on nylon+fiberglass composite materials is an ingenious technology that combines nylon and fiberglass to give a unique metallic appearance. This innovative coating t...view Safety Issues in CNC Turning TechnologyApril 25, 2023Turning is a part of mechanical processing in lathe machining. Lathe machining mainly uses the turning tool to process the rotating workpiece. Lathes are mainly used to process shafts, discs, sleeves,...view
Safety Issues in CNC Turning TechnologyApril 25, 2023Turning is a part of mechanical processing in lathe machining. Lathe machining mainly uses the turning tool to process the rotating workpiece. Lathes are mainly used to process shafts, discs, sleeves,...view An Ultimate Guide to Medical Device ManufacturingMarch 13, 2024Nowadays, manufacturing medical devices is becoming more and more important. This article will let you know more about medical device manufacturing.view
An Ultimate Guide to Medical Device ManufacturingMarch 13, 2024Nowadays, manufacturing medical devices is becoming more and more important. This article will let you know more about medical device manufacturing.view Which Is Easier to Weld, Aluminum or Stainless Steel?October 26, 2023This is because the melting point of stainless steel is higher than that of aluminum alloys, which makes it more stable during the welding process. Aluminum alloys are prone to the risk of being burned through because of their low melting point during the welding process. In addition, aluminum alloys are also susceptible to the formation of an aluminum oxide film on the surface in air, which has a much higher melting point than aluminum itself, making it more difficult to weld.view
Which Is Easier to Weld, Aluminum or Stainless Steel?October 26, 2023This is because the melting point of stainless steel is higher than that of aluminum alloys, which makes it more stable during the welding process. Aluminum alloys are prone to the risk of being burned through because of their low melting point during the welding process. In addition, aluminum alloys are also susceptible to the formation of an aluminum oxide film on the surface in air, which has a much higher melting point than aluminum itself, making it more difficult to weld.view