Aluminium extrusion is a process of forcing aluminium alloy material through a die to create a continuous shape or product. The material can be solid, liquid, or semi-solid, and it can be metal, plastic, ceramic, or food. The die is a tool that has a hole or an opening of the desired cross-sectional profile, such as round, square, or complex. The material is pushed through the die by a ram, a screw, or a piston, and it emerges from the other end as a long and uniform product that has the same cross-section as the die.
The aluminium extrusion process is based on the principle of plastic deformation, which means that the material changes its shape permanently under a certain amount of pressure and temperature. The material is subjected to compressive and shear forces that cause it to flow and conform to the shape of the die. The aluminium extrusion process can produce products with various lengths, diameters, and wall thicknesses, depending on the size and shape of the die.
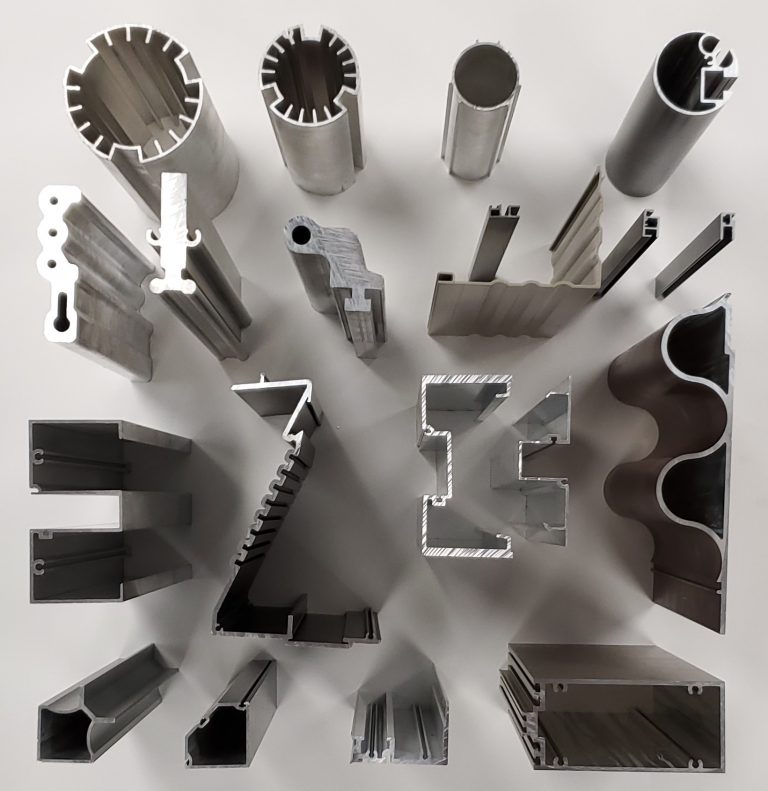

• It can create very complex cross-sections that are difficult or impossible to produce by other methods, such as casting, forging, or machining.
• It can work with materials that are brittle or have low ductility, such as ceramics or glass, because the material encounters only compressive and shear stresses, and not tensile stresses that can cause cracking or fracture.
• It can create products with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy, because the material flows smoothly and uniformly through the die, and there is no need for further machining or polishing.
• It can create products with varying material properties, such as density, porosity, or color, by controlling the pressure, temperature, and composition of the material during the aluminium extrusion process.
• It can create products with high strength and durability, because the material undergoes a favorable grain structure and orientation that aligns with the direction of the material flow.
• It can reduce the material waste and the environmental impact, because the material is used only where it is needed, and the excess or unused material can be recycled and reused for future aluminium extrusion processes.

Aluminium extrusion is used to produce aluminium products, such as windows, doors, curtain walls, roofs, and facades, from materials such as aluminium 6063, 6061, and 6082. These products are used for various purposes, such as structural, thermal, acoustic, and aesthetic.
Aluminium extrusion is used to produce aluminium products, such as frames, rails, bumpers, and wheels, from materials such as aluminium 6061, 6082, and 7075. These products are used for various purposes, such as lightweight, fuel efficiency, and safety.
Aluminium extrusion is used to produce aluminium products, such as heat sinks, cases, and connectors, from materials such as aluminium 6063, 6061, and 1050. These products are used for various purposes, such as heat dissipation, protection, and conductivity.
Aluminium extrusion is used to produce aluminium products, such as chairs, tables, cabinets, and shelves, from materials such as aluminium 6063, 6061, and 6082. These products are used for various purposes, such as durability, functionality, and design.
The aluminium extrusion process consists of several steps and components, which are described below:
The first step of the aluminium extrusion process is to prepare the material that will be extruded. The material is usually an aluminium alloy, which is a mixture of aluminium and other elements, such as copper, magnesium, silicon, or zinc, that enhance the properties and performance of the aluminium. The material is cast into a cylindrical shape, called a billet, which has a diameter and a length that match the size and the capacity of the extruder. The billet is then heated to a temperature that is below its melting point, but high enough to make it soft and pliable, usually between 350°C and 500°C. The heating process also homogenizes the material, which means that it makes the material uniform in composition and structure.
The second step of the aluminium extrusion process is to feed the heated billet into the extrusion press, which is a machine that applies a high pressure to the material and forces it through the die. The extrusion press consists of a container, a ram, and a stem. The container is a hollow cylinder that holds the billet and aligns it with the die. The ram is a piston that moves back and forth inside the container and pushes the billet against the die. The stem is a rod that connects the ram and the billet and transfers the pressure from the ram to the billet. The extrusion press can be either horizontal or vertical, depending on the orientation of the container and the die. The extrusion press can also be either hydraulic or mechanical, depending on the type of power source that drives the ram. The extrusion press can generate a pressure that ranges from 50 to 1500 MPa, depending on the type and the size of the material and the product.
The third step of the aluminium extrusion process is to pass the material through the die, which is a tool that has a hole or an opening of the desired cross-sectional profile. The die is attached to the opposite end of the container, and it can be either fixed or movable, depending on the type of extrusion. The die can be made of various materials, such as steel, carbide, or diamond, depending on the type and the size of the material and the product. The die can also have various shapes and sizes, such as round, square, or complex, depending on the design and the specification of the product. The die determines the shape and the size of the product, as well as the extrusion ratio, which is the ratio of the cross-sectional area of the billet to the cross-sectional area of the product. The die also affects the extrusion speed, which is the rate at which the product exits the die, and the extrusion temperature, which is the temperature of the material and the product during the extrusion process.
The fourth step of the aluminium extrusion process is to collect the product that emerges from the die on a runout table, which is a platform that supports and transports the product. The runout table can be either stationary or movable, depending on the length and the weight of the product. The runout table can also have various features, such as rollers, belts, or conveyors, that facilitate the movement and the alignment of the product. The runout table can also have various devices, such as saws, shears, or punches, that cut or shape the product to the desired length or size.
The fifth step of the aluminium extrusion process is to cool the product that is collected on the runout table by a cooling system, which is a mechanism that lowers the temperature of the product and prevents it from warping or cracking. The cooling system can use various methods, such as air, water, or oil, to transfer the heat from the product to the surrounding environment. The cooling system can also use various techniques, such as spraying, dipping, or quenching, to control the rate and the uniformity of the cooling process. The cooling system can also use various devices, such as fans, pumps, or tanks, to circulate and regulate the cooling medium. The cooling system affects the properties and the performance of the product, such as the strength, the hardness, and the ductility, as well as the microstructure and the grain size of the material.
The sixth and final step of the aluminium extrusion process is to cut the product that is cooled by the cooling system by a cutting device, which is a tool that separates the product into individual pieces or segments. The cutting device can be either manual or automatic, depending on the type and the size of the product. The cutting device can also use various methods, such as sawing, shearing, or punching, to break or pierce the product. The cutting device can also use various features, such as blades, dies, or stamps, to create smooth or rough edges on the product. The cutting device determines the final length and the shape of the product, as well as the amount of material waste and the environmental impact of the extrusion process.
There are several types of aluminium extrusion, which differ in the direction of the material flow, the shape of the die, and the cross-sectional complexity. Each type of aluminium extrusion has its own advantages and disadvantages, and may be suitable for different materials and products.
The direction of the material flow refers to the relative movement of the material and the die during the aluminium extrusion process. There are three main types of aluminium extrusion based on the direction of the material flow: direct, indirect, and hydrostatic extrusion.
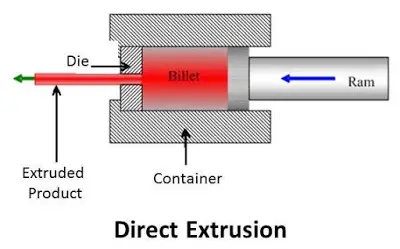
Direct extrusion, also known as forward extrusion, is the most common type of aluminium extrusion, where the material moves in the same direction as the ram, and the die is fixed at the opposite end of the extruder. The material is pushed through the die by the ram, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Direct extrusion is simple and economical, but it also has some drawbacks, such as high friction, high temperature, and high pressure, which can affect the quality and efficiency of the aluminium extrusion process. The following image shows a schematic diagram of the direct extrusion process.
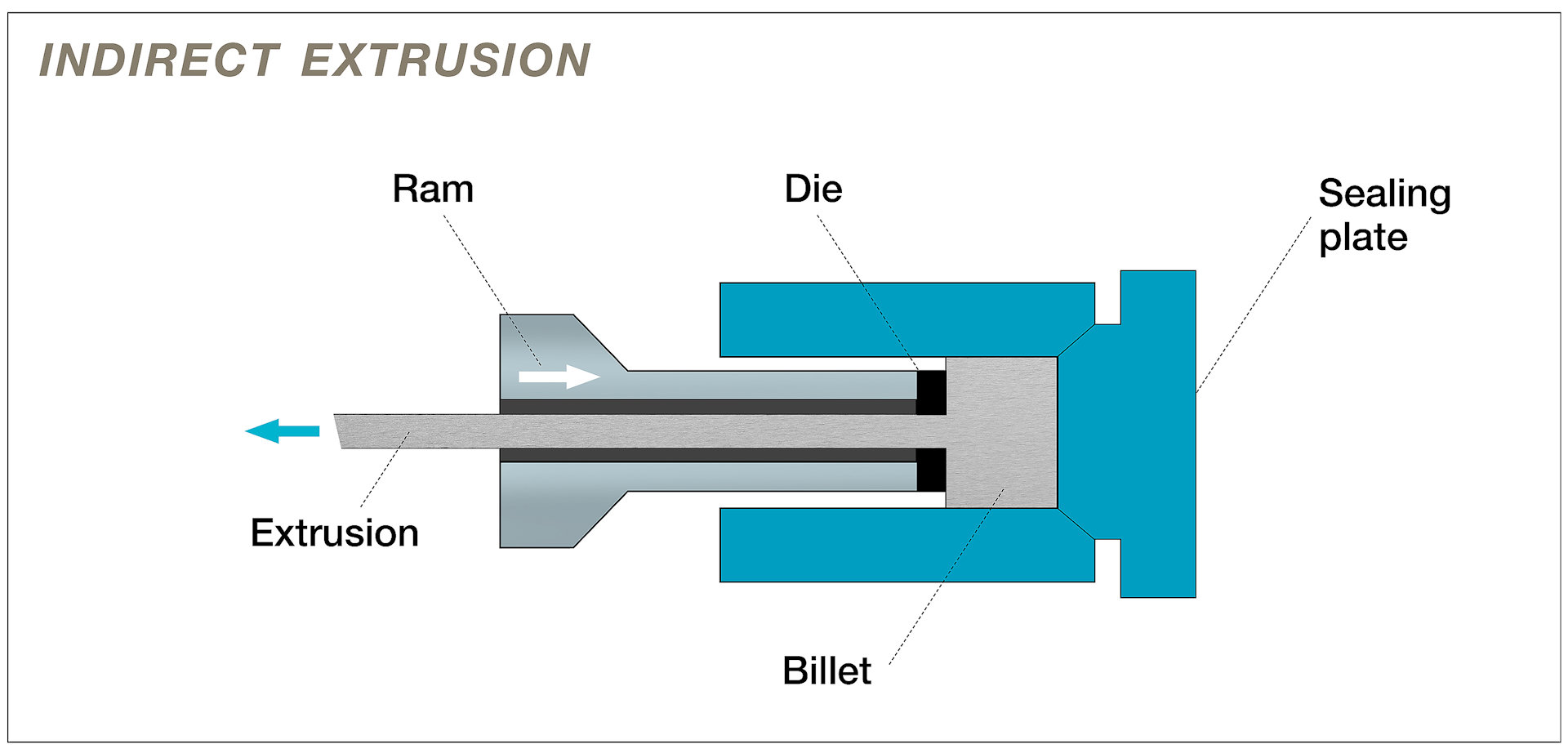
Indirect extrusion, also known as backward extrusion, is the opposite of direct extrusion, where the material moves in the opposite direction as the ram, and the die is attached to the ram. The material is pushed back by the ram, and it flows around the die, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Indirect extrusion has some advantages over direct extrusion, such as lower friction, lower temperature, and lower pressure, which can improve the quality and efficiency of the aluminium extrusion process. However, indirect extrusion also has some limitations, such as the need for a hollow ram, a larger extruder, and a more complex die design. The following image shows a schematic diagram of the indirect extrusion process.
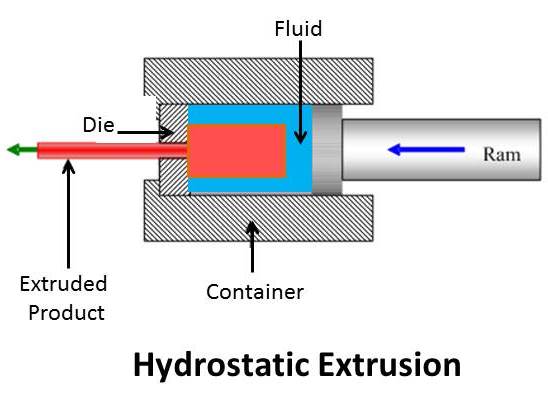
Hydrostatic extrusion, also known as liquid extrusion, is a special type of aluminium extrusion, where the material is surrounded by a pressurized fluid, such as oil or water, during the aluminium extrusion process. The fluid acts as a lubricant and a cushion, reducing the friction and the stress on the material and the extruder. The material can be pushed through the die by the ram, the fluid, or both, and it emerges from the other end as a product. Hydrostatic extrusion has some benefits over direct and indirect extrusion, such as higher extrusion ratio, higher extrusion speed, and higher material ductility, which can enable the aluminium extrusion of difficult materials and complex shapes. However, hydrostatic extrusion also has some drawbacks, such as the need for a sealed extruder, a high-pressure fluid system, and a high-cost and high-maintenance equipment. The following image shows a schematic diagram of the hydrostatic extrusion process.
Aluminium extrusion technology is constantly evolving and improving, as new methods and techniques are developed and applied to enhance the productivity, quality, and performance of the aluminium extrusion process and the product. Some of the current trends and developments of aluminium extrusion technology are:
Micro-extrusion is a type of aluminium extrusion that produces products with very small cross-sectional dimensions, usually less than 1 mm. Micro-extrusion requires special equipment, such as micro-dies, micro-presses, and micro-sensors, that can handle the high precision and accuracy required for the aluminium extrusion process. Micro-extrusion can produce products with various shapes and features, such as micro-tubes, micro-wires, micro-gears, and micro-springs, that are used for various purposes, such as micro-electronics, micro-mechanics, and micro-medical devices.
Co-extrusion is a type of aluminium extrusion that produces products with two or more different materials or layers, such as metal, plastic, or composite, that are extruded together through a single die. Co-extrusion requires special equipment, such as co-dies, co-presses, and co-feeders, that can control the flow and the temperature of the different materials during the aluminium extrusion process. Co-extrusion can produce products with various properties and functions, such as strength, stiffness, flexibility, and conductivity, that are used for various purposes, such as structural, electrical, thermal, and optical applications.
Multi-port extrusion is a type of aluminium extrusion that produces products with multiple hollow chambers or channels, such as tubes, pipes, or profiles, that are extruded simultaneously through a single die. Multi-port extrusion requires special equipment, such as multi-port dies, multi-port presses, and multi-port mandrels, that can create and maintain the shape and the size of the multiple chambers or channels during the aluminium extrusion process. Multi-port extrusion can produce products with various advantages and benefits, such as weight reduction, heat transfer, fluid flow, and sound absorption, that are used for various purposes, such as automotive, aerospace, and HVAC applications.
Aluminium extrusion technology can increase the productivity of the aluminium extrusion process and the product, by reducing the cycle time, increasing the output rate, and improving the material utilization. Aluminium extrusion technology can also enable the aluminium extrusion of new and complex shapes and products, that are otherwise difficult or impossible to produce by conventional methods.
Aluminium extrusion technology can lower the cost of the aluminium extrusion process and the product, by reducing the energy consumption, minimizing the material waste, and optimizing the process parameters. Aluminium extrusion technology can also reduce the need for post-processing and finishing operations, such as machining, polishing, or coating, that can add to the cost and the time of the production.
Aluminium extrusion technology can improve the quality of the aluminium extrusion process and the product, by enhancing the surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties of the product. Aluminium extrusion technology can also improve the consistency and the reliability of the product, by reducing the defects, deviations, and variations that can occur during the aluminium extrusion process.
• High complexity
Aluminium extrusion technology can increase the complexity of the aluminium extrusion process and the product, by requiring more advanced and sophisticated equipment, tools, and skills, that can increase the difficulty and the risk of the aluminium extrusion process. Aluminium extrusion technology can also create more challenges and problems, such as die wear, material degradation, and process instability, that can affect the quality and the performance of the aluminium extrusion process and the product.
Aluminium extrusion technology can increase the investment of the aluminium extrusion process and the product, by requiring more expensive and specialized equipment, tools, and materials, that can increase the initial and the operational cost of the aluminium extrusion process. Aluminium extrusion technology can also require more research and development, testing and validation, and maintenance and repair, that can add to the cost and the time of the production.
Richconn can produce aluminium products with various shapes and sizes, such as tubes, pipes, profiles, and sheets, from materials such as aluminium 6063, 6061, and 6082. Richconn can use different types of extrusion processes, such as direct, indirect, and hydrostatic extrusion, to meet your requirements and expectations. Richconn can also provide post-processing and finishing services, such as cutting, CNC machining service, drilling, bending, welding, and coating, to enhance the performance and the appearance of your aluminium products.
 How to Define Fits: Different Types of Fits in EngineeringMarch 5, 2024This article will shade some light on “fits”. To know more about “what is fits” will help you succeed in doing your projects. So let’s check it out.view
How to Define Fits: Different Types of Fits in EngineeringMarch 5, 2024This article will shade some light on “fits”. To know more about “what is fits” will help you succeed in doing your projects. So let’s check it out.view The Functional Advantages of Custom PVD Coating in Automotive DesignJanuary 5, 2024When it comes to automotive design, every detail matters. From the sleek lines of the exterior to the carefully crafted interior, each element plays a crucial role in creating a unique and memorable d...view
The Functional Advantages of Custom PVD Coating in Automotive DesignJanuary 5, 2024When it comes to automotive design, every detail matters. From the sleek lines of the exterior to the carefully crafted interior, each element plays a crucial role in creating a unique and memorable d...view Electrophoresis Plating in Corrosion ResistanceJanuary 5, 2024When it comes to protecting metal objects from corrosion, electrophoresis plating is a game-changer. This process not only enhances the appearance of the metal but also provides a robust shield agains...view
Electrophoresis Plating in Corrosion ResistanceJanuary 5, 2024When it comes to protecting metal objects from corrosion, electrophoresis plating is a game-changer. This process not only enhances the appearance of the metal but also provides a robust shield agains...view UNF Threads vs UNC Threads and What Are UNF Threads and UNC ThreadsNovember 17, 2023In the intricate world of CNC machining, understanding the nuances of UNF Threads and UNC Threads is paramount. These threading standards, Unified National Fine (UNF) and Unified National Coarse (UNC), serve as the bedrock of precision in mechanical engineering. Let's delve into the specifics, exploring their applications, differences, and the critical role they play in the realm of precision machining.view
UNF Threads vs UNC Threads and What Are UNF Threads and UNC ThreadsNovember 17, 2023In the intricate world of CNC machining, understanding the nuances of UNF Threads and UNC Threads is paramount. These threading standards, Unified National Fine (UNF) and Unified National Coarse (UNC), serve as the bedrock of precision in mechanical engineering. Let's delve into the specifics, exploring their applications, differences, and the critical role they play in the realm of precision machining.view Titanium vs. Aluminum: High Performance Metals for Machining and 3D PrintingOctober 11, 2023When you think of an outstanding combination of material properties for parts, light weight and strength come to mind. Of course, the same is true for aluminum and titanium. Both materials meet other important criteria, such as excellent corrosion resistance and heat tolerance.view
Titanium vs. Aluminum: High Performance Metals for Machining and 3D PrintingOctober 11, 2023When you think of an outstanding combination of material properties for parts, light weight and strength come to mind. Of course, the same is true for aluminum and titanium. Both materials meet other important criteria, such as excellent corrosion resistance and heat tolerance.view CNC POR: Demystifying the Key Technology in CNC MachiningNovember 2, 2023In the world of precision engineering and manufacturing, CNC technology plays a pivotal role. Among the various CNC techniques, CNC POR stands out as a critical component, offering unmatched precision, efficiency, and versatility.view
CNC POR: Demystifying the Key Technology in CNC MachiningNovember 2, 2023In the world of precision engineering and manufacturing, CNC technology plays a pivotal role. Among the various CNC techniques, CNC POR stands out as a critical component, offering unmatched precision, efficiency, and versatility.view