The architecture industry is undergoing profound change thanks to 3D printing. Architects are harnessing this technology to revolutionize the way they design, construct and experience buildings. With 3D printing, architects can transform digital designs into tangible objects, opening up endless possibilities. You can now create intricate geometries, customize designs, and optimize structures with unprecedented precision and efficiency. But that is not all. 3D printing is also influencing sustainability practices, materials research, and the way architectural models are communicated to customers and stakeholders.
From the beginning of a project to post-production, 3D printing is transforming the daily work of architects. In this blog, we explore some of the ways 3D printing is reshaping the architectural industry by redefining the boundaries of creativity and construction.
One of the key benefits of 3D printing in architecture is speed, particularly the ability to quickly prototype designs. Architects can quickly transform their digital concepts from CAD models to physical models, allowing them to better visualize and refine their ideas through a more realistic and immersive representation of the proposed building or space. These models are also a great way for architects to bring spatial qualities, proportions and aesthetics to life for clients and stakeholders. Canadian architecture firm Public City has had great success using 3D printed models that illustrate what drawings cannot do!
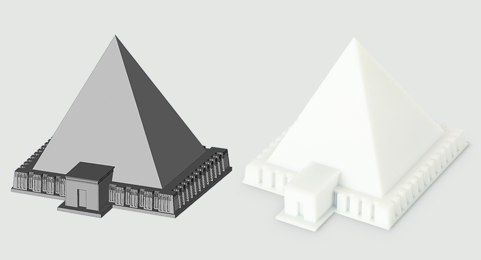
When the Metropolitan Museum wanted to recreate a historic pyramid complex, a CAD model of the pyramid was first created as an STL file (left) and then built in SL from a white, ABS-like thermoplastic material (right).
While architects have been using models for many years, traditional methods of model creation are labor-intensive and slow, meaning multiple iterations can be time-consuming and costly. 3D printing allows architects to produce successive versions of the model efficiently and in different 3d printing materials. This allows them to evaluate design concepts, test structural integrity, and quickly examine lighting and acoustics. Producing parts quickly promotes an iterative design process that leads to design improvements and better results.
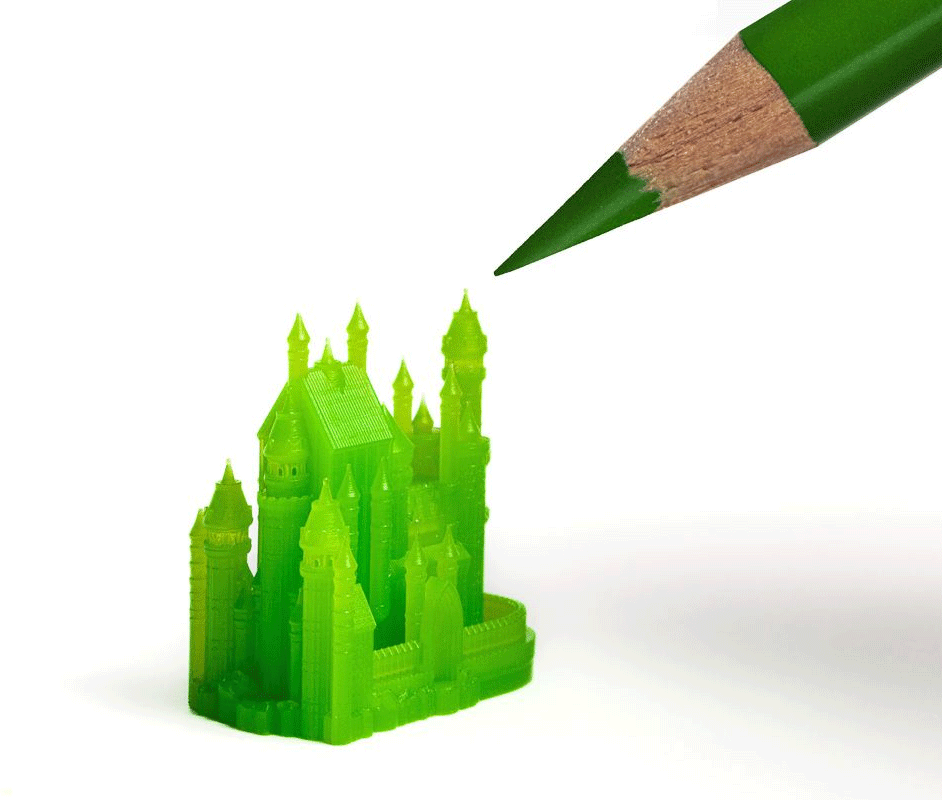

Architects are innovators. For centuries they have devised intricate designs with unique geometries that push construction methods to the limit, and they show no sign of slowing down. Unlike traditional production methods, 3D printing offers unparalleled freedom to create complex shapes, curves and patterns, allowing architects to push the boundaries of design - evidence of this is some of the best 3D printed pavilions in the world.
As an additive manufacturing process, 3D printing creates parts by building up one layer at a time, providing the ability to create intricate geometries with intricate details, even allowing architects to create interlocking parts as a single piece. This eliminates the need for separate components and simplifies the assembly process, reducing production time. This newfound ability to print interconnected parts to precise tolerances ensures a seamless fit and creates complex architectural features and connections.
The design freedom and speed of 3D printing have enabled architects to capitalize on the mass customization trend. Architects can create design solutions that meet the unique needs of each client or project. Instead of relying on standard designs, architects can adapt and modify their designs to meet specific spatial, functional and aesthetic desires. Creating parts in layers means architects can use multiple materials in a single print. The combination of materials expands the design possibilities and improves the visual and tactile qualities of architectural elements. This level of personalization improves customer satisfaction and creates a stronger connection between the built environment and its inhabitants.
3D printing allows architects to explore new structural possibilities and optimize the performance of buildings. The technology enables the creation of intricate lattice structures, lightweight components and optimized structural systems, allowing architects to test different structural configurations, evaluate their performance and refine designs accordingly.
You can design components with different densities, thicknesses and structural reinforcements, optimizing material distribution and weight while maintaining structural integrity. 3D printing can be used to create lightweight structures without compromising strength and structural integrity. Materials such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers and lightweight metal alloys can be used to produce load-bearing elements with a high strength-to-weight ratio. This allows architects to design more efficient and sustainable structures because less material is used and transportation costs are reduced.
When 3D printing parts, architects can benefit from a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, composites and even bio-based materials. 3D printing enables architects to experiment with new materials and develop innovative material compositions. Aside from the customer satisfaction benefits that come from combining multiple materials for mass customization, architects can create hybrid structures with unique properties and performance characteristics that open up new possibilities for architectural innovation. Check out this bridge in Glasgow, the UK's largest 3D printed structure, designed to reduce maintenance costs and reflect the region's industrial heritage.
3D printing has undoubtedly become an invaluable tool in architectural projects, offering architects unprecedented design freedom, rapid prototyping capabilities, sustainability benefits and even greater customer satisfaction. With technological advances, architects are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in design and construction. With 3D printing, the architecture industry is poised to usher in a new era of innovation, efficiency and sustainability on Earth and in space. Learn more about how 3D printing and other digital manufacturing methods deliver results that are literally out of this world.
To enable a variety of geometries, the parts can be printed using the sterolithography process (sla 3d printing). MicroFine Green™ is an SLA material
 5 Most Common Precision CNC Machining MethodsOctober 24, 2023CNC machining is a generic term used for a variety of machining applications. CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control and refers to the programmable features of a machine that allow it to perform many functions with minimal manual control. CNC machining is the manufacture of parts using CNC-controlled machines. The term describes a series of subtractive manufacturing processes that remove material from a bar or blank to produce a finished part. There are 5 different types of CNC equipment to perform the 5 common types of CNC Precision Machining.view
5 Most Common Precision CNC Machining MethodsOctober 24, 2023CNC machining is a generic term used for a variety of machining applications. CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control and refers to the programmable features of a machine that allow it to perform many functions with minimal manual control. CNC machining is the manufacture of parts using CNC-controlled machines. The term describes a series of subtractive manufacturing processes that remove material from a bar or blank to produce a finished part. There are 5 different types of CNC equipment to perform the 5 common types of CNC Precision Machining.view What Is the Failure of a Mechanical Part? How Many Forms of Failure of Parts Are There?October 26, 2023When the mechanical parts in the design of the predetermined period and under the specified conditions, can not complete the normal function, it is called failure. General mechanical parts failure form is based on the failure of the external morphological characteristics to the classification, including: wear failure, fracture failure, corrosion failure and distortion failure.view
What Is the Failure of a Mechanical Part? How Many Forms of Failure of Parts Are There?October 26, 2023When the mechanical parts in the design of the predetermined period and under the specified conditions, can not complete the normal function, it is called failure. General mechanical parts failure form is based on the failure of the external morphological characteristics to the classification, including: wear failure, fracture failure, corrosion failure and distortion failure.view Aluminum Alloy Anodic Oxidation Common ProblemsOctober 23, 2023Anodizing is one of the most common metal surface treatment operations performed on aluminum parts. It is an electrochemical process that involves immersing aluminum parts in a series of tanks to transform the aluminum surface into a durable and corrosion-resistant finish.view
Aluminum Alloy Anodic Oxidation Common ProblemsOctober 23, 2023Anodizing is one of the most common metal surface treatment operations performed on aluminum parts. It is an electrochemical process that involves immersing aluminum parts in a series of tanks to transform the aluminum surface into a durable and corrosion-resistant finish.view![Chamfer 101: Understanding Chamfers and Chamfered Edge [Quick Guide]](/uploads/image/20231123/14/chamfer-101-understanding-chamfers-and-chamfered-edge-quick-guide_400x400.webp) Chamfer 101: Understanding Chamfers and Chamfered Edge [Quick Guide]November 23, 2023Gain comprehensive knowledge about chamfers, including types, advantages and limitations, various methods of measurement and a comparative feature analysis.view
Chamfer 101: Understanding Chamfers and Chamfered Edge [Quick Guide]November 23, 2023Gain comprehensive knowledge about chamfers, including types, advantages and limitations, various methods of measurement and a comparative feature analysis.view Unlocking Precision: The Definitive Guide to Machined Surface Finish in CNC MachiningNovember 10, 2023Welcome to the realm of precision engineering, where the art of CNC machining meets the science of Machined Surface Finish. In this comprehensive exploration, we journey through the intricacies of this vital process, revealing its nuances and applications. As a leader in CNC machining services, Richconn is your trusted partner in achieving unparalleled quality and precision.view
Unlocking Precision: The Definitive Guide to Machined Surface Finish in CNC MachiningNovember 10, 2023Welcome to the realm of precision engineering, where the art of CNC machining meets the science of Machined Surface Finish. In this comprehensive exploration, we journey through the intricacies of this vital process, revealing its nuances and applications. As a leader in CNC machining services, Richconn is your trusted partner in achieving unparalleled quality and precision.view CNC Machined Motorcycle Parts: Precision Craftsmanship by RichconnNovember 14, 2023Rev up your expectations as we delve into the intricate world of CNC machined motorcycle parts. I'm excited to guide you through the details, showcasing how Richconn is your go-to source for precision solutions. Let's ride into the comprehensive exploration!view
CNC Machined Motorcycle Parts: Precision Craftsmanship by RichconnNovember 14, 2023Rev up your expectations as we delve into the intricate world of CNC machined motorcycle parts. I'm excited to guide you through the details, showcasing how Richconn is your go-to source for precision solutions. Let's ride into the comprehensive exploration!view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru 


