Galvanization and galvannealing are two distinct coating processes that entail applying a zinc coating to a sheet metal component. Despite their similar-sounding names, they serve different purposes, involve different procedures, have varying levels of acceptance, and yield different outcomes, all of which influence their popularity. The disparities in the manufacturing processes will ultimately dictate the steel's characteristics. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the variances between these two coating methods in order to select the most suitable one for your project. In this article, you have the outline of the basic similarities and differences between galvanized vs galvannealed steel to help you make the best choice.
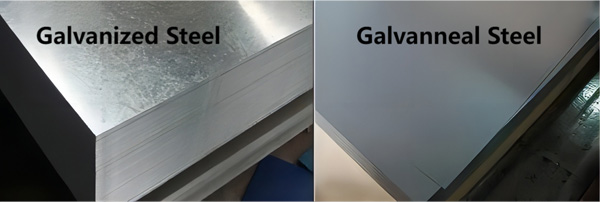
What does galvanized steel look like? Galvanized steel is characterized by its distinctive look and offers a range of properties that contribute to its widespread usage across different industries. Here are the detailed properties of galvanized steel:
Durability
Galvanized steel is renowned for its outstanding durability. The zinc coating acts as a robust shield against moisture, chemicals, and environmental factors, ensuring that steel galvanized is resistant to damage and wear. It can endure harsh conditions, including outdoor settings, with minimal degradation.
Exceptional Protection
The zinc coating on galvanizing steel offers superb protective properties, safeguarding the underlying steel from rust, oxidation, and corrosion. Galvanized steel is particularly well-suited for applications that require long-term corrosion protection, such as construction, infrastructure, and outdoor equipment.
Self-Healing Ability
Galvanized steel possesses a unique self-healing attribute. In case of scratches or damage to the zinc coating, a protective layer of zinc oxide and zinc carbonate forms over the affected area, effectively sealing it off from further corrosion. This self-healing feature helps maintain the steel's integrity and prolong its lifespan, making galvanized steel a dependable, long-lasting solution for applications that demand exceptional corrosion resistance.
Easy Maintenance
Galvanized steel is low-maintenance and does not require frequent repainting or recoating to preserve its corrosion resistance. The zinc coating offers durable protection, minimizing the need for regular upkeep, touch-ups, or replacements.
Versatility
Galvanized steel is incredibly versatile and can be tailored through fabrication, forming, or welding to fulfill unique needs. This adaptability renders galvanized steel suitable for diverse applications in sectors such as construction, automotive, agriculture, and manufacturing industries.
Cost-Effectiveness
Galvanized steel presents a cost-effective solution in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance. With its prolonged durability and resistance to corrosion, galvanized steel minimizes the requirements for frequent repairs, replacements, and associated expenses. It emerges as a dependable and economical choice for a wide array of applications.

Galvannealed steel exhibits unique properties that set it apart from other steel coatings. Here are the detailed characteristics of galvannealed steel:
Corrosion Resistance
Galvannealed steel demonstrates superior resistance to corrosion as a result of the zinc-iron alloy layer that is created during the galvannealing process. This zinc-iron alloy layer acts as a strong protective shield against rust and corrosion, enhancing the durability of galvannealed steel, especially in challenging environmental conditions.
Paint Adhesion
A significant characteristic of galvannealed steel is its outstanding paint adhesion capability. The textured surface produced by the galvannealing process, which is matte and rough, offers an optimal texture for paint adhesion. This particular attribute is essential in scenarios where steel requires painting or coating for added protection or decorative purposes, including applications like automotive body panels and appliances.
Weldability
Galvannealed steel is known for its excellent weldability, making it easier to weld and fabricate. The zinc-iron alloy layer formed during the galvannealing process provides beneficial properties for welding, assisting in reducing weld spatter and creating strong weld joints. This attribute is advantageous for industries that involve extensive welding operations, such as automotive manufacturing and construction.
The production of galvanized steel entails multiple stages to coat the steel with a zinc layer, which enhances its resistance to corrosion. The comprehensive process description of manufacturing galvanized steel is outlined as follows:
1. Surface Preparation
The steel to be galvanized is first thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, rust, or contaminants. This is commonly achieved by dunking the steel in a degreasing solution or employing chemical cleansers. The objective is to guarantee a pristine and even surface for effective adherence of the zinc coating.
2. Acid Pickling
Following the initial cleaning process, the steel is submerged in an acid solution, typically a diluted blend of hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid. Referred to as acid pickling, this stage eliminates any residual mill scale, rust, or oxides from the surface of the steel. Additionally, it serves to etch the surface, generating a coarse texture that enhances the adhesion between the steel and the zinc coating.
3. Fluxing
After the steel has been pickled, the next step is fluxing. Flux, typically a compound containing zinc ammonium chloride and additional additives, is administered onto the surface of the steel. This process assists in eliminating any lingering oxides, facilitates the zinc coating's flow, and readies the surface for galvanization.
4. Galvanization
The steel is immersed in a tank of molten zinc at a temperature of around 815°C to 850°C. Additional alloying elements like aluminum may be present to enhance the coating properties. The molten zinc reacts with the steel, creating a protective layer that covers the steel surface.
5. Removal and Cooling
Once the steel has been completely coated with zinc, it is gradually removed from the zinc bath to facilitate the drainage of any excess zinc. Subsequently, the steel is cooled either through air cooling or by rapid cooling in water. This process helps in solidifying the zinc coating and ensuring its strong adhesion to the steel surface.
Galvannealing is similar to galvanizing, but it adds to the annealing process. Using the hot-dip galvanization, after cleaning, pickling, fluxing, and galvanizing, you anneal the sheet metal part by heating it to about 10500F in an annealing oven.
The annealing process melts the iron part of the steel. The melted iron travels to the outermost part and forms an alloy with the zinc coating. Consequently, galvanneal steel parts are more durable, weldable, and less susceptible to damage than galvanized steel. Other post-processing procedures you can also introduce include temper rolling for a smooth surface.
Although galvanized and galvannealed steels have some similarities, there are key differences that can help determine the best material for your product between these steel types.
1. Manufacturing Process
Galvanized steel is manufactured by immersing steel in a molten zinc bath at a precise temperature of 450°C. The zinc coating provides a protective layer that shields the steel from corrosion by acting as a barrier between the steel and the environment.
The production process of galvannealed steel closely resembles that of galvanized steel, involving the immersion of steel in a molten zinc solution. Subsequently, the steel is heated in an annealing furnace to a higher temperature of approximately 1050°F to undergo annealing. This process causes the underlying iron to migrate to the surface, resulting in the formation of a zinc-iron alloy coating. The creation of this zinc-iron alloy coating adheres to the steel, enhancing its durability and corrosion resistance.
2. Coating
Galvanized steel is typically coated with a thin layer of pure zinc, presenting a polished appearance, with a potential minor iron content, similar to that found in stainless steel. This coating is measured in ounces per square foot, typically ranging from 0.30 oz/ft² (G30) to 2.35 oz/ft² (G235).
In contrast, galvannealed steel is often coated with a zinc-iron alloy layer, which results in a matte finish and comprises three distinct layers (gamma, delta, and zeta). The coating thickness can be measured in ounces per square foot, typically falling between 0.40 oz/ft² (A40) and 0.60 oz/ft² (A60). Additionally, manufacturers anneal galvannealed steel after applying the coating.
3. Properties
Galvanized steel features a shiny and spangled appearance, providing enhanced durability and protection against corrosion, rendering it appropriate for outdoor use. Nonetheless, its soft composition renders it susceptible to scratches.
In addition to the three main points mentioned above, the following table compares more distinctions between galvanized steel and galvannealed steel across various aspects.
Property | Galvanized Steel | Galvannealed Steel |
Weldability | Good | Excellent |
Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
Edge Protection | Standard | Enhanced |
Self-Healing | Yes | No |
Aesthetic Options | Various color options are available | Suitable for post-forming painting or coating |
Paintability After Forming | Yes | Yes |
Heat Resistance | Moderate | Moderate |
Cost-effectiveness | Cost-effective | Cost-effective |
Maintenance | Minimal maintenance required | Minimal maintenance required |
Galvannealed and galvanized steel are versatile sheet metal options suitable for a range of applications. Each type of steel possesses unique characteristics, indicating that neither galvannealed nor galvanized steel is universally superior for all uses. Therefore, selecting between galvannealed vs galvanized should be based on the specific requirements of your products.
Richconn is the top choice as your partner when seeking expert guidance to determine the most suitable steel type for your project. With profound knowledge in machining, their team of professionals is fully capable of aiding you in machining metal parts, whether they are made of galvannealed or galvanized steel.
 The Role of CNC Automotive Parts in Automotive IndustryJune 17, 2024CNC machining is often used for complex designs, small products and parts. With CNC machine tools, a wide range of parts can be processed more accurately.With the rapid development of the automotive i...view
The Role of CNC Automotive Parts in Automotive IndustryJune 17, 2024CNC machining is often used for complex designs, small products and parts. With CNC machine tools, a wide range of parts can be processed more accurately.With the rapid development of the automotive i...view DESIGN TIP: Thermoplastics and Thermosets in ComparisonOctober 18, 2023There are two main categories of plastic materials: thermoplastics and thermosets, which differ in their behavior under heat. In this design tip, we present a few considerations to keep in mind when using these materials.view
DESIGN TIP: Thermoplastics and Thermosets in ComparisonOctober 18, 2023There are two main categories of plastic materials: thermoplastics and thermosets, which differ in their behavior under heat. In this design tip, we present a few considerations to keep in mind when using these materials.view Tips for Selecting Trustworthy CNC Manufacturing Shops for CNC PartsApril 28, 2024This article introduces CNC manufacturing and provides you with professional advice and considerations for selecting reliable CNC manufacturing shops.view
Tips for Selecting Trustworthy CNC Manufacturing Shops for CNC PartsApril 28, 2024This article introduces CNC manufacturing and provides you with professional advice and considerations for selecting reliable CNC manufacturing shops.view Top 10+ Must-have Machinist ToolsFebruary 26, 2024Understanding the right machinist tools can boost productivity. This article highlights three essential tool categories.view
Top 10+ Must-have Machinist ToolsFebruary 26, 2024Understanding the right machinist tools can boost productivity. This article highlights three essential tool categories.view American Scientific Research Has Found A Fast And Effective Processing Method Of Low-Temperature Titanium AlloyMay 30, 2022Titanium is widely used in the aerospace industry because of its high strength and low density. However, compared with steel, aluminum, and other metals, its hot processing cost is high and it is at a...view
American Scientific Research Has Found A Fast And Effective Processing Method Of Low-Temperature Titanium AlloyMay 30, 2022Titanium is widely used in the aerospace industry because of its high strength and low density. However, compared with steel, aluminum, and other metals, its hot processing cost is high and it is at a...view The Functional Advantages of Custom PVD Coating in Automotive DesignJanuary 5, 2024When it comes to automotive design, every detail matters. From the sleek lines of the exterior to the carefully crafted interior, each element plays a crucial role in creating a unique and memorable d...view
The Functional Advantages of Custom PVD Coating in Automotive DesignJanuary 5, 2024When it comes to automotive design, every detail matters. From the sleek lines of the exterior to the carefully crafted interior, each element plays a crucial role in creating a unique and memorable d...view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru