Laser cutting technology has revolutionized the manufacturing and design industries with its precision and efficiency. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of Ultra-High Precision laser cutting, exploring its technology, applications, advantages, and challenges.
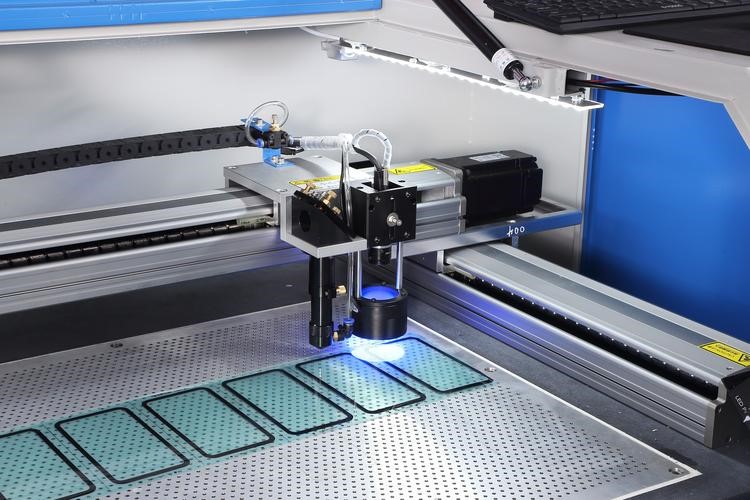

Ultra-High Precision laser cutting involves the use of focused laser beams to precisely cut through materials. The technology relies on the principles of optics and is characterized by its ability to achieve intricate cuts with minimal heat-affected zones.
Different types of lasers are employed in Ultra-High Precision cutting, including CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) lasers. Each type offers unique advantages, influencing their suitability for various applications.
The effectiveness of Ultra-High Precision laser cutting systems depends on several key components. These include the laser source, beam delivery system, CNC controller, cutting head, and assist gas system. A well-integrated and synchronized system ensures optimal cutting performance.
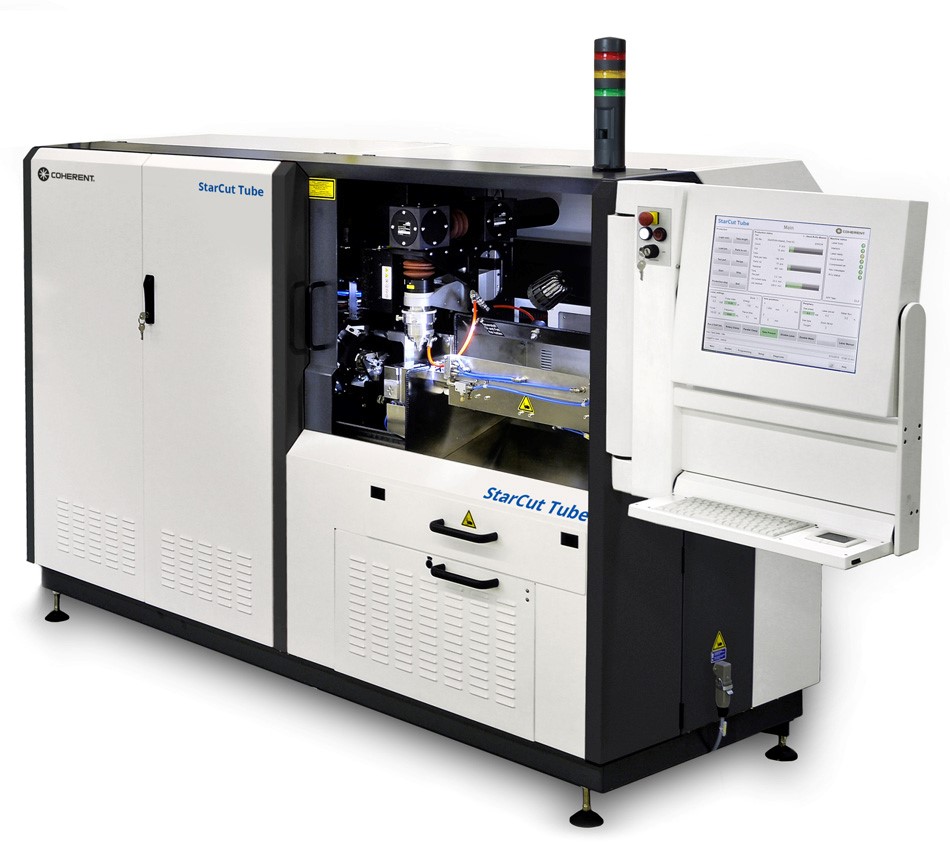

Laser Source: The choice of laser source, whether CO2 or fiber, impacts the cutting speed and quality.
Beam Delivery System: Efficient beam delivery is crucial for maintaining focus and precision.
CNC Controller: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems govern the movement of the cutting head, ensuring accuracy.
Cutting Head: The cutting head, equipped with lenses and nozzles, plays a vital role in directing the laser beam.
Assist Gas System: The use of assist gases, such as nitrogen or oxygen, aids in the cutting process.
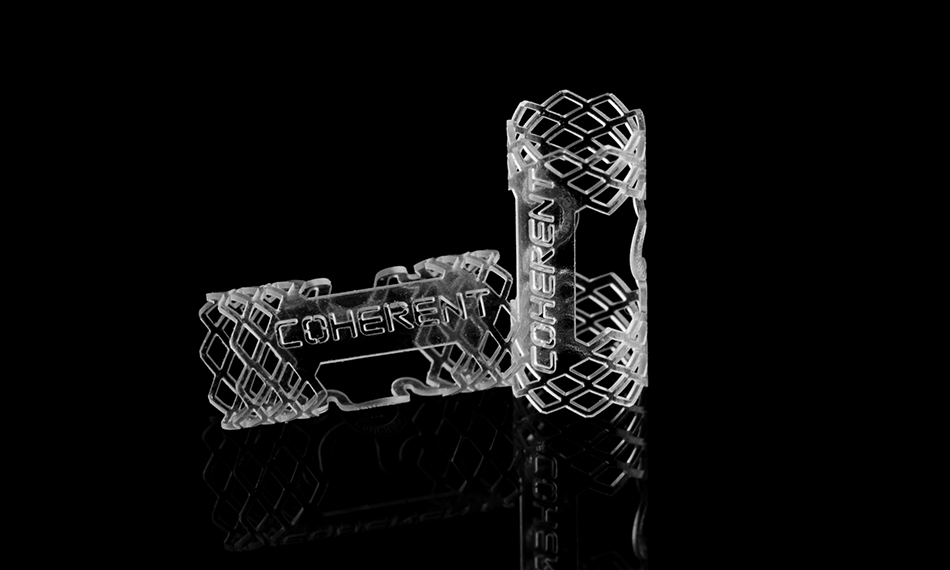

Several factors influence the precision of Ultra-High Precision laser cutting, including material properties, laser power, cutting speed, and focus control.
Material Properties: Different materials require adjustments in laser settings for optimal cutting results.
Laser Power and Intensity: Adequate power and intensity are essential for cutting through various materials.
Cutting Speed and Acceleration: Adjusting the speed and acceleration affects both efficiency and precision.
Focus Control: Maintaining a consistent focus is crucial for achieving accurate cuts.
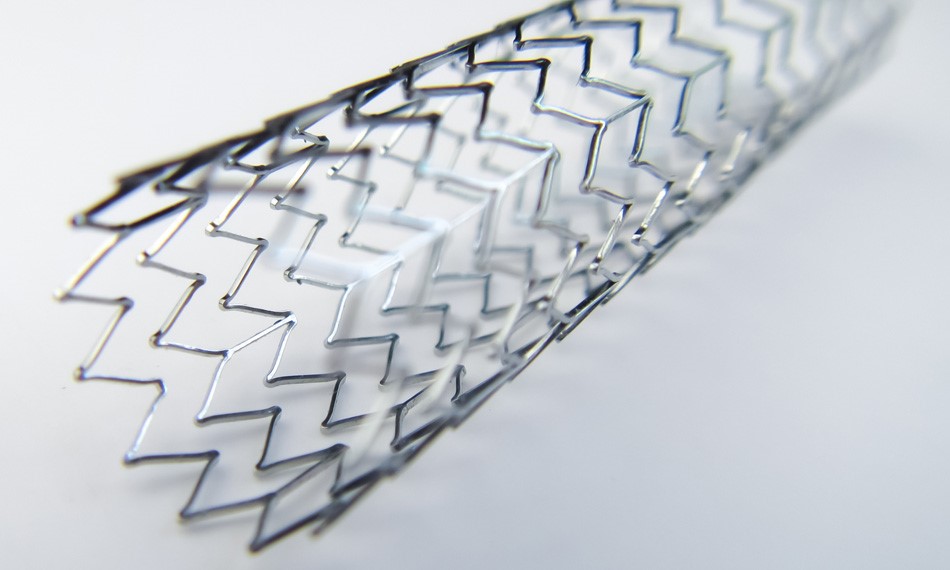
Ultra-High Precision laser cutting finds applications across various industries due to its versatility and accuracy.
Semiconductor industry: widely used in precision processing and manufacturing of semiconductor carriers.
Automotive Industry: Used for manufacturing intricate components with tight tolerances.
Aerospace Sector: Ideal for cutting lightweight materials in aircraft production.
Electronics Manufacturing: Precise cutting of electronic components for enhanced performance.
Medical Device Production: Creating intricate parts for medical devices with high precision,Such as: nitinol bracket.
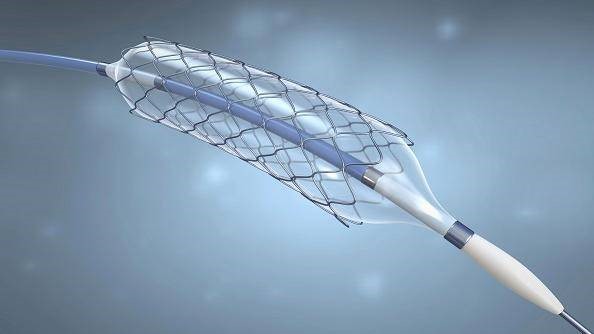
Art and Design: Enabling artists and designers to achieve intricate and detailed cuts.
The adoption of Ultra-High Precision laser cutting provides several advantages for manufacturers and designers.
Accuracy and Precision: Achieve intricate and precise cuts for complex designs.
Versatility in Material Compatibility: Cut various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Reduced Waste and Increased Efficiency: Minimize material waste and enhance production efficiency.

While Ultra-High Precision laser cutting offers numerous benefits, it comes with its set of challenges.
Thermal Effects: The heat generated during cutting may lead to thermal effects and material distortion.
Maintenance and Operating Costs: Ultra-High Precision systems require regular maintenance, impacting operational costs.
Skill Requirements for Operators: Skilled operators are essential for optimizing the performance of these systems.
The continuous evolution of laser cutting technology brings forth innovative features.
Adaptive Optics: Systems with adaptive optics adjust in real-time for optimal cutting performance.
Fiber Laser Advancements: Fiber lasers offer improved efficiency and reliability in cutting operations.
Integration with AI and Automation: Incorporating artificial intelligence enhances precision and automation in laser cutting processes.
The future of Ultra-High Precision laser cutting holds exciting possibilities.
Continuous Advancements in Laser Technology: Ongoing research and development will lead to more advanced laser cutting systems.
Increased Use in Small-Scale Industries: As technology becomes more accessible, smaller industries will leverage Ultra-High Precision laser cutting for enhanced production.
While Ultra-High Precision laser cutting is powerful, it's essential to compare it with alternative cutting technologies.
Waterjet Cutting: Contrasting the benefits and drawbacks of waterjet cutting.
Plasma Cutting: Comparing precision levels with plasma cutting.
Traditional Mechanical Cutting: Analyzing the efficiency and precision of traditional mechanical cutting methods.
Beyond its technical aspects, Ultra-High Precision laser cutting contributes to a greener environment.
Energy Efficiency: Laser cutting is relatively energy-efficient compared to some traditional methods.
Minimization of Waste: Precision cutting reduces material waste, contributing to sustainability.
Compliance with Environmental Regulations: Meeting environmental standards through cleaner cutting processes.
Before adopting Ultra-High Precision laser cutting, businesses should consider key factors.
Factors to Consider: Material compatibility, system integration, and operational costs.
Best Practices: Implementing best practices to maximize the benefits of Ultra-High Precision laser cutting.
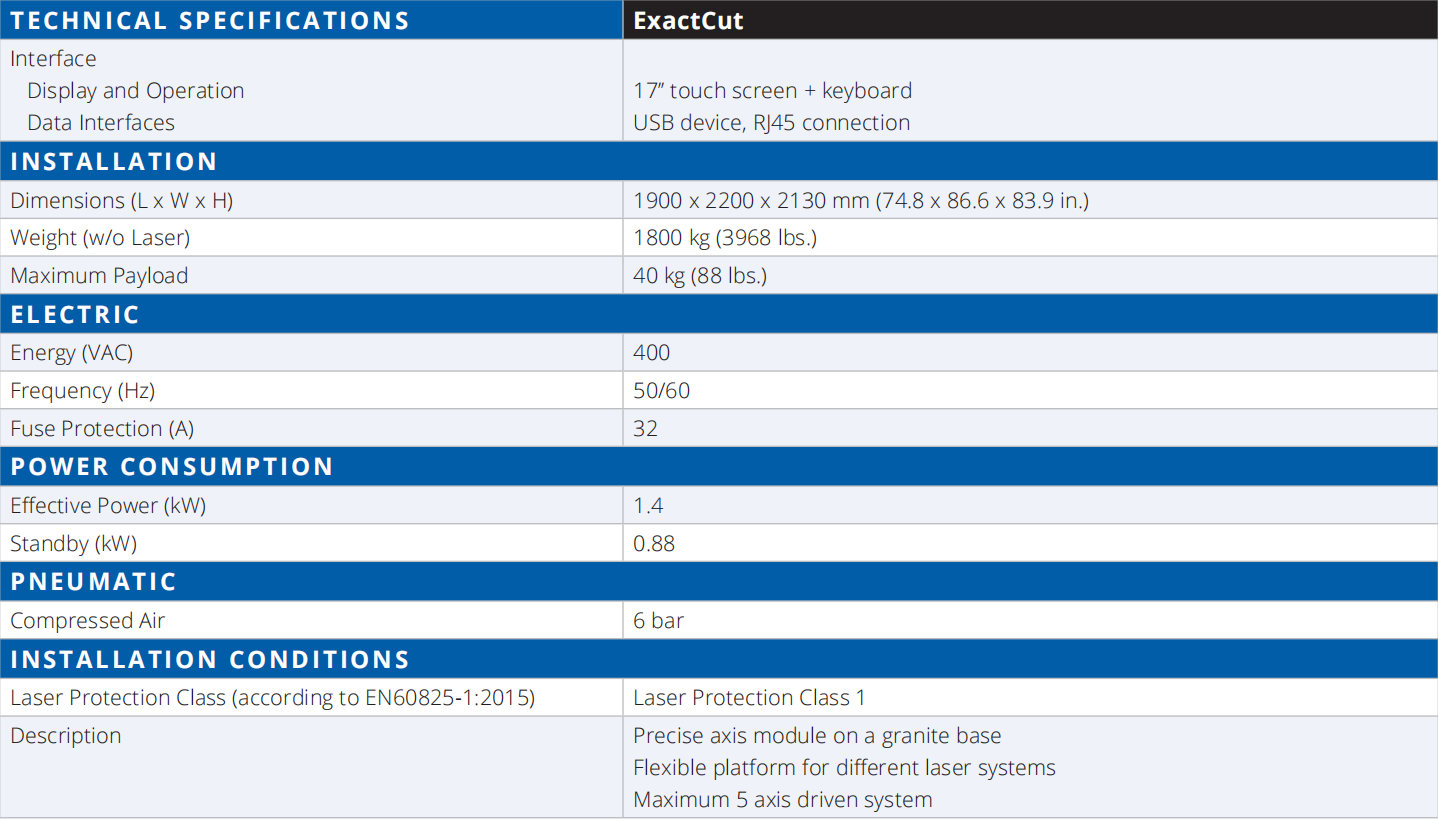
We have ultra-high-precision laser equipment, which can accept the ultra-high-precision manufacturing needs of various industries, please see the figure below for specific equipment parameters
Welcome to contact:
In conclusion, Ultra-High Precision laser cutting technology has transformed the manufacturing landscape. Its ability to provide accurate and intricate cuts across various materials makes it a valuable asset in numerous industries. As technology continues to evolve, we can anticipate even greater advancements, expanding the reach of Ultra-High Precision laser cutting.
Is Ultra-High Precision laser cutting suitable for all materials?
Ultra-High Precision laser cutting is versatile but may require adjustments for different materials.
How does laser cutting compare to traditional mechanical cutting in terms of speed?
Laser cutting is often faster, especially for intricate designs, due to its precision.
What maintenance is required for Ultra-High Precision laser cutting systems?
Regular cleaning, alignment checks, and lens replacements are common maintenance tasks.
Can Ultra-High Precision laser cutting be cost-effective for small businesses?
While initial costs may be higher, the efficiency and reduced waste can make it cost-effective over time.
What safety measures should be taken when using Ultra-High Precision laser cutting systems?
Operators should wear appropriate protective gear, and safety protocols must be strictly followed.
 Basic of Gear Manufacturing: A Guide to Learn about Gear Production ProcessesAugust 29, 2023There is no single process for manufacturing gear because several processes are required based on the type and application. The gears need to be in absolutely perfect condition to adapt to strenuous c...view
Basic of Gear Manufacturing: A Guide to Learn about Gear Production ProcessesAugust 29, 2023There is no single process for manufacturing gear because several processes are required based on the type and application. The gears need to be in absolutely perfect condition to adapt to strenuous c...view Unlocking the World of Machined Bushes: Your Comprehensive GuideNovember 8, 2023Are you ready to delve into the fascinating world of machined bushes? If you're curious about what machined bushes are, how they are made, where they are used, and how to choose the right ones for your specific needs, you've come to the right place. I'm here to guide you through this journey of discovery.view
Unlocking the World of Machined Bushes: Your Comprehensive GuideNovember 8, 2023Are you ready to delve into the fascinating world of machined bushes? If you're curious about what machined bushes are, how they are made, where they are used, and how to choose the right ones for your specific needs, you've come to the right place. I'm here to guide you through this journey of discovery.view CNC Machining Services and Engineered Machined Products: Meeting Manufacturing NeedsNovember 7, 2023Are you looking to understand the world of CNC machining and engineered machined products better? You're in the right place! I'm here to guide you through the intricate world of CNC machining, engineered machined products, and how Richconn can be your trusted partner in this journey.view
CNC Machining Services and Engineered Machined Products: Meeting Manufacturing NeedsNovember 7, 2023Are you looking to understand the world of CNC machining and engineered machined products better? You're in the right place! I'm here to guide you through the intricate world of CNC machining, engineered machined products, and how Richconn can be your trusted partner in this journey.view Machining Inspection ProcessOctober 19, 2023A good precision machine shop must have a first-class inspection process and inspection equipment. Here is a brief introduction to Richconn's inspection standards.view
Machining Inspection ProcessOctober 19, 2023A good precision machine shop must have a first-class inspection process and inspection equipment. Here is a brief introduction to Richconn's inspection standards.view Understanding machining tools: types, uses and selectionNovember 1, 2023Machining tools are vital tools in manufacturing, used to cut, chip, grind and shape a wide range of materials, from metals to plastics to wood. Different tool types are used for different processes and materials to meet a variety of machining needs. Below are five common types of machining tools that are used in a wide range of manufacturing and processing applications.view
Understanding machining tools: types, uses and selectionNovember 1, 2023Machining tools are vital tools in manufacturing, used to cut, chip, grind and shape a wide range of materials, from metals to plastics to wood. Different tool types are used for different processes and materials to meet a variety of machining needs. Below are five common types of machining tools that are used in a wide range of manufacturing and processing applications.view Exploring Nylon: A World of PossibilitiesSeptember 28, 2023Nylon's remarkable strength and versatility have made it a cornerstone of the textile industry. From silky stockings to rugged outdoor wear, nylon fibers have revolutionized our wardrobes.view
Exploring Nylon: A World of PossibilitiesSeptember 28, 2023Nylon's remarkable strength and versatility have made it a cornerstone of the textile industry. From silky stockings to rugged outdoor wear, nylon fibers have revolutionized our wardrobes.view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru