Laser Etching is a high-precision processing technique widely used to create fine patterns, markings, and engravings on a variety of materials. It utilizes the high energy of a laser beam to gradually remove the surface of a material to create depth, patterns or text. Laser Etching is a non-contact processing method that offers a high degree of precision, control and sophistication, making it widely used in a variety of industries.
The working principle of laser etching is based on the high energy and highly focused nature of the laser beam. In general, laser etching consists of the following key steps:
Energy transfer: A powerful laser beam is focused onto a small spot that has a very high energy density. This means that the laser beam can be highly focused, concentrating the light energy in a very small area.
Material absorption: After the laser beam hits the surface of a material, the material absorbs the light energy. The material that absorbs the light energy heats up rapidly until it reaches or exceeds its melting or vaporization point, depending on the amount of laser energy.
Material Removal: Once the material reaches a high enough temperature, it melts or vaporizes and is then broken up or evaporated by the energy of the laser beam. This results in the removal of material, which creates the desired pattern or indentation on the surface of the material.
Motion Control: Typically, the workpiece (object being processed) is subjected to precise motion control by the laser beam. This can be accomplished by moving the workpiece, moving the laser beam, or both at the same time. Motion control determines the final result of the laser etching.
Cooling and Curing: The etched surface needs to be cooled to ensure that the material re-solidifies and maintains the desired shape. Cooling is usually accomplished by stopping the laser irradiation or through additional cooling systems.
The key to laser etching is precise control of the energy, focus and motion of the laser beam, as well as the absorption and removal of material. This process allows for a very high degree of precision and sophistication without touching the surface of the workpiece.
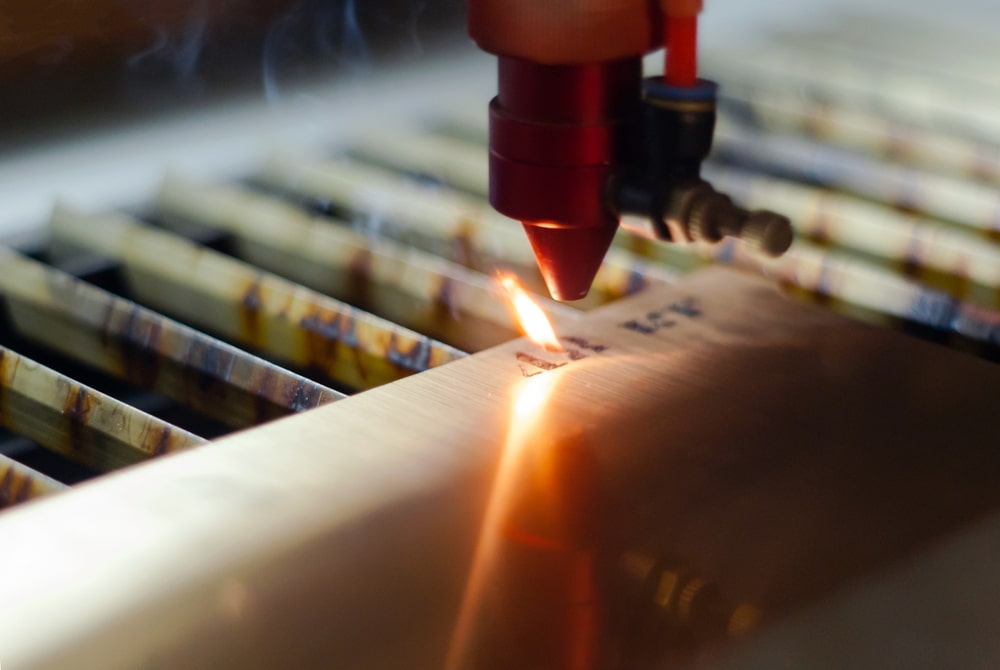

Laser etching is used in a wide variety of applications including, but not limited to, the following areas:
Metal Processing: laser etching can be used to scribe, mark and cut a variety of metal materials such as steel, aluminum and copper.
Plastic processing: It is also used to create logos, patterns and text on plastic products.
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS: laser etching is used for circuit board manufacturing and marking on microelectronic devices.
Medical devices: laser etching is used for marking, serial numbering and labeling of medical devices.
MEDICAL DEVICES: Marking and etching on medical devices to ensure product traceability and safety.
Automotive Industry:
Automotive parts: laser etching is used for markings, serial numbers and patterns on automotive parts.
Automotive glass: marking and scribing of anti-counterfeiting marks and patterns on automotive glass.
Decorative items: laser etching can be used for fine patterns and artwork on wood, glass, stone and leather products.
Jewelry: Intricate designs and logos are etched on jewelry and jewelry.
Aircraft parts: for marking and scribing aerospace parts to ensure a high degree of traceability and quality control.
SPACE EXPLORATION: Marking and logos on spacecraft and satellites to identify different components.
Packaging: to add brand logos, anti-counterfeiting features and serial numbers to packaging.
CUSTOMIZED PRODUCTS: Laser etching is used to personalize and customize consumer products such as phone cases, wallets and water bottles.
Laboratory equipment: laser etching is used in scientific laboratories to mark instruments and equipment.
MICROMACHINING: Laser etching is used in micro- and nanofabrication to fabricate microstructures and nanodevices.
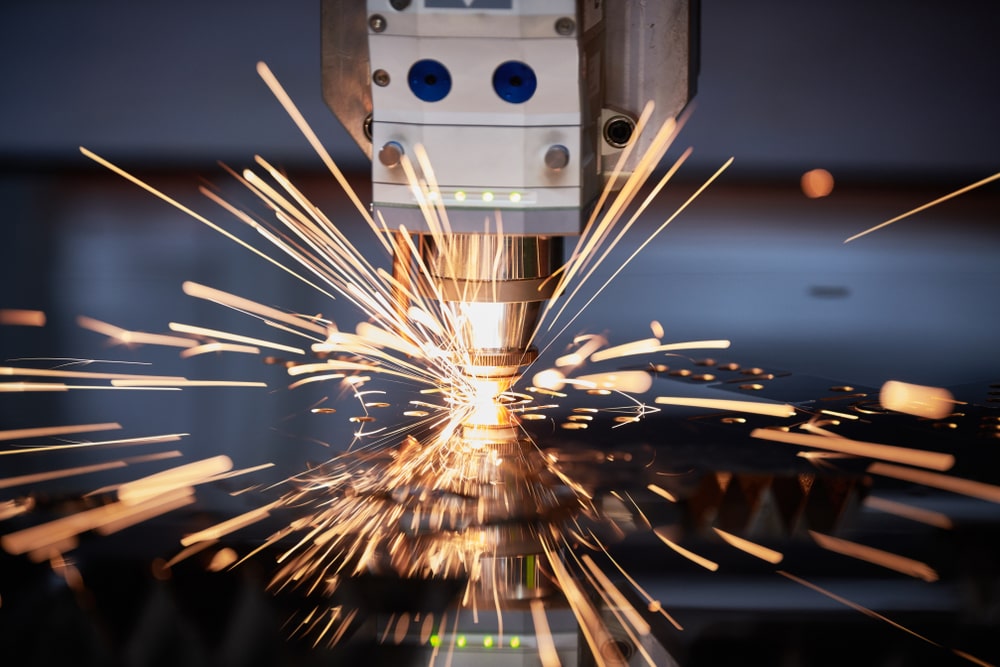

Laser etching is a versatile process that can be applied to various materials, including glass, metal, wood, aluminum, and stainless steel. Each material presents its own set of challenges and challenges. material presents its own set of challenges and advantages when it comes to laser etching.
Applications. Laser etched glass is commonly used for decorative purposes, such as creating intricate designs on glassware, glass awards, and decorative glass panels. It is also used in the automotive industry for adding logos, patterns, and information to automotive glass.
Advantages. Laser etching on glass produces precise, high-resolution designs. It provides a frosted or translucent appearance, depending on the desired effect.
Challenges. The main challenge with glass is the potential for cracking or chipping if not properly controlled, as the laser generates heat during the process.
Laser Etched QR Code.
Applications. QR codes can be laser etched onto various materials, including metal, plastic, and paper. They are commonly used for product labeling, marketing, and inventory tracking.
Advantages. Laser-etched QR codes are highly durable and can withstand environmental conditions, making them suitable for long-term use.
Challenges. The size and complexity of the QR code may affect the speed and precision of the laser etching process.
Laser Etching Metal.
Applications. Laser etching is extensively used in the metalworking industry for marking serial numbers, logos, and barcodes on metal components, such as machine parts, tools, and aerospace components.
Advantages. It provides permanent and highly precise markings on metal surfaces without affecting the structural integrity of the material.
Challenges. Some metals, like stainless steel, may require more laser power to etch effectively. Adjusting the laser parameters for different metals is crucial.
Adjusting the laser parameters for different metals is crucial.
Applications. Laser etching on wood is often used in woodworking, engraving intricate designs on wooden furniture, personalized gifts, and decorative items.
Advantages. Laser etching on wood produces fine details and can create both shallow and deep engravings, depending on the desired effect.
Challenges. The type and density of wood can affect the etching depth and quality. Care must be taken to avoid excessive burning or charring.
Applications. Aluminum is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. Laser etching is employed to mark serial numbers, part information, and logos on aluminum components.
Advantages. Laser etching on aluminum offers high precision and durability. It is resistant to wear and corrosion.
Advantages: Laser etching on aluminum offers high precision and durability. Different aluminum alloys may require adjustments to laser parameters for optimal results.
Challenges: Different aluminum alloys may require adjustments to laser parameters for optimal results. Stainless steel is commonly used in kitchen appliances, medical equipment, and architectural applications. Laser etching is used for branding, identification, and decorative purposes.
Advantages. Laser etching on stainless steel produces permanent, corrosion-resistant markings with high contrast.
Challenges: Stainless steel is a tough material, and etching it may require higher laser power and slower processing speeds compared to other materials.
Different types of laser equipment can be adapted to the nature and requirements of the material to achieve the best etching results.
Laser etching equipment typically varies depending on the application and type of material. Here are some common types of laser etching equipment:
CO2 Laser Etching Machines: These machines use carbon dioxide lasers and are suitable for many non-metallic materials such as plastics, wood, leather and glass. They are commonly used for decorative items, signs, packaging and woodworking.
Fiber Laser Etching Machines: Fiber lasers are suitable for materials such as metals and plastics. They offer high precision and speed, making them very popular in areas such as automotive, medical devices and electronics manufacturing.
UV Laser Etchers: These machines use UV lasers and are suitable for applications where high precision and microfabrication are required, such as microelectronic devices and semiconductor manufacturing.
Nd:YAG Laser Etchers: These machines use neodymium-doped YAG crystals as the laser medium and are suitable for etching materials such as metals, ceramics and plastics.
Direct Laser Writers (DLW): DLW systems use a highly focused laser beam to directly write materials, typically for the fabrication of micro and nano devices and structures.
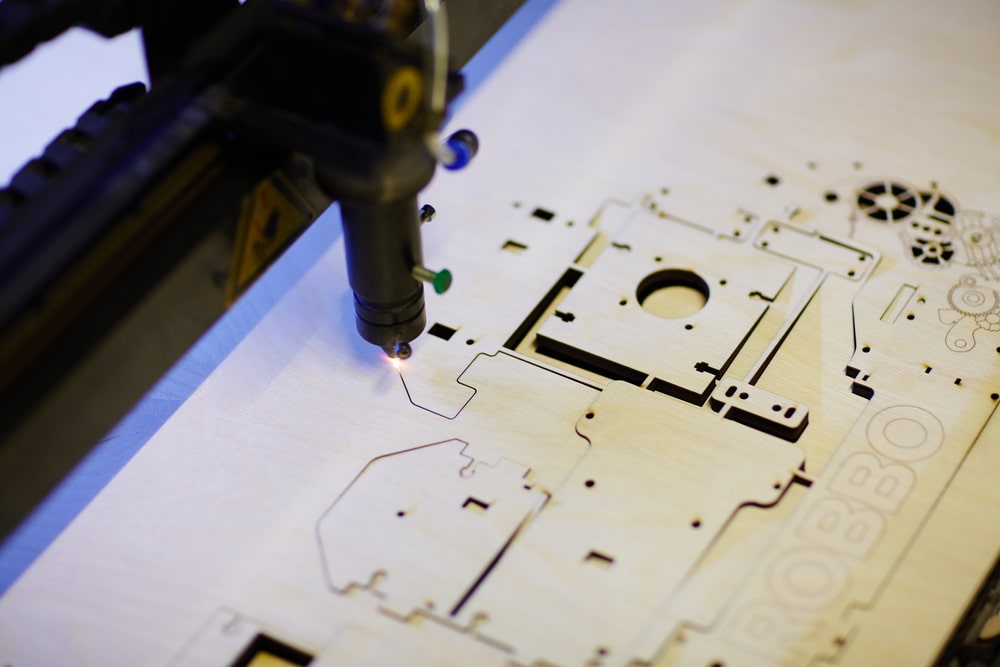
Laser Etching and Laser Engraving are two methods of processing materials using laser technology that are similar in many ways, but also have some key differences. This article will discuss the differences between Laser Etching and Laser Engraving in detail, including the principle of operation, areas of application, materials and end results.
Laser etching is a non-contact processing method that works based on the following steps:
Energy transfer: A high-energy laser beam is focused onto a small spot on the surface of the material.
Material Absorption: The material absorbs the energy of the laser beam, resulting in an increase in temperature.
Etching process: When the material reaches a high enough temperature, it can melt or vaporize, and then the energy of the laser beam can gradually remove the surface of the material to form the desired pattern, logo or text.
MOTION CONTROL: Typically, the workpiece is subjected to precise motion control under the laser beam to create specific shapes and patterns.
Laser engraving also uses a laser beam, but works on a slightly different principle:
Energy Transfer: Similar to etching, the laser beam is focused onto a small spot on the surface of the material.
Material Absorption: The material absorbs the energy of the laser beam, resulting in a localized heating.
Engraving Process: Unlike etching, laser engraving creates deep indentations or grooves in the surface of the material by controlling the intensity and duration of the laser beam, causing localized evaporation or oxidation of the material. This is equivalent to carving a pattern of depressions into the surface of the material.
Motion Control: Similar to etching, the workpiece is subjected to precise motion control under the laser beam.
Laser etching is mainly used in the following application areas:
Marking and labeling: Laser etching is used to create logos, markings, serial numbers and text on the surface of a material to improve product identification and traceability.
Decorative and Artwork: It is commonly used to create beautiful patterns and designs on decorative items, artwork, gifts and jewelry.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing: Marks and logos are added to circuit boards, semiconductor devices and electronic components for quality control.
Medical Devices: Laser etching can be used for markings, logos and serial numbers on medical devices to ensure the quality and safety of medical products.
Laser engraving is mainly used in the following application areas:
Engraving and Depth Cutting: Laser engraving can be used to create deep indentations, grooves and patterns on the surface of materials. This is used in the manufacturing industry to create decorative patterns or depth markings.
Printing rollers and molds: It can be used to manufacture printing rollers, molds and stencils to create intricate patterns on paper, plastic and metal.
Industrial Manufacturing: In industry, laser engraving can be used to engrave and mark mechanical parts and tools.
Personalized Products: Laser engraving is commonly used for personalized and customized products such as personalized gifts, woodwork and home décor.
Laser etching is commonly used to engrave, mark and symbolize a wide range of materials, including metal, plastic, glass, ceramics, leather, wood, stone and more. It has a relatively wide range of applications.
Laser engraving is mainly used for materials that can produce deep engravings on the surface, such as metal, wood, plastic, stone and ceramics. Due to its large engraving depth, it is usually used for applications that require deep markings or indentations.
The end result of laser etching is usually a flat logo, mark or pattern on the surface of the material. Because laser etching gradually removes material from the surface of the material, the etch is shallow, but usually very precise.
The end result of laser engraving is to produce deep indentations, grooves or three-dimensional patterns on the surface of the material. These indentations have a depth that can be seen and touched, and are therefore often used in decoration, ornamentation, and industrial manufacturing.
Laser etching and laser engraving are two different laser processing technologies that differ significantly in terms of how they work, their areas of application, the materials they are applied to, and the end result. Laser etching is primarily used to create flat logos, marks and patterns, while laser engraving is used to create deep indentations and three-dimensional patterns on the surface of a material. The choice of which technique to use usually depends on the specific application requirements and material properties. Either way, laser technology offers high precision, quality and non-contact processing methods used in a wide variety of industrial and creative fields.
When you need precision machining and marking services, Richconn is the perfect choice! Not only are we an exceptional CNC machining service provider, but we also offer you laser etching services. Let us help you achieve the following goals:
Precision machining: Our CNC machining equipment is highly accurate and efficient, allowing us to manufacture precision parts and components for you.
Marking and labeling: Whether you need to create logos, markings, serial numbers, or patterns on metal, plastic, wood, or other materials, our laser etching technology ensures long-lasting, high-quality results.
Customization: We can tailor our processing and marking solutions to meet your unique project requirements.
Multi-material applications: No matter what material your project involves, we have experience processing and marking a wide range of materials, including metals, glass, ceramics, plastics, and more.
Controlled Delivery: Our dedication to timely delivery and project management ensures that your project stays on schedule.
When you choose Richconn, you'll receive high-quality, high-precision machining and marking services that meet your needs and help you achieve project success. Contact us for more details!
 CNC Machining and AI: How Artificial Intelligence is Impacting the FieldOctober 25, 2023Artificial Intelligence is having a profound impact on CNC machining services, transforming operations and delivering many benefits. Here are some of the key areas where AI is playing a major role:view
CNC Machining and AI: How Artificial Intelligence is Impacting the FieldOctober 25, 2023Artificial Intelligence is having a profound impact on CNC machining services, transforming operations and delivering many benefits. Here are some of the key areas where AI is playing a major role:view Metal CNC Machine: The Beginner’s Guide to Aluminum CNC MachineMarch 27, 2024Aluminum CNC machine is one of the most common types of metal CNC machines. Let’s have a look at its types, processes, applications and benefits.view
Metal CNC Machine: The Beginner’s Guide to Aluminum CNC MachineMarch 27, 2024Aluminum CNC machine is one of the most common types of metal CNC machines. Let’s have a look at its types, processes, applications and benefits.view DESIGN TIP: Thermoplastics and Thermosets in ComparisonOctober 18, 2023There are two main categories of plastic materials: thermoplastics and thermosets, which differ in their behavior under heat. In this design tip, we present a few considerations to keep in mind when using these materials.view
DESIGN TIP: Thermoplastics and Thermosets in ComparisonOctober 18, 2023There are two main categories of plastic materials: thermoplastics and thermosets, which differ in their behavior under heat. In this design tip, we present a few considerations to keep in mind when using these materials.view What Is Prototype Manufacturing? Process, Benefits, and Vital TipsOctober 25, 2023A good understanding of prototype manufacturing will help you make the best choice for your project. Learn more about it from this passage.view
What Is Prototype Manufacturing? Process, Benefits, and Vital TipsOctober 25, 2023A good understanding of prototype manufacturing will help you make the best choice for your project. Learn more about it from this passage.view Comprehensive Insights into Metal Polishing Techniques and BenefitsJanuary 26, 2024Metal polishing is a reliable post-treatment process to enhance the surface quality of machined metal parts. Read on to discover more about metal polish.view
Comprehensive Insights into Metal Polishing Techniques and BenefitsJanuary 26, 2024Metal polishing is a reliable post-treatment process to enhance the surface quality of machined metal parts. Read on to discover more about metal polish.view Five Axis CNC Machine Tool: Precision Machining of Carbon Fiber Composite MaterialsMay 22, 2023Further CNC cutting and drilling of raw carbon fiber parts is necessary to meet the precision requirements or assembly needs. According to new material introductions, carbon fiber reinforced composite...view
Five Axis CNC Machine Tool: Precision Machining of Carbon Fiber Composite MaterialsMay 22, 2023Further CNC cutting and drilling of raw carbon fiber parts is necessary to meet the precision requirements or assembly needs. According to new material introductions, carbon fiber reinforced composite...view