Nowadays, there are various types of lathe tools used in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathe machines. Each tool is designed for specific applications and provides different functions. These lathe machine tools exhibit diverse structures, material compositions, and functions, contributing to a wide range of applications in part manufacturing.
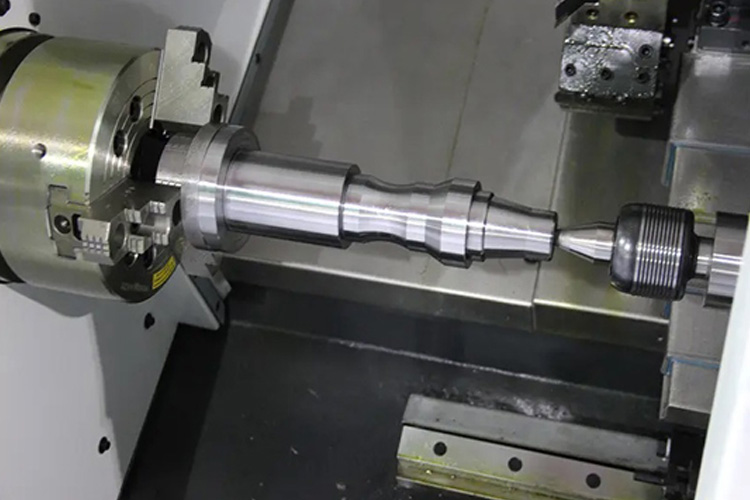

What is a lathe machine? A lathe is a machining tool that rotates a workpiece about its axis, allowing for precision operations such as turning, facing, boring, threading and drilling. The essence of a tools lathe lies in its capability to shape materials by selectively removing excess material, resulting in a finished product of the desired form and dimensions.
The basic components of a lathe CNC machine include the main spindle, which rotates the workpiece, and the cutting tool, responsible for material removal. Workpieces are secured in place by a clamping mechanism to ensure stability during the machining process. Lathe machines can vary in size and complexity, from small bench lathes to large industrial CNC lathe machines that automate and enhance the machining process.
As mentioned above, CNC lathe machine is a type of machining tool that utilizes computer numerical control technology to govern the motion and actions of cutting tools and workpieces. The machine is capable of executing various turning operations such as turning, facing, drilling, tapping, and grooving. CNC lathe machines can produce precise and intricate parts based on the design and dimensions specified by a computer program, demonstrating high efficiency and accuracy.
CNC lathe machines come with a variety of components, types, and configurations, which depend on factors like their shape, materials, direction, and structure. Different CNC lathe machines offer distinct advantages and find applications in various fields.
A CNC machine lathe consists of components that collectively facilitate precision machining. These main parts include:
Headstock: Positioned on the left side of the machine.
Central to the main action, it houses the main spindle where motor-generated power is applied.
Tailstock: Located on the right side of the machine.
Moves along the bed, providing crucial support to the workpiece and ensuring stability during machining.
Bed: Forms the lathe's base.
Serves as the foundation for attaching all lathe cutting tools.
Spindles: Integral to the headstock, where the main spindle is housed.
Plays a key role in the rotation of the workpiece.
Motor: Positioned below the bed, near the headstock.
Generates the power required for the lathe's operations. It can be electric (common) or hydraulic.
Tool Rest: Responsible for adjusting the height and rotation of the lathe.
A crucial component for supporting and maneuvering cutting tools during the machining process.
Lathe machines encompass various types, each tailored to specific machining needs. Notable categories include CNC lathes, speed lathes, turret lathes, and engine lathes.
CNC Lathes:
Automated for precision and efficiency, CNC lathes offer controlled machining processes, finding wide applications across industries.
Speed Lathes:
Designed for lighter tasks, Speed lathes excel in simplicity, making them ideal for woodworking applications.
Engine Lathes:
Versatile and general-purpose, Engine lathes adapt to diverse applications, proving reliable in various machining tasks.
Turret Lathes:
Known for rapid tool changes, Turret lathes are efficient in high-volume production and adept at handling intricate designs.
Diverse CNC lathe configurations also cater to specific machining requirements, offering versatility and precision in manufacturing processes. Notable examples include:
2-Axis CNC Lathe:
It often features X and Z axes and executes operations such as outer/inner diameter machining, facing, drilling, and tapping. It fully utilizes a turret-mounted cutting tool.
3-Axis CNC Lathe:
It incorporates the X, Z, and C axes and performs milling, boring, and turning operations. It employs a live tool system for tool rotation.
It integrates X, Z, C, and Y axes and facilitates off-center operations like eccentric drilling, tapping, and milling. It often utilizes a live tool system for rotation.
Multi-Spindle CNC Lathe:
It is equipped with multiple spindles for simultaneous rotation of different workpieces. It utilizes multiple turrets for varied tool movements and enables concurrent machining operations on diverse workpieces in a single setup for better productivity and efficiency.
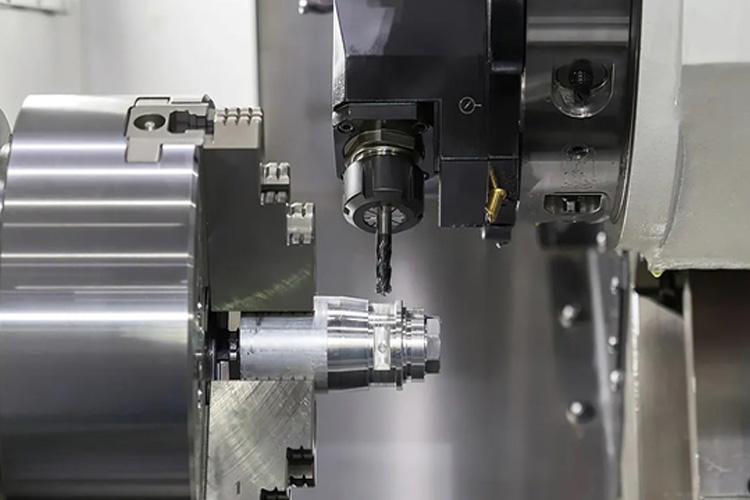

CNC lathe tools can produce precise and complex parts with high efficiency and accuracy. There are many classifications of CNC lathe tools, depending on their shape, material, direction, and structure. Different types of CNC lathe tools have different advantages and applications in CNC machining.
Lathing tools play a pivotal role in shaping workpieces during the machining process.
Turning Tools:
Turning tools are the workhorses of lathing, tasked with the removal of material along the length of a rotating workpiece. This results in the desired outcome of a final part with a meticulously reduced diameter. These tools come in various shapes and sizes, adapting to the intricacies of different turning operations.
Facing Tools:
Precision in creating smooth or textured surfaces is the forte of facing tools. Specifically designed for facing operations, these tools excel in the systematic removal of material layers. The outcome is a surface finish that meets the specifications, be it smooth for aesthetic appeal or rough for enhanced grip.
Boring Tools:
Boring tools, armed with a boring bar and cutting tool, undertake the crucial task of enlarging existing holes or crafting internal shapes within a workpiece. Their design ensures accuracy and efficiency, making them vital for applications demanding precision in internal dimensions.
Chamfering Tools:
The creation of chamfers, those slanting edges on the corners of workpieces, is the domain of chamfering tools. Crafted from high-speed steel or carbide, these tools bring finesse to the workpiece's edges, simultaneously enhancing aesthetics and functionality.
Thread Cutting Tools:
In the realm of cylindrical workpieces, thread cutting tools come into play, fashioning intricate spiral thread patterns. The determination of thread angles relies on the nose angles of these tools, making them indispensable for creating threaded components like bolts, nuts, and screws.
Knurling Tools:
Adding texture and grip to workpiece surfaces, knurling tools employ two or more metal rolling wheels with embossed patterns. These wheels meticulously create raised patterns, enhancing both the visual appeal and functionality of the machined part.

Some lathe cutting tools are designed for specific purposes or applications, such as grooving, parting, threading, etc. Below are some of the common types of lathe cutting tools classified based on their specialization.
Forming Tools:
Forming tools combine turning and grooving to shape complex parts with precision.
Applications: Essential in CNC precision machining, especially for contouring concave or convex shapes like gears.
Taper Turning Tools:
They are tailored for machining tapered surfaces, crucial for creating conical features.
Applications: Widely used in automotive and manufacturing for crafting components like shafts, cones, and nozzles.
Grooving Tools:
They create grooves on cylindrical surfaces, with V-shaped and square-cutting variations.
Applications: Suitable for making slots, grooves, or parting at specific cut depths. Efficient chip evacuation enhances performance.
Parting Tools:
Parting tools help to cut off parts from the main body, essential in separating finished parts from bar stock.
Applications: Various types, including standard, angled, and insert parting tools, cater to diverse cutting needs.
Threading Tools:
Threading tools can create external or internal threads by the thread tool lathe, commonly used in bolts, nuts, and screws.
Applications: Different types, such as single-point, multi-point, tap, and die, cater to various threading requirements.
CNC lathe tools are crafted from various materials, each selected based on workpiece characteristics, machining operations, and desired outcomes. There are several kinds of materials for CNC lathe tools. The most common ones include:
High-speed steel (HSS):
Composition: Alloy elements like tungsten, carbon, vanadium, and chromium.
Advantages:
1. High hardness, strength, and wear resistance;
2. Suitable for rough and semi-finish machining of metals like steel, aluminum, and cast iron;
3. Easy to sharpen with a long tool life.
Carbide:
Composition: Hard particles of tungsten carbide bonded with metals like cobalt or nickel.
Advantages:
1. Very hard and wear-resistant;
2. Suitable for cutting almost all materials, including hard metals like stainless steel and titanium;
3. Operates at high speeds with a longer tool lifespan.
Diamond:
Composition: Synthetic diamond crystals grown under high pressure and temperature.
Advantages:
1. Hardest and most wear-resistant tools;
2. Suitable for cutting extremely hard materials like glass or ceramics;
3. Provides an excellent surface finish. Operates at high speeds with a long tool life.
Ceramic:
Composition: Ceramic compounds like aluminum oxide or silicon nitride.
Advantages:
1. Very hard and heat-resistant;
2. Suitable for cutting hard metals like cast iron and heat-resistant alloys;
3. Ideal for high-speed cutting and dry machining. Provides an excellent surface finish.

The positioning of turning tools holds significant sway in molding the workpiece.
Right-Hand Tools: Remove materials as they move from right to left.
Advantages:
1. Common in CNC machining, cost-effective;
2. Cut towards the chuck, enhancing chip evacuation.
3. Ideal for turning, facing, threading, and creating flat surfaces on the workpiece end.
Left-Hand Tools: Remove materials as they move from left to right.
Advantages:
1. Less common, hence more expensive.
2. Cut away from the chuck, with chip formation towards the chuck.
3. Preferable for back turning, creating sharp shoulders on the workpiece back, and suitable for short workpieces ungripped by the sub-spindle chuck.
Round Nose Tools: Rough nose tools with narrow tips and no side or back rake angles.
Advantages:
1. Versatile for cutting in both right and left directions.
2. Ideal for achieving a smooth finish, complex profiling, contouring curved surfaces, and rounding corners.
Lathe tools are categorized based on their structure into three major types, each serving specific machining needs:
Single Body Tools:
They are constructed from a single material such as carbide, high-speed steel, or ceramic. It is known for its robustness, single body tools are go-to options for machinists seeking reliability and consistency in their machining endeavors. Single body tools are known for strength and widely applicable in standard machining operations.
Welding Lathe Cutting Tools:
The welding technique allows for the formation of cutting tools with unique geometries, facilitating modifications for novel applications and the seamless replacement of cutting inserts. They allow for custom geometries, modifications for new applications, and replacement of cutting inserts. They are cost-effective and versatile, especially suitable for adapting tools to new or complex parts.
Clamp Lathe Cutting Tools:
They utilize temporary joining methods, with a replaceable insert clamped to a tool holder. A lathe tool holder is a device that holds lathe cutting tools in place during machining. It comes in various lathe tool holder types. These include single-body tools, welding lathe cutting tools, clamp lathe cutting tools, etc. They are especially applicable in operations with a constant need for replaceable tool bits in a manual lathe machine.
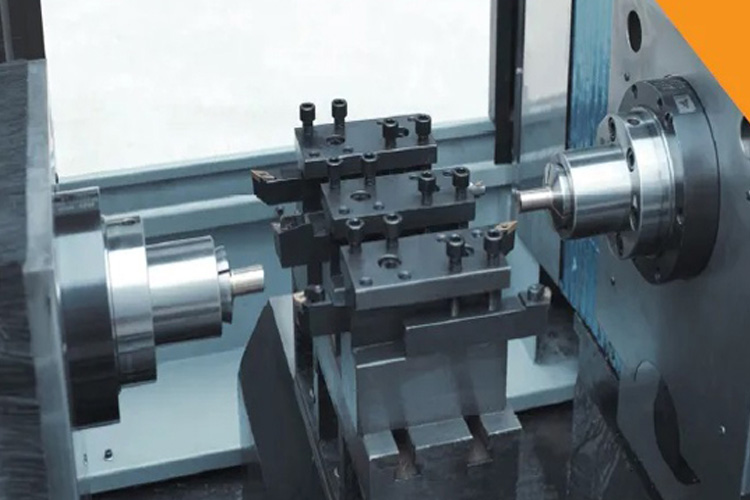

Selecting the right lathe tool is a critical decision in machining, and several key considerations play a pivotal role in ensuring optimal performance. Here are factors to take into account:
✔ Type of Lathe Machine:
Different lathe machines, such as 2-axis, 3-axis, 4-axis, or multi-spindle, have varying capabilities and tooling requirements. The machine type dictates features like live tool systems for multiple-axis rotation in advanced machines or simpler turrets for basic movements in 2-axis lathes.
✔ Material of the Workpiece:
The workpiece material often includes metal, wood, plastic, or ceramic options, which may influence the tool selection. Material properties like hardness, toughness, and heat resistance determine the appropriate tool material, such as carbide, diamond, ceramic, high-speed steel, or natural fiber.
✔ Machining Operation:
Different operations, including turning, facing, boring, threading, or grooving, demand specific tools tailored to their purposes. For instance, turning operations may require tools with perpendicular cutting edges like turning or chamfering tools, while threading operations may necessitate tools with V-shaped or U-shaped cutting edges like thread cutting tools or taps.
✔ Required Accuracy and Surface Finish:
The desired accuracy and surface finish levels, categorized as rough, semi-finish, or finish, set standards for dimensional tolerance, surface roughness, and quality. Lathing tools must align with these requirements, with rough operations benefiting from high cutting speeds and low feed rates, and finish operations requiring low cutting speeds and high feed rates.
In recent years, technological innovations have significantly transformed the landscape of lathe cutting tools, enhancing precision, efficiency, and versatility. Key advances include:
✔ Advanced Materials:
The utilization of advanced materials has become prevalent, offering improved properties such as hardness, thermal stability, toughness, and wear resistance. High-performance carbide grades, ceramics like silicon nitride and alumina, and coatings such as TiAlN and AlTiN contribute to elevated tool performance.
✔ Custom Tooling:
With the rising demand for complex and customized parts, lathe cutting tools are evolving to be more flexible and adaptable. Some manufacturers offer fast and flexible custom tooling services, leveraging advanced design software, cloud technology, and automation to create tailor-made tools that meet specific customer needs.
✔ Improved Tools Geometry:
Modern turning tools now boast enhanced geometry designed to optimize machining efficiency. Chip breakers have been integrated to improve chip evacuation and surface finish. Additionally, tools incorporate variable helix and pitch designs, reducing vibration and ensuring stability during lathe operations.
✔ New Machining Techniques:
To address the demand for higher productivity and efficiency, lathe cutting tools are designed to perform multiple and complex machining operations in a single setup. New machining techniques, such as high-feed milling, plunge milling, turn milling, and trochoidal milling, utilize different types of cutting tools to achieve faster material removal rates, improved surface finish, and lower tool wear.
✔ Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and CNC Lathe Programming:
CAD software and CNC lathe programming tools enable virtual prototyping of lathe-cutting tools, facilitating the optimization of geometries before actual production. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) further allows manufacturers to simulate tool behavior under diverse machining conditions, leading to the development of stronger and more efficient cutters.
✔ Sensor Integration:
Some lathe tool bits now feature integrated sensors that monitor real-time parameters like temperature and vibration. This data allows manufacturers to optimize tool performance, reduce wear, and maximize tool lifespan.
✔ Coating Technology:
To withstand cutting forces and temperatures when working with hard materials, lathe cutting tools incorporate advanced coating technologies. Physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) are employed to apply thin layers of hard and heat-resistant materials, enhancing performance and tool life.

If you're in search of a trusted partner to meet your tools for the lathe machining requirements or procure custom machined parts, look no further than Richconn.
Richconn specializes in CNC machining and rapid prototyping services, catering primarily to the automotive, electronics, medical, and industrial sectors. Positioned at the forefront of the industry, Richconn employs advanced equipment, a professional team, and a flexible supply chain to offer tailored manufacturing solutions for a wide array of metal parts and molds. From alloy CNC machining and carbon fiber manufacturing to titanium manufacturing, Richconn stands out as a versatile and reliable partner.
Lathe machines, versatile tools for shaping workpieces, utilize various lathe machine tools tailored for specific functions. As you can see, a comprehensive understanding of lathe CNC machine components, types, and tool classifications is crucial for achieving optimal machining results. When selecting lathe tools, it is essential to consider factors such as the type of lathe machine, workpiece material, machining operation, and desired accuracy.
Q1: How do lathe tools contribute to CNC lathe machining?
A: In CNC lathe machining, lathes tools are automated and controlled by computer programs to achieve precision and efficiency in shaping workpieces. CNC lathe tools are crucial for achieving complex designs and accurate dimensions.
Q2: Are lathe tools interchangeable between different lathe machines?
A: In general, lathe tools are designed to fit specific tool holders or tool posts that are compatible with the lathe machine. While some tooling systems may be interchangeable between machines of the same type, it is crucial to ensure compatibility and proper tool alignment for safe and efficient operation.
Q3: What is a lathe facing tool, and how is it used in machining?
A: A lathe facing tool is designed for facing operations, where material layers are removed to create a smooth or rough surface on the workpiece. It is crucial for achieving flat and even surfaces.
Q4: How do I choose the right tools for a lathe machine?
A: Selecting the right tools for the lathe involves understanding the capabilities and requirements of the specific lathe machine, considering factors such as axis configuration, spindle speed, and tool holder compatibility.
Q5: How does Richconn cater to lathe tooling needs in CNC machining?
A: Richconn specializes in CNC machining and offers a range of service lathe tooling s, including alloy CNC machining, carbon fiber manufacturing, and titanium manufacturing. With a professional team and advanced equipment, Richconn provides tailored manufacturing solutions to meet diverse lathe tooling requirements.
 The Application of CNC Machining in Mechanical Equipment - CNC PartsMay 13, 2024Discover the wide range of applications and future trends of CNC machined parts in mechanical equipment. From high precision to increased efficiency, this technology is pushing forward the industry. Explore the possibilities now!view
The Application of CNC Machining in Mechanical Equipment - CNC PartsMay 13, 2024Discover the wide range of applications and future trends of CNC machined parts in mechanical equipment. From high precision to increased efficiency, this technology is pushing forward the industry. Explore the possibilities now!view A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing CNC Machining ToolsJuly 19, 2023Description:Discover how to select suitable CNC machining tools through this comprehensive guide. Explore key considerations for choosing CNC machining tools, different tool types, and expert advice t...view
A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing CNC Machining ToolsJuly 19, 2023Description:Discover how to select suitable CNC machining tools through this comprehensive guide. Explore key considerations for choosing CNC machining tools, different tool types, and expert advice t...view How to Use a 5-Axis Machining Center for Titanium Alloy Custom Parts?July 27, 2023As an engineer of five-axis machining centers, I will share with you the method of machining titanium alloy special-shaped parts using a five-axis machining center and the key points of titanium alloy...view
How to Use a 5-Axis Machining Center for Titanium Alloy Custom Parts?July 27, 2023As an engineer of five-axis machining centers, I will share with you the method of machining titanium alloy special-shaped parts using a five-axis machining center and the key points of titanium alloy...view GD&T Overview: What are the GD&T Symbols?August 23, 2023GDT symbols are the language used in engineering drawings to communicate design specifications and requirements for manufactured parts. GD&T symbol helps designers and manufacturers precisely defi...view
GD&T Overview: What are the GD&T Symbols?August 23, 2023GDT symbols are the language used in engineering drawings to communicate design specifications and requirements for manufactured parts. GD&T symbol helps designers and manufacturers precisely defi...view How Much is a CNC Machine?September 21, 2023The cost of a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of machine, its size, capabilities, brand, and whether it's new or used.view
How Much is a CNC Machine?September 21, 2023The cost of a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of machine, its size, capabilities, brand, and whether it's new or used.view What is Counter Sink? Your Comprehensive GuideOctober 8, 2023A countersink is a conical hole that is typically drilled or milled into a material, such as wood, metal, or plastic, to allow the head of a screw or fastener to sit flush with or below the surface of the material.view
What is Counter Sink? Your Comprehensive GuideOctober 8, 2023A countersink is a conical hole that is typically drilled or milled into a material, such as wood, metal, or plastic, to allow the head of a screw or fastener to sit flush with or below the surface of the material.view