Some parts manufactured in the automotive industry can only function if they are connected to other parts during the assembly process. As a result, automotive parts manufacturing relies on designs that have high tolerances and incorporate connecting mechanism features, of which fasteners are very common.
Fasteners are critical in automotive component manufacturing because they contribute to the assembly and function of automotive components. There are different types of automotive fasteners based on material, composition and intended function. Here's a look at the different fasteners, their functions, and their possible applications.
The most common way to categorize automotive fasteners used in vehicles is to use the material of composition. They are generally categorized into two main groups, metal and plastic, each with different properties and functions depending on the material.
Classification according to the use of constituent materials is the most common method of classifying fasteners for business. Generally divided into two categories of metal and plastic, according to the characteristics of the material, each has different properties and functions.

Typically, metal automotive fasteners come from iron, aluminum alloys and copper. Depending on the material chosen, they can exhibit varying degrees of mechanical properties such as strength, durability and corrosion resistance.
Metal automotive fasteners come in different forms, including bolts, nuts, springs and screws. They are durable, reusable and suitable for connecting and securing heavy vehicles, suspensions and engine parts.
Metal automotive fasteners can also be surface finished for better functionality and aesthetics. Common examples suitable for automotive parts manufacturing include galvanizing and anodizing for improved rust resistance and durability.

Plastic automotive fasteners are a better option for those looking for optimal mechanical performance and more refined aesthetics. They are a popular choice for manufacturing fasteners, including pins, spacers, connectors, and washers.
Plastic fasteners are primarily made of vinyl, which is known for its tensile strength and brittleness. As a result, they are suitable for manufacturing replaceable or single-use fasteners. In addition, they cost less than metal fasteners and do not conduct electricity or rust.
In addition to being categorized by material, another way to categorize automotive fasteners is by function. Here are the common types you need to know about:

A nut is a small metal part made using iron or aluminum alloys that helps in fastening car parts. While there are several types of nut fasteners, the most common is the hexagonal nut, which is characterized by its hexagonal shape. Other types of nut fasteners used in the automotive industry include:
Cap nuts are accessible only from one side and have a smooth domed surface on the other side to prevent injury.
Cylindrical nuts are cylindrical and can be inserted into a hole perpendicular to the axis of the bolt.
Flange nuts have hexagonal heads with an increased diameter at the bottom. Therefore, they do not require a washer.
Knurled nuts have a larger grain diameter so you can tighten them by hand.

A bolt is a fastener with a long threaded shaft and a non-tapered end. The unthreaded portion, called the shank, provides precision and reduces wear. In addition, depending on the face placed on the bolt, the shank can extend beyond the part interface.
Made from metals such as iron and aluminum alloys, bolts are a simple but irreplaceable option. Like nuts, the most common is the hexagonal bolt with a hexagonal head. It is used along with nuts or washers to secure automotive parts such as engine components, instrument panels, and suspension arms. Different types of automotive bolts include:
Hex flange bolts have a washer under the hex head, which helps in force distribution and securing the part.
Carriage bolts have domed and enlarged heads.
Locating bolts have self-locking and free-spinning hex heads which prevent loosening due to vibration.
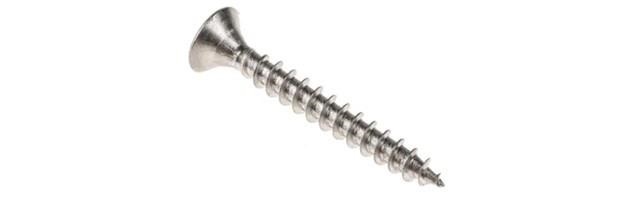
A screw is a fastener with a fully tapered shaft that holds two parts together. It can cut threads in holes (self-tapping screws) or fit into threaded holes in parts (machine screws). Unlike a bolt, it does not require a washer or nut because the threads hold it in place.
As with automotive nuts and bolts, the most common screw is the hexagonal screw. It is similar to a hexagonal bolt, but it does not have a shank. Other types of screw fasteners used in the automotive industry include:
Countersunk head screws: machine screws with tapered heads that are flush with the surface of the part.
Cap screws are automotive screws with a barrel head and assembly sleeve.
Flat head screws: machine screws with a socketed hemispherical head.
Wood screws.
Self-tapping screws.
Coach screw: a large self-tapping screw with a hexagonal head that provides high torque during installation.
There are several types of fasteners used in automobiles. Each offers a different level of performance and reliability. The following fasteners are commonly used in automotive design.
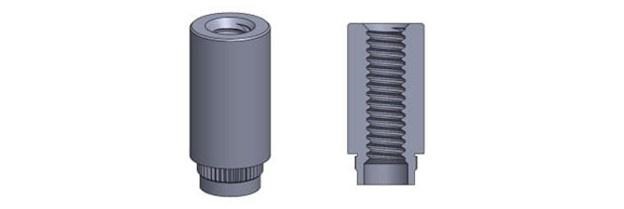
Self-riveting fasteners are disposable and permanent fasteners for joining automotive panels. They have serrated bite rings that prevent rotation and are available in different styles and functions, including pins, nuts, studs, louvers and standoff fasteners.

A rivet is a fastener that has a head and tail at each end. It is mainly made of steel or aluminum and helps in achieving permanent component assembly. There are several types of rivets, including solid rivets, blind rivets, tubular rivets, and open end rivets, suitable for joining two or more automotive parts.

Blind threaded inserts have blind threads that allow them to be mounted on one side of a panel. These inserts are suitable for joining tubes, extrusions etc.

Double-ended bolts are fasteners with external threads that look like screws without heads (some have heads). They are usually permanent fasteners and are usually welded to the parts to be joined. Additionally, you can thread them on both ends so that they can be paired with nuts. A common type of double-ended bolt suitable for automobiles is the wheel double-ended bolt used to secure automobile wheels.

A washer is a disk with a thin, flat surface and a hole in the center. When used with nuts and bolts, it helps distribute the load/pressure on the bolt and prevents the nut from loosening. It comes in different shapes and styles, and its function depends on the automotive part you want to connect.
In automotive parts assembly, washers are applied to axle bearings or joints to prevent loosening, reduce friction, prevent leaks, or distribute pressure.

Clips are important fasteners made of plastic or metal that serve both automotive and non-automotive functions. They come in a variety of designs, but offer a more straightforward solution. In automotive parts manufacturing, they are suitable for positioning or securing different parts, including interior panels, door cards or plastic bumpers (plastics). Clamps can be reused or not.

Clamps are a common type of automotive fastener suitable for securing parts such as hoses and tubes attached to the engine. They are usually metal, although some are plastic. They are applied to tighten the screws of the fasteners, thus tightening the components.

Springs are metal fasteners that exhibit elastic deformation, such as spring clips, pins and washers. As such, they serve to create tension between two automotive components.
The elastic deformation they exhibit ensures a strong connection while allowing for easy assembly and disassembly of parts. An example of the application of spring fasteners in the automotive industry is the use of R-clips to prevent the wheels from falling off the end of the axle.

Pin fasteners hold automotive parts in place but allow some movement. They can be plastic and metal and come in different types.
In the automotive industry, common types include cotter pins that prevent axial movement, so they are used in wheels. Another example is cotter pins used in off-road vehicles and U-shaped clevis pins used in vehicle braking systems.
These types of automotive fasteners have special designs that make them suitable for certain industries, materials and applications. They are suitable in automotive parts manufacturing when the part manufacturer requires a special design due to the uniqueness of its shape, material composition or application. Before special fasteners are used, they need to be tested to ensure they perform well.

These fasteners use surface mounting techniques, which involve adhering the fastener directly to the pads on the surface of the printed circuit board. Surface mounting techniques eliminate damage to automotive components during installation, increase assembly speed, and reduce scrap.

Broached fasteners can be used for studs, nuts, standoffs, etc., pressed and attached to non-tough materials or tough materials with a maximum hardness of aluminum. They are easy to install and are suitable for situations where surface mounting is not suitable.

SI® inserts are special fasteners for connecting plastic parts that require a firm and permanent thread. In addition, they are suitable for units that require frequent assembly and disassembly.

Choosing the right type of automotive fastener is important. However, in addition to selection, proper tightening of fasteners is critical to their function.
In some cases, tightening becomes important. For example, improper tightening of the engine can result in loose bolts, which can prevent the car from starting. Additionally, improperly tightened fasteners in vehicle brakes can increase the likelihood of an accident.
Because of the associated risks, it is also important to choose the right fasteners, as the wrong fastener pairs can seriously affect vehicle performance or cause damage to parts.
Choosing the right type of automotive fasteners is a critical process. Therefore, you need a reliable manufacturer of automotive fasteners. At Richconn, we can help you manufacture different types of automotive fasteners according to your needs.
Our engineering team is experienced in different automotive fastener manufacturing processes, such as CNC machining services, sheet metal services, and 3D printing services, and can answer your questions or provide design suggestions for your designs. We can manufacture high-quality and high-precision plastic and metal types of automotive fasteners to keep your vehicle functioning properly. Click "Quote Now" to upload your design and get an instant quote.
 Snap Fit 101: All You Need to Know About Snap FittingSeptember 19, 2023For a better understanding of snap fitting, we will go through the various types, benefits, and applications of snap fitting and the best tips on designing snap fits.view
Snap Fit 101: All You Need to Know About Snap FittingSeptember 19, 2023For a better understanding of snap fitting, we will go through the various types, benefits, and applications of snap fitting and the best tips on designing snap fits.view CNC Machining: Insights into Mass and Small Batch ProductionsJuly 19, 2024Dive into the detailed exploration of CNC machining to empower your business decisions! Let’s discover the pros of mass and small batch production, shifts in the industry, and tips for choosing the best.view
CNC Machining: Insights into Mass and Small Batch ProductionsJuly 19, 2024Dive into the detailed exploration of CNC machining to empower your business decisions! Let’s discover the pros of mass and small batch production, shifts in the industry, and tips for choosing the best.view Unveiling the Precision World of Machined Gears: A Richconn PerspectiveNovember 10, 2023In the intricate tapestry of mechanical engineering, machined gears stand as the unsung heroes, translating rotational motion with unparalleled precision. These gears are meticulously crafted to meet the demanding requirements of various industries, ensuring seamless operation in complex machinery.view
Unveiling the Precision World of Machined Gears: A Richconn PerspectiveNovember 10, 2023In the intricate tapestry of mechanical engineering, machined gears stand as the unsung heroes, translating rotational motion with unparalleled precision. These gears are meticulously crafted to meet the demanding requirements of various industries, ensuring seamless operation in complex machinery.view Exploring the World of Cold Machined Parts: Unveiling the Secrets of Performance and ManufacturingNovember 14, 2023In the realm of precision engineering, the term cold machined parts sparks curiosity and a quest for knowledge. As we delve into this intricate domain, my aim is to unravel the mysteries surrounding these components, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of their technology, applications, and performance.view
Exploring the World of Cold Machined Parts: Unveiling the Secrets of Performance and ManufacturingNovember 14, 2023In the realm of precision engineering, the term cold machined parts sparks curiosity and a quest for knowledge. As we delve into this intricate domain, my aim is to unravel the mysteries surrounding these components, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of their technology, applications, and performance.view What Are the Precautions for EDM Machining?October 27, 2023EDM is a relatively new metal working technique compared to rotary tooling, shearing and forging. A fast pulsed high-voltage discharge (spark) passes through the gap between the electrode and the grounded workpiece, removing material from the workpiece by erosion.view
What Are the Precautions for EDM Machining?October 27, 2023EDM is a relatively new metal working technique compared to rotary tooling, shearing and forging. A fast pulsed high-voltage discharge (spark) passes through the gap between the electrode and the grounded workpiece, removing material from the workpiece by erosion.view Extrusion Blow Molding: A Guide to the Process, Materials, and ApplicationsDecember 5, 2023Extrusion blow molding is a process of forming hollow plastic parts by extruding a molten tube of polymer and inflating it with air inside a mold. It is one of the most common and versatile methods of producing plastic containers, such as bottles, jars, jugs, and drums.view
Extrusion Blow Molding: A Guide to the Process, Materials, and ApplicationsDecember 5, 2023Extrusion blow molding is a process of forming hollow plastic parts by extruding a molten tube of polymer and inflating it with air inside a mold. It is one of the most common and versatile methods of producing plastic containers, such as bottles, jars, jugs, and drums.view
 EN
EN
 ru
ru 


